Chapter 11 Fundamentals of Nervous System
... Repolarization – the membrane returns to its resting membrane potential Hyperpolarization – the inside of the membrane becomes more negative than the resting potential ...
... Repolarization – the membrane returns to its resting membrane potential Hyperpolarization – the inside of the membrane becomes more negative than the resting potential ...
Endocrinology – general, hypothalamus, pituitary
... Neurotransmitters and endocrine hormones are two of the four major classes of soluble intercellular signalling molecules: the others are autacoids (a pharmacological term for paracrine agents such as histamine) and cytokines (in some ways very much like hormones, they are non-immunoglobulin signalli ...
... Neurotransmitters and endocrine hormones are two of the four major classes of soluble intercellular signalling molecules: the others are autacoids (a pharmacological term for paracrine agents such as histamine) and cytokines (in some ways very much like hormones, they are non-immunoglobulin signalli ...
PDF
... the amount of silver impregnation and staining intensity for cresyl violet. The central portions of our tissue blocks, which were exposed to the least mordant and silver nitrate demonstrated the most robust Nissl staining. The superficial areas, with good silver stain, had faint cresyl violet staini ...
... the amount of silver impregnation and staining intensity for cresyl violet. The central portions of our tissue blocks, which were exposed to the least mordant and silver nitrate demonstrated the most robust Nissl staining. The superficial areas, with good silver stain, had faint cresyl violet staini ...
Skeletal System
... motor activities Nearly spinal nerves and many cranial nerves contain both somatic and autonomic fibers Most of the body’s adaptations to changing internal and external conditions involve both skeletal activity and enhanced response of visceral organs ...
... motor activities Nearly spinal nerves and many cranial nerves contain both somatic and autonomic fibers Most of the body’s adaptations to changing internal and external conditions involve both skeletal activity and enhanced response of visceral organs ...
Central Nervous System
... End in axon terminals Axon terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters Axon terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap Synaptic cleft—gap between adjacent neurons Synapse—junction between nerves ...
... End in axon terminals Axon terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters Axon terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap Synaptic cleft—gap between adjacent neurons Synapse—junction between nerves ...
No Slide Title
... Excitation of Myelinated Nerve myelinated nerve fiber to a point source stimulation ...
... Excitation of Myelinated Nerve myelinated nerve fiber to a point source stimulation ...
section4
... – corrected by hyperventilation, pushes reaction to the left by “blowing off ” CO2 CO2 (expired) + H2O H2CO3 HCO3- + H+ ...
... – corrected by hyperventilation, pushes reaction to the left by “blowing off ” CO2 CO2 (expired) + H2O H2CO3 HCO3- + H+ ...
MARMORATAl - Journal of Neuroscience
... antigens are first expressed and the order in which they are expressed by different cells or tissues. Three of the mAbs produced by Zipser and McKay (Zipser, B., and R. McKay (1981) Nature 289: 549-554) were screened: Lan3-1, Lan3-5, and Lan3-6. Each mAb shows a different pattern of labeling in the ...
... antigens are first expressed and the order in which they are expressed by different cells or tissues. Three of the mAbs produced by Zipser and McKay (Zipser, B., and R. McKay (1981) Nature 289: 549-554) were screened: Lan3-1, Lan3-5, and Lan3-6. Each mAb shows a different pattern of labeling in the ...
Skeletal System
... Recall that the somatic motor system innervates skeletal muscles Each somatic motor neuron runs from the central nervous system all the way to the muscle being innervated, and that each motor unit consists of a single neuron plus the skeletal muscle cells it innervates Typical somatic motor axons ar ...
... Recall that the somatic motor system innervates skeletal muscles Each somatic motor neuron runs from the central nervous system all the way to the muscle being innervated, and that each motor unit consists of a single neuron plus the skeletal muscle cells it innervates Typical somatic motor axons ar ...
