The Nervous System
... of connective tissue called meninges. • Bathed in cerebrospinal fluid which acts as a shock absorber. ...
... of connective tissue called meninges. • Bathed in cerebrospinal fluid which acts as a shock absorber. ...
Function
... The function of the myelin sheath: •to provide an insulation layer around the axon •to speed up impulse conduction: nerve impulses jump from node to node across the intervening internodal segment of myelin sheath ( the axon directly exposed to the extracelluar fluidal ions at nodes of Ranvier, wher ...
... The function of the myelin sheath: •to provide an insulation layer around the axon •to speed up impulse conduction: nerve impulses jump from node to node across the intervening internodal segment of myelin sheath ( the axon directly exposed to the extracelluar fluidal ions at nodes of Ranvier, wher ...
Answers - Mosaiced.org
... 91. Period during which Na+ channels will not open in response to stimulus, however large. Therefore no action potentials can be generated. 92. No – skeletal muscle is an example of one that doesn’t 93. K+ channels remain open, so permeability to K+ is greater than at rest. Na+ channels are shut so ...
... 91. Period during which Na+ channels will not open in response to stimulus, however large. Therefore no action potentials can be generated. 92. No – skeletal muscle is an example of one that doesn’t 93. K+ channels remain open, so permeability to K+ is greater than at rest. Na+ channels are shut so ...
THE NEuRoN - Big Picture
... function properly. Others (oligodendrocytes) wrap neurons in an insulating myelin sheath, which can become damaged in neurodegenerative conditions such as stroke, spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis and cerebral palsy. A better understanding of how neurons interact with glial cells may help in fi ...
... function properly. Others (oligodendrocytes) wrap neurons in an insulating myelin sheath, which can become damaged in neurodegenerative conditions such as stroke, spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis and cerebral palsy. A better understanding of how neurons interact with glial cells may help in fi ...
Bursting the unfolded protein response accelerates axonal
... duration of the stress stimuli to orchestrate adaptive or pro-apoptotic mechanisms, determining cell fate. ER stress has emerged as an important event driving neurodegeneration in pathological conditions of the CNS and PNS (reviewed in Li et al., 2013; Hetz and Mollereau, 2014). Axonal damage to the ...
... duration of the stress stimuli to orchestrate adaptive or pro-apoptotic mechanisms, determining cell fate. ER stress has emerged as an important event driving neurodegeneration in pathological conditions of the CNS and PNS (reviewed in Li et al., 2013; Hetz and Mollereau, 2014). Axonal damage to the ...
Neural and Hormonal Systems
... Neurons communicate with each without actually touching one another! Synapse – fluid-filled gap between axon terminal of one neuron and dendrite of another Neurotransmitter – chemical messengers that travel across synapse from one neuron to the next Reuptake – sending neuron reabsorbs excess neurotr ...
... Neurons communicate with each without actually touching one another! Synapse – fluid-filled gap between axon terminal of one neuron and dendrite of another Neurotransmitter – chemical messengers that travel across synapse from one neuron to the next Reuptake – sending neuron reabsorbs excess neurotr ...
Chapter 9
... The outer layer of myelin is surrounded by a ____________ (__________ ____________) made up of the __________ and _______________ of the Schwann cell. b. ______________________ in the myelin sheath between Schwann cells are called ____________________________. ...
... The outer layer of myelin is surrounded by a ____________ (__________ ____________) made up of the __________ and _______________ of the Schwann cell. b. ______________________ in the myelin sheath between Schwann cells are called ____________________________. ...
chapter nervous system i: basig strugture and function
... The body uses two systems to coordinate and integrate the functions of body systems so that the intemal environment remains stable. These systems are the nervous system and the endocrine system. Chapter 10 begins with a discussion of the general functions of the nervous system, the types of ceils th ...
... The body uses two systems to coordinate and integrate the functions of body systems so that the intemal environment remains stable. These systems are the nervous system and the endocrine system. Chapter 10 begins with a discussion of the general functions of the nervous system, the types of ceils th ...
Nervous System Nervous system
... Depending on the situation, the autonomic nervous system can speed up or slow down these functions The autonomic nervous system has two divisions: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system ...
... Depending on the situation, the autonomic nervous system can speed up or slow down these functions The autonomic nervous system has two divisions: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system ...
3E-F Worksheet 1. Sensory receptors that are classed by location
... 10. The muscles of the eyebrows are the _____________muscle which __________eyebrows and the _______________ muscles which move the eyebrows____________. o\/o 3F3 11. In the sensory tunic of the retina the photoreceptors cells are made up of ______which respond to dim ________and are used for ______ ...
... 10. The muscles of the eyebrows are the _____________muscle which __________eyebrows and the _______________ muscles which move the eyebrows____________. o\/o 3F3 11. In the sensory tunic of the retina the photoreceptors cells are made up of ______which respond to dim ________and are used for ______ ...
intro to psych ch3 biological bases of behavior
... An action potential (nerve impulse) sweeps down the axon Ion channels open and sodium ions rush in ...
