Autonomic
... digestion is ceased, your liver ramps up glucose release, your pupils dilate, salivary production decreases, sweat increases. ...
... digestion is ceased, your liver ramps up glucose release, your pupils dilate, salivary production decreases, sweat increases. ...
hydroxytryptamine-containing neurons in the snail Effect of
... ganglia of untreated controls, but if the treatment with nerve growth factor was stopped the enzyme activities of both the operated and control ganglia returned within 6 weeks to the same values as in animals who had received no treatment with nerve growth factor. Thus nerve growth factor was unable ...
... ganglia of untreated controls, but if the treatment with nerve growth factor was stopped the enzyme activities of both the operated and control ganglia returned within 6 weeks to the same values as in animals who had received no treatment with nerve growth factor. Thus nerve growth factor was unable ...
Nervous system Lab - Sonoma Valley High School
... A) List two striking characteristics of neurons. B) Characterize a nerve impulse. C) Explain how ions play a role in creating an impulse. D) Explain how ion channels play a role in nerve impulses. E) Characterize a neuron that is resting regarding charges, ion concentrations. F) Explain the role of ...
... A) List two striking characteristics of neurons. B) Characterize a nerve impulse. C) Explain how ions play a role in creating an impulse. D) Explain how ion channels play a role in nerve impulses. E) Characterize a neuron that is resting regarding charges, ion concentrations. F) Explain the role of ...
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... Explain why the NTs discussed above do not continually stimulate the post-synaptic neuron's membrane. ...
... Explain why the NTs discussed above do not continually stimulate the post-synaptic neuron's membrane. ...
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... Explain why the NTs discussed above do not continually stimulate the post-synaptic neuron's membrane. ...
... Explain why the NTs discussed above do not continually stimulate the post-synaptic neuron's membrane. ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... information needed for the neuron to fire. For example, your friend is talking in a low voice, so low that you don’t even hear it. Stimulus threshold is the lowest your friend can talk to you so that you actually pick up the sound, which is why the definition states that it is the minimum amount o ...
... information needed for the neuron to fire. For example, your friend is talking in a low voice, so low that you don’t even hear it. Stimulus threshold is the lowest your friend can talk to you so that you actually pick up the sound, which is why the definition states that it is the minimum amount o ...
• In vertebrates
... • In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNS • Cranial nerves originate in the brain and mostly terminate in organs of the head and upper body • Spinal nerves originate in the spinal cord and extend to parts of the body be ...
... • In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNS • Cranial nerves originate in the brain and mostly terminate in organs of the head and upper body • Spinal nerves originate in the spinal cord and extend to parts of the body be ...
Nervous System PPT - New Paltz Central School District
... Barrier (BBB), Form Pial Glial Layer a protective layer along the CNS Oligodendrocytes: Produce myelin covering for neurons in the CNS Microglia: Very small until activated by an injury then work as a phagocytes. Alzheimer’s produces a lot of microglia Ependymal Cells – Line canals and produce cereb ...
... Barrier (BBB), Form Pial Glial Layer a protective layer along the CNS Oligodendrocytes: Produce myelin covering for neurons in the CNS Microglia: Very small until activated by an injury then work as a phagocytes. Alzheimer’s produces a lot of microglia Ependymal Cells – Line canals and produce cereb ...
lesson 6
... 1) synthesized and released by neurons 2) released at the nerve terminal in a 'chemically identifiable' form 3) the chemical should reproduce the activity of the presynaptic neuron 4) can be blocked by competitive antagonist based on concentration 5) active mechanisms to stop the function of the neu ...
... 1) synthesized and released by neurons 2) released at the nerve terminal in a 'chemically identifiable' form 3) the chemical should reproduce the activity of the presynaptic neuron 4) can be blocked by competitive antagonist based on concentration 5) active mechanisms to stop the function of the neu ...
Schwann cells
... A. Neural injuries may cause permanent dysfunction B. If axons alone are destroyed, cell bodies often survive, and the axons may regenerate 1. In PNS macrophages destroy axon distal to the injury a. Axon filaments grow peripherally from injured site ...
... A. Neural injuries may cause permanent dysfunction B. If axons alone are destroyed, cell bodies often survive, and the axons may regenerate 1. In PNS macrophages destroy axon distal to the injury a. Axon filaments grow peripherally from injured site ...
Skeletal, Muscular, Nervous (5days)
... Smooth muscle is found in the lining of the body’s passageways and hollow internal organs, such as in the digestive tract, the urinary bladder, the lining of the blood vessels, and passageways into the lungs. ...
... Smooth muscle is found in the lining of the body’s passageways and hollow internal organs, such as in the digestive tract, the urinary bladder, the lining of the blood vessels, and passageways into the lungs. ...
Researcher studies nervous system development
... neurodevelopmental disorders, like multiple sclerosis or epilepsy, occur. Multiple sclerosis is a disease that damages the myelin sheath on the nerve cells, creating problems for the transmission of the electrical signals. ...
... neurodevelopmental disorders, like multiple sclerosis or epilepsy, occur. Multiple sclerosis is a disease that damages the myelin sheath on the nerve cells, creating problems for the transmission of the electrical signals. ...
