Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 9 Textbook Notes: The Nervous
... _____________________: Controls the autonomic nervous system ____________: Assists the medulla in its activities, especially breathing _____________________: Coordinates movement and balance B. The Forebrain (aka cerebrum) _____________________: An ancient system associated with emotions, in ...
... _____________________: Controls the autonomic nervous system ____________: Assists the medulla in its activities, especially breathing _____________________: Coordinates movement and balance B. The Forebrain (aka cerebrum) _____________________: An ancient system associated with emotions, in ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump, using ATP, restores the ...
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump, using ATP, restores the ...
Chapter 6 Chapter Review Questions Q2. This would be a
... a) Because the colour and texture of the chameleon changes rapidly, it indicates that this is under the control of the nervous. If it were under the control of the endocrine (hormonal) system the chameleon would not be able to change as rapidly as hormones are slower to act than neurons. b) As darke ...
... a) Because the colour and texture of the chameleon changes rapidly, it indicates that this is under the control of the nervous. If it were under the control of the endocrine (hormonal) system the chameleon would not be able to change as rapidly as hormones are slower to act than neurons. b) As darke ...
File
... Branch like structures of a neuron that received chemical messages from the terminal buttons of adjacent neurons. ...
... Branch like structures of a neuron that received chemical messages from the terminal buttons of adjacent neurons. ...
neurology_lec13_9_5_2011 - Post-it
... We will talk about cranial nerves : #2 , #3, #4, #6 Optic nerve -2ed cranial nerve -Purely sensory -type of fiber ( SSA- special sesory afferent ) but olfactory nerve ( SVA ) -start at optic disc as converge of ganglion cells axons till optic chiasm – it’s also called optic tract because it’s all li ...
... We will talk about cranial nerves : #2 , #3, #4, #6 Optic nerve -2ed cranial nerve -Purely sensory -type of fiber ( SSA- special sesory afferent ) but olfactory nerve ( SVA ) -start at optic disc as converge of ganglion cells axons till optic chiasm – it’s also called optic tract because it’s all li ...
Nervous System Development
... •At about the time a child reaches puberty the “pruning” process kicks in, and streamlines the networks to about 500 trillion connections. •This pruning isn’t a random process. The synapses which have been used repeatedly tend to remain. Those which haven’t been used often enough are eliminated. ...
... •At about the time a child reaches puberty the “pruning” process kicks in, and streamlines the networks to about 500 trillion connections. •This pruning isn’t a random process. The synapses which have been used repeatedly tend to remain. Those which haven’t been used often enough are eliminated. ...
AP – All or nothing
... – Stimulus is strong enough to cause an AP – It is an ‘all or nothing event’ because once it starts, it travels to the synapse. ...
... – Stimulus is strong enough to cause an AP – It is an ‘all or nothing event’ because once it starts, it travels to the synapse. ...
UNIT 4 – HOMEOSTASIS 8.1 – Human Body Systems and H
... - See Figure 8.16, pg 359 - A nerve impulse (action potential) travels down the length of the axon until it reaches the ...
... - See Figure 8.16, pg 359 - A nerve impulse (action potential) travels down the length of the axon until it reaches the ...
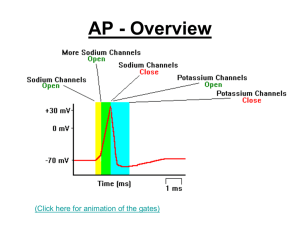
SOP007_HoffmanReflex
... muscle fibres via a reflex loop involving sensory nerve fibres (H-reflex) as well as direct motor activation via the alpha motor neurons (M-wave). The H-reflex itself is recorded through electromyography (EMG; muscle activity) from the muscle being studied. The most common use of the H-reflex techni ...
... muscle fibres via a reflex loop involving sensory nerve fibres (H-reflex) as well as direct motor activation via the alpha motor neurons (M-wave). The H-reflex itself is recorded through electromyography (EMG; muscle activity) from the muscle being studied. The most common use of the H-reflex techni ...
Brain_s Building Blocks-Student
... SENDING INFORMATION: NERVE IMPULSE (CONT.) • All-or-None law – if an action potential starts at the beginning of the axon, the action potential will continue at the same speed segment to segment to the very end of the axon • Nerve impulse – nerve impulse is made up of ___________________________, w ...
... SENDING INFORMATION: NERVE IMPULSE (CONT.) • All-or-None law – if an action potential starts at the beginning of the axon, the action potential will continue at the same speed segment to segment to the very end of the axon • Nerve impulse – nerve impulse is made up of ___________________________, w ...
The vertebrate nervous system is regionally specialized
... producing an excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic potential (EPSP or IPSP). After release, the neurotransmitter diffuses out of the synaptic cleft, is taken up by surrounding cells, or is degraded by enzymes. A single neuron has many synapses on its dendrites and cell body. Whether it generates an ...
... producing an excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic potential (EPSP or IPSP). After release, the neurotransmitter diffuses out of the synaptic cleft, is taken up by surrounding cells, or is degraded by enzymes. A single neuron has many synapses on its dendrites and cell body. Whether it generates an ...
23. Parasympathetic nervous system
... Visceral sensory and autonomic neurons participate in visceral reflex arcs • Many are spinal reflexes such as defecation and micturition reflexes • Some only involve peripheral neurons: spinal cord not involved (not shown)* *e.g. “enteric” nervous system: 3 neuron reflex arcs entirely within the wa ...
... Visceral sensory and autonomic neurons participate in visceral reflex arcs • Many are spinal reflexes such as defecation and micturition reflexes • Some only involve peripheral neurons: spinal cord not involved (not shown)* *e.g. “enteric” nervous system: 3 neuron reflex arcs entirely within the wa ...
