neurons and the nervous system
... neuron. Carries messages away from the cell body Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between Schwann cells. Function: Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping ...
... neuron. Carries messages away from the cell body Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between Schwann cells. Function: Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping ...
LECTURE18.Olfaction&Taste
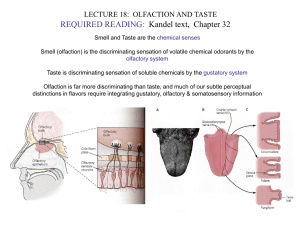
... and are continuously regenerated from basal cells Apical microvilli of taste cells are exposed to saliva through the taste pore Tasty substance is sensed at microvilli by several mechanisms, but always induces depolarization and action potential generation ...
... and are continuously regenerated from basal cells Apical microvilli of taste cells are exposed to saliva through the taste pore Tasty substance is sensed at microvilli by several mechanisms, but always induces depolarization and action potential generation ...
Ch. 14 The Peripheral Nervous System
... – Rootlets enter via foramen magnum, exits through jugular foramen ...
... – Rootlets enter via foramen magnum, exits through jugular foramen ...
A zebrafish model exemplifies the long preclinical period of motor
... on a zebrafish model of ALS that contributes to the concept of preclinical change. Specifically, we have developed a sod1 zebrafish model of ALS/motor neuron disease (MND) and demonstrated that zebrafish, like mice and humans, show hallmark features of ALS, suggesting that the zebrafish provides an excel ...
... on a zebrafish model of ALS that contributes to the concept of preclinical change. Specifically, we have developed a sod1 zebrafish model of ALS/motor neuron disease (MND) and demonstrated that zebrafish, like mice and humans, show hallmark features of ALS, suggesting that the zebrafish provides an excel ...
Primary motor cortex
... when volunteers read words on a video screen: the primary visual cortex and an additional part of the visual system, both in the back of the left hemisphere. Other brain regions become especially active when subjects hear words through ear-phones, as seen in the PET scan on the right. To create thes ...
... when volunteers read words on a video screen: the primary visual cortex and an additional part of the visual system, both in the back of the left hemisphere. Other brain regions become especially active when subjects hear words through ear-phones, as seen in the PET scan on the right. To create thes ...
Hamstring Injuries
... muscle increasing the stress on tendons (tendonitis), they may adhere one muscle to another muscle or they may adhere the nerve to the muscle (nerve entrapment). An experienced Active Release provider can locate and treat adhesions on the muscles; subsequently restoring normal function. As you move ...
... muscle increasing the stress on tendons (tendonitis), they may adhere one muscle to another muscle or they may adhere the nerve to the muscle (nerve entrapment). An experienced Active Release provider can locate and treat adhesions on the muscles; subsequently restoring normal function. As you move ...
MOTOR ph226 2015
... side of the body •Cortical representation of each body part is proportionate in size to the skill of that part being used for fine voluntary movement •Therefore the area involved in hand movement and in speech have large representation in the cortex (more than half of primary motor cortex) •Both ind ...
... side of the body •Cortical representation of each body part is proportionate in size to the skill of that part being used for fine voluntary movement •Therefore the area involved in hand movement and in speech have large representation in the cortex (more than half of primary motor cortex) •Both ind ...
Nervous System
... the brain by way of the senses (touch, smell, see, etc.) Integration: the interpretation or translation of ...
... the brain by way of the senses (touch, smell, see, etc.) Integration: the interpretation or translation of ...
Biology 232 - Request a Spot account
... 3) basal stem cells – divide and differentiate to produce new receptors olfactory glands – in underlying connective tissue secrete mucus on surface – dissolves odorant molecules Vomeronasal Organ – specialized olfactory organ within incisive bones of some species, may communicate with nasal cavity a ...
... 3) basal stem cells – divide and differentiate to produce new receptors olfactory glands – in underlying connective tissue secrete mucus on surface – dissolves odorant molecules Vomeronasal Organ – specialized olfactory organ within incisive bones of some species, may communicate with nasal cavity a ...
Special Senses - Everglades High School
... Depending on the distance of the object you are looking at, the lens must change shape (with contraction of ciliary body) to focus light waves on the retina. The ability to change and focus on objects at different distances is called accommodation. The image is also inverted as the light waves trave ...
... Depending on the distance of the object you are looking at, the lens must change shape (with contraction of ciliary body) to focus light waves on the retina. The ability to change and focus on objects at different distances is called accommodation. The image is also inverted as the light waves trave ...