The Torah of Life - The Torah Science Foundation
... program that starts with a germinating seed and culminates in fruits and new seeds. The Tree of Life symbolizes the creation of life, and the evolution of life from the perspective of the Torah. “Knowledge” in Hebrew also means “consciousness.” The Tree of Knowledge of Good and Evil symbolizes the “ ...
... program that starts with a germinating seed and culminates in fruits and new seeds. The Tree of Life symbolizes the creation of life, and the evolution of life from the perspective of the Torah. “Knowledge” in Hebrew also means “consciousness.” The Tree of Knowledge of Good and Evil symbolizes the “ ...
Glia–Neuron Interactions in Nervous System Function
... hundred years after Cajal’s writings, we still lack clear‐cut evidence to distinguish among the possibilities described above. Indeed, given our current state of understanding, it is still very possible that glia perform both neuron‐ dependent and neuron‐independent functions in the nervous system. ...
... hundred years after Cajal’s writings, we still lack clear‐cut evidence to distinguish among the possibilities described above. Indeed, given our current state of understanding, it is still very possible that glia perform both neuron‐ dependent and neuron‐independent functions in the nervous system. ...
Anatomy Written Exam #2 Cranial Nerves Introduction Embryological
... either mossy fibers or climbing fibers Those from the spinal cord, vestibular nuclei, and pons end as mossy fibers, which branch to supply several folia and end in granular layer 1. Axons of granule cells pass towards cortex and enter molecular layer, where they bifurcate and form parallel fibers ...
... either mossy fibers or climbing fibers Those from the spinal cord, vestibular nuclei, and pons end as mossy fibers, which branch to supply several folia and end in granular layer 1. Axons of granule cells pass towards cortex and enter molecular layer, where they bifurcate and form parallel fibers ...
Neurobiology of injury to the developing brain.
... 200025, P.R. China Spinal Cord and Brain Injury Research Group Stark Neurosciences Research Institute and Department of Neurological Surgery Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis, IN 46202, U.S.A. ...
... 200025, P.R. China Spinal Cord and Brain Injury Research Group Stark Neurosciences Research Institute and Department of Neurological Surgery Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis, IN 46202, U.S.A. ...
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy - Remarkable Podiatrist at Foot
... slowly and worsens over time. Some patients have this condition long before they are diagnosed with diabetes. Having diabetes for several years may increase the likelihood of having diabetic neuropathy. The loss of sensation and other problems associated with nerve damage make a patient prone to dev ...
... slowly and worsens over time. Some patients have this condition long before they are diagnosed with diabetes. Having diabetes for several years may increase the likelihood of having diabetic neuropathy. The loss of sensation and other problems associated with nerve damage make a patient prone to dev ...
full text pdf
... Simula et al. (2001) have revealed that the number of neurons associated with the possum SO is significantly higher within the distal region (duodenal end) of the sphincter than in the more proximal part. Furthermore, they found that approximately (approx.) 50% of all SO associated nerve cells were ...
... Simula et al. (2001) have revealed that the number of neurons associated with the possum SO is significantly higher within the distal region (duodenal end) of the sphincter than in the more proximal part. Furthermore, they found that approximately (approx.) 50% of all SO associated nerve cells were ...
Core Lab #1 - Reflex Responses
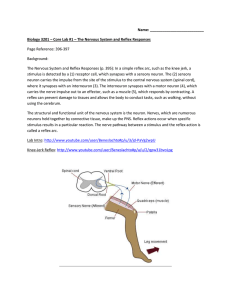
... stimulus is detected by a (1) receptor cell, which synapses with a sensory neuron. The (2) sensory neuron carries the impulse from the site of the stimulus to the central nervous system (spinal cord), where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which ...
... stimulus is detected by a (1) receptor cell, which synapses with a sensory neuron. The (2) sensory neuron carries the impulse from the site of the stimulus to the central nervous system (spinal cord), where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which ...