1 How the Nervous System Works
... synapse between the axon tip of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron. Notice that a small gap separates these two structures. For a nerve impulse to be carried along at a synapse, it must cross the gap between the axon and the next structure. The axon tips release chemicals that carry the i ...
... synapse between the axon tip of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron. Notice that a small gap separates these two structures. For a nerve impulse to be carried along at a synapse, it must cross the gap between the axon and the next structure. The axon tips release chemicals that carry the i ...
Senses
... Refraction and Focus Refraction occurs when light enters the eye and bends in order to focus. Images appear upside down when they reach the retina, but are perceived as right side up by the brain. If the lens is normal, the light always focuses on the retina. In myopia and hyperopia the shape if th ...
... Refraction and Focus Refraction occurs when light enters the eye and bends in order to focus. Images appear upside down when they reach the retina, but are perceived as right side up by the brain. If the lens is normal, the light always focuses on the retina. In myopia and hyperopia the shape if th ...
2.1.2. The Purpose: Acquaint the student by subject to neurologies
... The subject of nervous disease, to studying exploring clinical manifestations of the diseases of the nervous system and devisinging methods of their diagnostics, treatments and preventive maintenances. The First information about disease of the nervous system meet in written source of the deep antiq ...
... The subject of nervous disease, to studying exploring clinical manifestations of the diseases of the nervous system and devisinging methods of their diagnostics, treatments and preventive maintenances. The First information about disease of the nervous system meet in written source of the deep antiq ...
I. Neurons are the anatomical elements of neural systems
... deficits a. it is possible to interrupt the primary visual pathway, so as to produce complete while certain visual behaviors, such as the pupillary light reflexes, remain intact and normal b. brain lesions that involve one or more of the subsidiary pathways without affecting the primary visual pathw ...
... deficits a. it is possible to interrupt the primary visual pathway, so as to produce complete while certain visual behaviors, such as the pupillary light reflexes, remain intact and normal b. brain lesions that involve one or more of the subsidiary pathways without affecting the primary visual pathw ...
Chapter 9 Senses - msubillings.edu
... protein enzyme called opsin (globular protein located in the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane) and retinal (yellow pigment) in loose chemical connection. When light strikes the rod it causes a shape change in the retinal portion of the rhodopsin which in turn causes a shape change in the o ...
... protein enzyme called opsin (globular protein located in the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane) and retinal (yellow pigment) in loose chemical connection. When light strikes the rod it causes a shape change in the retinal portion of the rhodopsin which in turn causes a shape change in the o ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... slowest group is the cytoskeletal components. Mitochondria are transported down from the cell body at an intermediate rate. The retrograde flow from the synaptic telodendria back into the soma, returns any excess of material from degradation or reprocessing. The retrograde flow permits any excess pr ...
... slowest group is the cytoskeletal components. Mitochondria are transported down from the cell body at an intermediate rate. The retrograde flow from the synaptic telodendria back into the soma, returns any excess of material from degradation or reprocessing. The retrograde flow permits any excess pr ...
Biology and Behaviour 40s
... appropriate leg muscle to contract. The response is a muscular jerk that happens quickly and does not involve your brain. Humans have lots of hard-wired reflexes like this, but as tasks become more complex, the pathway "circuitry" gets more complicated and the brain gets involved. ...
... appropriate leg muscle to contract. The response is a muscular jerk that happens quickly and does not involve your brain. Humans have lots of hard-wired reflexes like this, but as tasks become more complex, the pathway "circuitry" gets more complicated and the brain gets involved. ...
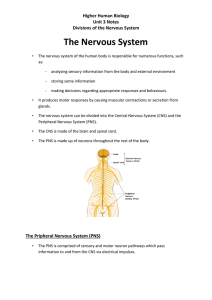
The Nervous System - Cathkin High School
... The nervous system of the human body is responsible for numerous functions, such as: ...
... The nervous system of the human body is responsible for numerous functions, such as: ...
Topic 8.1 Neurones and nervous responses File
... Myelinated axons: The myelin sheath electrical insulator acts as an _____________. Action potentials cannot form where myelin is present. Therefore they can only form Node of Ranvier at the _____________where there is no myelin. Therefore local circuits can node and a form between one ___ neighbour ...
... Myelinated axons: The myelin sheath electrical insulator acts as an _____________. Action potentials cannot form where myelin is present. Therefore they can only form Node of Ranvier at the _____________where there is no myelin. Therefore local circuits can node and a form between one ___ neighbour ...
Nervous System - Thephysicsteacher
... Permit impulses in one direction only – neurotransmitters only present on one side of the synapse. Allow localisation of a response rather than a total body response (chaos!). Protect against over-stimulation, as they will slow down if overloaded. Their complicated interconnections allow for ...
... Permit impulses in one direction only – neurotransmitters only present on one side of the synapse. Allow localisation of a response rather than a total body response (chaos!). Protect against over-stimulation, as they will slow down if overloaded. Their complicated interconnections allow for ...