BIO 218 F 2012 Ch 14 Martini Lecture Outline
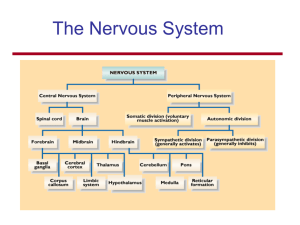
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal cord Integrates and processes information Can function with the brain Can function independently of the brain The brain Integrates and processes information Can function with the spinal cord Can function independently of the spinal cord ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal cord Integrates and processes information Can function with the brain Can function independently of the brain The brain Integrates and processes information Can function with the spinal cord Can function independently of the spinal cord ...
BIO 218 F 2012 Ch 14 Martini Lecture Outline
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal cord Integrates and processes information Can function with the brain Can function independently of the brain The brain Integrates and processes information Can function with the spinal cord Can function independently of the spinal cord ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal cord Integrates and processes information Can function with the brain Can function independently of the brain The brain Integrates and processes information Can function with the spinal cord Can function independently of the spinal cord ...
Lecture 1- Electromyography
... Needle EMG does not introduce any electrical stimulation instead it records the intrinsic electrical activity of skeletal muscle fibers. Normally a muscle is silent at rest after ...
... Needle EMG does not introduce any electrical stimulation instead it records the intrinsic electrical activity of skeletal muscle fibers. Normally a muscle is silent at rest after ...
Nervous Systems
... 28.7 Chemical synapses enable complex information to be processed Some neurotransmitters – excite a receiving cell, and – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
... 28.7 Chemical synapses enable complex information to be processed Some neurotransmitters – excite a receiving cell, and – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
Slide 1
... 28.7 Chemical synapses enable complex information to be processed Some neurotransmitters – excite a receiving cell, and – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
... 28.7 Chemical synapses enable complex information to be processed Some neurotransmitters – excite a receiving cell, and – others inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. ...
Chapter 15
... The MRI revealed multiple infarctions at the level of the basal ganglia and perhaps the brain stem. The neuro report from the hospital suggested that the patient has right lower facial droop, poor movement of most facial muscles, exaggerated smile, and excessive laughter or crying. 1. Does this clin ...
... The MRI revealed multiple infarctions at the level of the basal ganglia and perhaps the brain stem. The neuro report from the hospital suggested that the patient has right lower facial droop, poor movement of most facial muscles, exaggerated smile, and excessive laughter or crying. 1. Does this clin ...
Structural Repair and Functional Recovery Following Cerebral
... does not follow the shortest path to the presumptive bud site, as would be expected if guidance by a soluble factor gradient were the primary mechanism. Recent observations performed with the help of Dr. Keith We are currently investigating the ability Snyder indicate that the initial guidance of so ...
... does not follow the shortest path to the presumptive bud site, as would be expected if guidance by a soluble factor gradient were the primary mechanism. Recent observations performed with the help of Dr. Keith We are currently investigating the ability Snyder indicate that the initial guidance of so ...
The Crash Course in Head, Neck, and Arm By Mike Sughrue
... meets the scala tympani. I later read that this was false, however over time I have found that my error was actually rather helpful in describing the course of many nerves. Hence in this system, the term pre-trematic refers to a branch of each nerve that leaves the skull rostral to a plane through t ...
... meets the scala tympani. I later read that this was false, however over time I have found that my error was actually rather helpful in describing the course of many nerves. Hence in this system, the term pre-trematic refers to a branch of each nerve that leaves the skull rostral to a plane through t ...
Neurological Control of Movement. Chapter 3.
... All muscle fibers within a single motor unit are of the same fiber type. Motor units are recruited in an orderly manner, so that specific ones are called on each time a specific activity is performed. ...
... All muscle fibers within a single motor unit are of the same fiber type. Motor units are recruited in an orderly manner, so that specific ones are called on each time a specific activity is performed. ...
Lecture Exam 2 Study Guide
... - Compare and contrast temporal and spatial summation. - How does one neuron inhibit the activity of another neuron? - How is synaptic activity modulated (regulated)? - Why is synaptic activity so susceptible to drugs? What disorders are results of faulty synaptic transmission? Chapter 9 – Central N ...
... - Compare and contrast temporal and spatial summation. - How does one neuron inhibit the activity of another neuron? - How is synaptic activity modulated (regulated)? - Why is synaptic activity so susceptible to drugs? What disorders are results of faulty synaptic transmission? Chapter 9 – Central N ...
Senses - Peoria Public Schools
... Pain Receptors • Consist of free nerve endings are located in the skin and internal tissues, except the nervous tissue of the brain • Stimulated when tissue is damaged • Usually specific to the type of pain • Adapt very little, if at all ...
... Pain Receptors • Consist of free nerve endings are located in the skin and internal tissues, except the nervous tissue of the brain • Stimulated when tissue is damaged • Usually specific to the type of pain • Adapt very little, if at all ...
The Psychopathology of Pain
... The differences between acute and chronic pain reflect neuronal plasticity Usually due to inflammatory changes in the neuron environment – Tissue damage accumulation of endogenous factors released by activated nociceptors or non-neural cells (eg, mast cells, basophils, platelets, Mθ, PMNs, endothe ...