... An action potential (nerve impulse) sweeps down the axon Ion channels open and sodium ions rush in ...
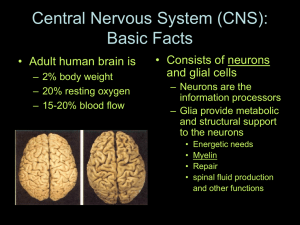
Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
Central Nervous System
... After inside flooded with Na+, K+ gates open (they are slower to respond) and let K+ out which are repelled by + inside Na+ gates remain closed The inside becomes negative while outside become positive and this repolarizes membrane ...
... After inside flooded with Na+, K+ gates open (they are slower to respond) and let K+ out which are repelled by + inside Na+ gates remain closed The inside becomes negative while outside become positive and this repolarizes membrane ...
Unit Three Nervous System
... – The disease is caused by bacteria. – The symptoms include severe headache and stiffness of the neck. – Meningitis can be fatal. – Antibiotics are used to treat meningitis. ...
... – The disease is caused by bacteria. – The symptoms include severe headache and stiffness of the neck. – Meningitis can be fatal. – Antibiotics are used to treat meningitis. ...
Chapter 12-13 Summary
... Chapter 12-13 NOTE: This was originally prepared for BIOL 2404, however many parts overlap with 2401. I’ve added additional references. Use this knowing it may not cover everything. Nervous System: (These are very important chapters.) ...
... Chapter 12-13 NOTE: This was originally prepared for BIOL 2404, however many parts overlap with 2401. I’ve added additional references. Use this knowing it may not cover everything. Nervous System: (These are very important chapters.) ...
Structure of a Neuron
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
ANATOMICAL TERMS
... The more dendrite a neuron has the more information it can receive 5 to 135 micro metres in diameter o Axon - a cylindrical and relatively unbranched for most of its length Specialised for rapid conduction of nerve signals to points remote from the ...
... The more dendrite a neuron has the more information it can receive 5 to 135 micro metres in diameter o Axon - a cylindrical and relatively unbranched for most of its length Specialised for rapid conduction of nerve signals to points remote from the ...
File - Hardman`s AP Biology
... • The limbic system is a complex set of structures that lies on both sides of the thalamus, just under the cerebrum. It includes the hypothalamus, the hippocampus, the amygdala, and several other nearby areas. It appears to be primarily responsible for our emotional life, and has a lot to do with t ...
... • The limbic system is a complex set of structures that lies on both sides of the thalamus, just under the cerebrum. It includes the hypothalamus, the hippocampus, the amygdala, and several other nearby areas. It appears to be primarily responsible for our emotional life, and has a lot to do with t ...
B) Nervous System Introduction NtG Spring
... Formed by ___________________________ which wrap themselves around the axon in jelly-roll fashion Central nervous system Formed by ______________________________ _______________________ of ____________________________ Adjacent Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes do not touch each other so t ...
... Formed by ___________________________ which wrap themselves around the axon in jelly-roll fashion Central nervous system Formed by ______________________________ _______________________ of ____________________________ Adjacent Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes do not touch each other so t ...
The Nervous System - Plain Local Schools
... • Neurons have the ability to conduct nerve impulses very quickly, but how does one cell communicate with another cell? • Adjacent neurons communicate by releasing chemicals across tiny gaps that separate them, called synapses (synaptic cleft) • The chemicals, known as neurotransmitters, are release ...
... • Neurons have the ability to conduct nerve impulses very quickly, but how does one cell communicate with another cell? • Adjacent neurons communicate by releasing chemicals across tiny gaps that separate them, called synapses (synaptic cleft) • The chemicals, known as neurotransmitters, are release ...
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems - Biology at Mott
... The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is composed of nerves and ganglia ...
... The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is composed of nerves and ganglia ...
Lecture ppt 1 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Line the cavities of CNS and spinal cord; cilia Oligodendrocytes Produce myelin sheaths in CNS (see later slide) ...
... Line the cavities of CNS and spinal cord; cilia Oligodendrocytes Produce myelin sheaths in CNS (see later slide) ...
NOB Ch 6 Answers - MCC Year 12 Biology
... (Note: In addition to these rapid changes in blood pressure, hormonal responses also occur when blood pressure falls, such as the release of the hormones adrenalin and noradrenalin from the adrenal gland. These hormones are released when the adrenal gland receives stimulation from the sympathetic ne ...
... (Note: In addition to these rapid changes in blood pressure, hormonal responses also occur when blood pressure falls, such as the release of the hormones adrenalin and noradrenalin from the adrenal gland. These hormones are released when the adrenal gland receives stimulation from the sympathetic ne ...
NEUROGLIA (Glial cells) Supporting cells of the CNS and PNS
... •Reclaims K+ for use in the sodium potassium pump •Metabolizes glucose for metabolic function and ATP production •Reclaims Ach ...
... •Reclaims K+ for use in the sodium potassium pump •Metabolizes glucose for metabolic function and ATP production •Reclaims Ach ...