Mark Time Reflex
... • Like the primary receptor of the muscle spindle, the tendon organ has both dynamic and static responses responding when tension increases (dynamic response) and settling down to a lower level of steady-state firing (static response). • When the Golgi organs of a muscle are stimulated by increased ...
... • Like the primary receptor of the muscle spindle, the tendon organ has both dynamic and static responses responding when tension increases (dynamic response) and settling down to a lower level of steady-state firing (static response). • When the Golgi organs of a muscle are stimulated by increased ...
Molecules of Emotion
... of emotions, their distribution in the body's nerves has all kinds of significance. This very much reflects some of Sigmund Freud's thinking in that the body is the unconscious mind. Due to the many years of research conducted by Dr. Pert and many others, the emotional brain can no longer be conside ...
... of emotions, their distribution in the body's nerves has all kinds of significance. This very much reflects some of Sigmund Freud's thinking in that the body is the unconscious mind. Due to the many years of research conducted by Dr. Pert and many others, the emotional brain can no longer be conside ...
ANPS 019 Black 11-14
... Salt and sour receptors -chemically gated ion channels *salt and sour work directly on ion channel Sweet, bitter and umani receptors -gustducins – g proteins *use a second messenger cascade that will eventually affect ion channel ...
... Salt and sour receptors -chemically gated ion channels *salt and sour work directly on ion channel Sweet, bitter and umani receptors -gustducins – g proteins *use a second messenger cascade that will eventually affect ion channel ...
Investigating the Effect of Knockout APP and Increased Calcium
... tau peptide containing the microtubule binding domain. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 6:461-467. (http://content.iospress.com/download/journal-ofalzheimers-disease/jad00350?id=journal-of-alzheimers-disease%2Fjad00350) ...
... tau peptide containing the microtubule binding domain. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 6:461-467. (http://content.iospress.com/download/journal-ofalzheimers-disease/jad00350?id=journal-of-alzheimers-disease%2Fjad00350) ...
Nicotine toxicity
... Many of the effects of nicotine result from its effects on the neuromucular system which is made up of the brain and muscle. In order to understand the physiological response to nicotine, I would like to review with you some of the physiology of the neuromuscuar system. The neuromuscular system is c ...
... Many of the effects of nicotine result from its effects on the neuromucular system which is made up of the brain and muscle. In order to understand the physiological response to nicotine, I would like to review with you some of the physiology of the neuromuscuar system. The neuromuscular system is c ...
The Role of Neurotrophins in Neurotransmitter Release
... high-frequency synaptic transmission, synapses may use two alternative modes of synaptic vesicle retrieval, the conventional slow endosomal recycling or a faster rapid retrieval at the active zone, referred to as “kiss-and-run.” By modulating Ca2+ microdomains associated with voltage-gated Ca2+ chan ...
... high-frequency synaptic transmission, synapses may use two alternative modes of synaptic vesicle retrieval, the conventional slow endosomal recycling or a faster rapid retrieval at the active zone, referred to as “kiss-and-run.” By modulating Ca2+ microdomains associated with voltage-gated Ca2+ chan ...
Note - Reza Shadmehr
... Extrafusal muscle fibers change based on their history of activation Slide 6. A muscle fiber cannot split to form a new fiber. So a muscle can become bulkier only if the individual fibers become thicker. This happens by addition of new myofibrils. The process starts when there is additional stress a ...
... Extrafusal muscle fibers change based on their history of activation Slide 6. A muscle fiber cannot split to form a new fiber. So a muscle can become bulkier only if the individual fibers become thicker. This happens by addition of new myofibrils. The process starts when there is additional stress a ...
ciliated mucous membrane
... Identify the largest part of a neuron. Cell body Identify the long part of the neuron. Axon Identify the structures that can wrap around the axon to speed up impulses. Schwann cells Identify the last part of the neuron that send the impulse to the next neuron. Terminal branches Identify the space be ...
... Identify the largest part of a neuron. Cell body Identify the long part of the neuron. Axon Identify the structures that can wrap around the axon to speed up impulses. Schwann cells Identify the last part of the neuron that send the impulse to the next neuron. Terminal branches Identify the space be ...
Handout - Science in the News
... Inhibitory: Describes a neuron or neurotransmitter that makes other neurons less likely to send an impulse. Ion: Electrically charged molecule. Ion channel: Openings in the membrane that surround all cells to allow and control the flow of ions. The membrane is otherwise impermeable to ions. Membrane ...
... Inhibitory: Describes a neuron or neurotransmitter that makes other neurons less likely to send an impulse. Ion: Electrically charged molecule. Ion channel: Openings in the membrane that surround all cells to allow and control the flow of ions. The membrane is otherwise impermeable to ions. Membrane ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.