... The differences between acute and chronic pain reflect neuronal plasticity Usually due to inflammatory changes in the neuron environment – Tissue damage accumulation of endogenous factors released by activated nociceptors or non-neural cells (eg, mast cells, basophils, platelets, Mθ, PMNs, endothe ...
HERE
... Click on > Back Button then Click on > Right Arrow - Depolarization 12. Describe the axon at the end of the depolarization phase. __________________________________________________________ 13. At the end of the depolarization phase, what is the tendency for movement of a sodium ion at the mouth of ...
... Click on > Back Button then Click on > Right Arrow - Depolarization 12. Describe the axon at the end of the depolarization phase. __________________________________________________________ 13. At the end of the depolarization phase, what is the tendency for movement of a sodium ion at the mouth of ...
The Nervous System
... Degenerative disease of the brain. The person usually loses the ability to remember, think correctly and speak. The condition usually gets worse over time once it starts. It may take years to ...
... Degenerative disease of the brain. The person usually loses the ability to remember, think correctly and speak. The condition usually gets worse over time once it starts. It may take years to ...
FIGURE LEGNEDS FIGURE 24.1 A dorsal root ganglion cell is a
... corpuscle and the type I slowly adapting afferents that end as Merkel’s disks. Deep receptors include a rapidly adapting receptor enclosed by a Pacinian corpuscle and a type II slowly adapting afferent in some species. Those SAII afferents are associated with Ruffini corpuscles in domestic cats but ...
... corpuscle and the type I slowly adapting afferents that end as Merkel’s disks. Deep receptors include a rapidly adapting receptor enclosed by a Pacinian corpuscle and a type II slowly adapting afferent in some species. Those SAII afferents are associated with Ruffini corpuscles in domestic cats but ...
Chapter 15 - Las Positas College
... thought. You involuntarily experience countless smooth muscle and cardiac muscle contractions and gland secretions that provide a stable internal environment for you. Some of the important visceral functions under the regulation of the ANS are maintenance of heart rate and blood pressure, digestion, ...
... thought. You involuntarily experience countless smooth muscle and cardiac muscle contractions and gland secretions that provide a stable internal environment for you. Some of the important visceral functions under the regulation of the ANS are maintenance of heart rate and blood pressure, digestion, ...
A Model of Extraforaminal Brachial Plexus Injury in Neonatal Mice
... injury in humans. While others have developed models of intraforaminal injury in neonatal rats, the current model has three distinct advantages: 1. The postganglionic nature of the lesion more closely recreates the neurologic pathophysiology of the typical upper trunk lesion in humans, which is most ...
... injury in humans. While others have developed models of intraforaminal injury in neonatal rats, the current model has three distinct advantages: 1. The postganglionic nature of the lesion more closely recreates the neurologic pathophysiology of the typical upper trunk lesion in humans, which is most ...
BPPV - 4 - MM3 Admin
... response in this disorder is neural, rather than mechanical stimulation of the sense organ. Loss of the inhibitory action of otolith organs on canal activation caused by degeneration of otolith neurons (saccular, utricular) is a possible explanation of the brief canal response induced by the positio ...
... response in this disorder is neural, rather than mechanical stimulation of the sense organ. Loss of the inhibitory action of otolith organs on canal activation caused by degeneration of otolith neurons (saccular, utricular) is a possible explanation of the brief canal response induced by the positio ...
Chapter 12 Nervous System Review Assignment
... b. depolarization at the adjacent node of Ranvier. c. repolarization at the adjacent region of the membrane. d. depolarization at the adjacent region of the membrane. ____ 28. Multiple sclerosis is a disorder characterized by the breakdown of the myelin sheath around axons in the central nervous sys ...
... b. depolarization at the adjacent node of Ranvier. c. repolarization at the adjacent region of the membrane. d. depolarization at the adjacent region of the membrane. ____ 28. Multiple sclerosis is a disorder characterized by the breakdown of the myelin sheath around axons in the central nervous sys ...
Sensation
... Appears by sensory disturbance in distal parts of extremities as "socks" on legs and "gloves" on arms The “stocking-glove” pattern of sensory loss is typical for peripheral neuropathy ...
... Appears by sensory disturbance in distal parts of extremities as "socks" on legs and "gloves" on arms The “stocking-glove” pattern of sensory loss is typical for peripheral neuropathy ...
FREE Sample Here
... 27. Which lobe of the cerebral cortex processes auditory information and supports language comprehension and production? a. occipital lobe c. parietal lobe b. temporal lobe d. frontal lobe ANS: B PTS: 1 REF: The Nervous System: Control of Behavior and Physiological Functions 28. Which lobe of the ce ...
... 27. Which lobe of the cerebral cortex processes auditory information and supports language comprehension and production? a. occipital lobe c. parietal lobe b. temporal lobe d. frontal lobe ANS: B PTS: 1 REF: The Nervous System: Control of Behavior and Physiological Functions 28. Which lobe of the ce ...