The Nervous System * Crash Course Biology
... terminal buttons of one cell and diffuses to the dendrites on the next neuron The Action Potential The sodium-potassium _____________ moves ions across the neurons membrane creating a net negative? positive? (circle one) charge inside the cell. The membrane also has proteins straddling it that do no ...
... terminal buttons of one cell and diffuses to the dendrites on the next neuron The Action Potential The sodium-potassium _____________ moves ions across the neurons membrane creating a net negative? positive? (circle one) charge inside the cell. The membrane also has proteins straddling it that do no ...
here - WPI
... cell’s membrane potential when the neurotransmitter is in place. This triggers a reaction from the cell that is particular to its function, which could be anything from the contraction of a muscle to the generation of another action potential (Society for Neuroscience, 2012). To facilitate the trave ...
... cell’s membrane potential when the neurotransmitter is in place. This triggers a reaction from the cell that is particular to its function, which could be anything from the contraction of a muscle to the generation of another action potential (Society for Neuroscience, 2012). To facilitate the trave ...
Psychology Chapter 3
... to 30 minutes. An MRI typically costs more than a CT scan. One advantage of an MRI is that it does not use radiation while CAT scans do. This radiation is harmful if there is repeated exposure. A PET scan uses nuclear medicine imaging to produce a three-dimensional picture of functional processes in ...
... to 30 minutes. An MRI typically costs more than a CT scan. One advantage of an MRI is that it does not use radiation while CAT scans do. This radiation is harmful if there is repeated exposure. A PET scan uses nuclear medicine imaging to produce a three-dimensional picture of functional processes in ...
Reading Part 5: The Nervous System
... The end of each axon contains many fine projections called axon terminals. From here a neuron can communicate with another thru the synapse (the gap between neurons). The axon terminal contains many membraneenclosed sacs called synaptic vesicles. They store many types of neurotransmitters which are ...
... The end of each axon contains many fine projections called axon terminals. From here a neuron can communicate with another thru the synapse (the gap between neurons). The axon terminal contains many membraneenclosed sacs called synaptic vesicles. They store many types of neurotransmitters which are ...
nervous_system_-_cns_and_pns_part_2_-_2015
... Gray matter of the spinal cord forms an “H” and contains neurons White matter consists of nerve fibers called “tracts” to and from the brain ...
... Gray matter of the spinal cord forms an “H” and contains neurons White matter consists of nerve fibers called “tracts” to and from the brain ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • Responds to stress, and plays a role in basic behaviors and bodily functions such as sex, eating, metabolism, reproduction, and growth ...
... • Responds to stress, and plays a role in basic behaviors and bodily functions such as sex, eating, metabolism, reproduction, and growth ...
Chapter 7: Structure of Nervous System
... CNS has oligodendrocytes, microglia, astrocytes and ependymal cells Each oligodendrocyte myelinates several CNS axons Ependymal cells appear to be neural stem cells. Other glial cells are involved in NS _______________________ Myelination In PNS each Schwann cell myelinates 1mm of 1 axon b ...
... CNS has oligodendrocytes, microglia, astrocytes and ependymal cells Each oligodendrocyte myelinates several CNS axons Ependymal cells appear to be neural stem cells. Other glial cells are involved in NS _______________________ Myelination In PNS each Schwann cell myelinates 1mm of 1 axon b ...
repo
... Ak/Y ; UAS Gal80ts, D::E/ Sco; F gal4, UAS RFP/ TM6b, Tb X Ak/ FM7; ∆B; P{EP}C/ TM3, Act GFP, Ser http://flybase.org/static_pages/docs/nomenclature/nomenclature3.html ...
... Ak/Y ; UAS Gal80ts, D::E/ Sco; F gal4, UAS RFP/ TM6b, Tb X Ak/ FM7; ∆B; P{EP}C/ TM3, Act GFP, Ser http://flybase.org/static_pages/docs/nomenclature/nomenclature3.html ...
4 lesson_15.4
... It consists of three main parts—the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain—and two smaller regions—the thalamus and the hypothalamus. ...
... It consists of three main parts—the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain—and two smaller regions—the thalamus and the hypothalamus. ...
My Reaction Test Score = Neural Transmission
... At the end (terminal button) of the axon the signal causes small sacks (vesicles) of chemicals to be released into the space between the end of the axon and the dendrite of the next neuron. These chemicals (neurotransmitters) travel across the space between the two neurons (synapse) and cause the ne ...
... At the end (terminal button) of the axon the signal causes small sacks (vesicles) of chemicals to be released into the space between the end of the axon and the dendrite of the next neuron. These chemicals (neurotransmitters) travel across the space between the two neurons (synapse) and cause the ne ...
Objectives 31
... - Cortical cells respond to stripes or edges with a particular orientation; simple cells have excitatory and inhibitory regions in the shape of oriented bars; complex cells respond to oriented lines of a particular length -other neurons are more concerned with color than with black/white contrast; t ...
... - Cortical cells respond to stripes or edges with a particular orientation; simple cells have excitatory and inhibitory regions in the shape of oriented bars; complex cells respond to oriented lines of a particular length -other neurons are more concerned with color than with black/white contrast; t ...
Homework
... and endocrine systems regulate conditions in the body. 3. Neurons transmit electrochemical impulses. 4. Sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons all have a role in sensation, thought and response. Essential Questions: 1. How does the structure of the nervous system allow it to function? 2. H ...
... and endocrine systems regulate conditions in the body. 3. Neurons transmit electrochemical impulses. 4. Sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons all have a role in sensation, thought and response. Essential Questions: 1. How does the structure of the nervous system allow it to function? 2. H ...