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters are the nervous system`s “off switches
... Aspartic Acid, also known as aspartate, is an excitatory neurotransmitter in the brainstem and spinal cord. Aspartic acid is the excitatory counterpart to glycine, an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Low levels have been linked to feelings of fatigue and low mood, whereas high levels have been linked t ...
... Aspartic Acid, also known as aspartate, is an excitatory neurotransmitter in the brainstem and spinal cord. Aspartic acid is the excitatory counterpart to glycine, an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Low levels have been linked to feelings of fatigue and low mood, whereas high levels have been linked t ...
Univerzita Karlova v Praze Přírodovědecká fakulta
... This review is focused on drugs of the group of opioids but, to a lesser extent, some attention is devoted also to amphetamine-type stimulants and cocaine and their effects on neuroglia. Opioids, mainly morphine, have been used for relieving pain for a long time. Their effects have been known since ...
... This review is focused on drugs of the group of opioids but, to a lesser extent, some attention is devoted also to amphetamine-type stimulants and cocaine and their effects on neuroglia. Opioids, mainly morphine, have been used for relieving pain for a long time. Their effects have been known since ...
Hormones
... hormones (so if it needs oxygenated blood it gets it from its own arteries) Hypothalamic hormones travel through the portal veins to the ANTERIOR PITUITARY where they stimulate or inhibit release of hormones from the anterior pituitary ...
... hormones (so if it needs oxygenated blood it gets it from its own arteries) Hypothalamic hormones travel through the portal veins to the ANTERIOR PITUITARY where they stimulate or inhibit release of hormones from the anterior pituitary ...
The Pathology of Multiple Sclerosis and Its Variants
... plaques. The demonstration of herpes viruses, in particular herpes I, II, and VI, in a significant proportion of MS plaques over the past decade (12,13), evidence that the anti-herpes drug acyclovir will reduce the number of attacks of MS (14), and, more recently, evidence for chlamydial infection ( ...
... plaques. The demonstration of herpes viruses, in particular herpes I, II, and VI, in a significant proportion of MS plaques over the past decade (12,13), evidence that the anti-herpes drug acyclovir will reduce the number of attacks of MS (14), and, more recently, evidence for chlamydial infection ( ...
Cranial Nerve I
... Regeneration involves coordinated activity among: Macrophages – remove debris Schwann cells – form regeneration tube and secrete growth factors ...
... Regeneration involves coordinated activity among: Macrophages – remove debris Schwann cells – form regeneration tube and secrete growth factors ...
Neuroscience - Thermo Fisher Scientific
... in the pathogenesis of human neurological diseases are highly regulated processes. Subtle changes in the environment of the complex neuronal network may cause either breakdown or creation of synaptic connections. Drug discovery screening for neurological diseases and compound neurotoxicity evaluatio ...
... in the pathogenesis of human neurological diseases are highly regulated processes. Subtle changes in the environment of the complex neuronal network may cause either breakdown or creation of synaptic connections. Drug discovery screening for neurological diseases and compound neurotoxicity evaluatio ...
1 The Brain and Behavior
... each of the brain's two hemispheres the overlying cortex is divided into four anatomically distinct lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital (see Figure 12B), originally named for the skull bones that encase them. These lobes have specialized functions. The frontal lobe is largely concerned ...
... each of the brain's two hemispheres the overlying cortex is divided into four anatomically distinct lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital (see Figure 12B), originally named for the skull bones that encase them. These lobes have specialized functions. The frontal lobe is largely concerned ...
What Are the Units of Brain Function?
... the cell body is increased immensely by extensions of the cell membrane into dendrites. The dendritic area is further increased by many small protrusions called dendritic spines. A neuron may have from 1 to 20 dendrites, each of which may have from one to many branches, and the spines on the branche ...
... the cell body is increased immensely by extensions of the cell membrane into dendrites. The dendritic area is further increased by many small protrusions called dendritic spines. A neuron may have from 1 to 20 dendrites, each of which may have from one to many branches, and the spines on the branche ...