path430_826-week10-PD
... promoter associated with sporadic PD in some studies, but not in others ...
... promoter associated with sporadic PD in some studies, but not in others ...
File
... • The same neurotransmitter can produce different effects in different types of cells. • There are five major classes of neurotransmitters: acetylcholine, biogenic amines, amino acids, neuropeptides, and gases. • Gases such as nitric oxide and carbon monoxide are local regulators in the PNS. ...
... • The same neurotransmitter can produce different effects in different types of cells. • There are five major classes of neurotransmitters: acetylcholine, biogenic amines, amino acids, neuropeptides, and gases. • Gases such as nitric oxide and carbon monoxide are local regulators in the PNS. ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... Definition: Whenever a muscle is stretched, excitation of the spindles causes reflexive contraction of the same muscle from which the signal originated and also of closely allied synergistic muscle. The basic circuit: Spindle Proprioceptor nerve fiber dorsal root of the spinal cord synapses with ant ...
... Definition: Whenever a muscle is stretched, excitation of the spindles causes reflexive contraction of the same muscle from which the signal originated and also of closely allied synergistic muscle. The basic circuit: Spindle Proprioceptor nerve fiber dorsal root of the spinal cord synapses with ant ...
Nervous System Reading from SparkNotes
... transmission are highly specialized cells known as neurons, which are the functional unit of the nervous system. The neuron is an elongated cell that usually consists of three main parts: the dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. The typical neuron contains many dendrites, which have the appearanc ...
... transmission are highly specialized cells known as neurons, which are the functional unit of the nervous system. The neuron is an elongated cell that usually consists of three main parts: the dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. The typical neuron contains many dendrites, which have the appearanc ...
Motor System & Behavior
... that the body is idle, so that no voluntary movement occurs. Now assume a ball has been spotted, and the motivation to grab the ball is born within the motivation areas of the cortex. The motor has currently no idea of how to actually get the ball, and cannot execute any movement yet because the mot ...
... that the body is idle, so that no voluntary movement occurs. Now assume a ball has been spotted, and the motivation to grab the ball is born within the motivation areas of the cortex. The motor has currently no idea of how to actually get the ball, and cannot execute any movement yet because the mot ...
Neurotransmitter Test Assessment
... Glutamate - is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain which is necessary for memory and learning. In fact, it is believed that 70% of the fast excitatory CNS synapses utilize glutamate as a transmitter. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the activity of signal-receiving neurons and pl ...
... Glutamate - is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain which is necessary for memory and learning. In fact, it is believed that 70% of the fast excitatory CNS synapses utilize glutamate as a transmitter. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the activity of signal-receiving neurons and pl ...
It takes all kinds to make a brain
... update the motor command centers about the outcome of the movements. The motor system can also generate an internal prediction of the planned actions to reduce delay. Previous studies have suggested that several cerebellar and cortical sites act as integration centers, where internal motor predictio ...
... update the motor command centers about the outcome of the movements. The motor system can also generate an internal prediction of the planned actions to reduce delay. Previous studies have suggested that several cerebellar and cortical sites act as integration centers, where internal motor predictio ...
Document
... must receive constant proprioceptor input about – Length of muscle (from muscle spindles) – Muscle tone: Amount of tension in muscle and ...
... must receive constant proprioceptor input about – Length of muscle (from muscle spindles) – Muscle tone: Amount of tension in muscle and ...
Anat3_01_Nervous_Tissue
... Vibration, touch, pressure, or tissue stretching can all distort the channel from its resting position, opening the gate. ...
... Vibration, touch, pressure, or tissue stretching can all distort the channel from its resting position, opening the gate. ...
W7 Lecture
... Panel 4: A and B are stimulated enough to cause a suprathreshold graded depolarization, so an action potential results. Panel 5: Neuron C causes a graded hyperpolarization; A and C effects add, cancel each other out. ...
... Panel 4: A and B are stimulated enough to cause a suprathreshold graded depolarization, so an action potential results. Panel 5: Neuron C causes a graded hyperpolarization; A and C effects add, cancel each other out. ...
- Eye, Brain, and Vision
... What happens when information is transferred from one cell to another at the synapse? In the first cell, an electrical signal, or impulse, is initiated on the part of an axon closest to the cell body. The impulse travels down the axon to its terminals. At each terminal, as a result of the impulse, a ...
... What happens when information is transferred from one cell to another at the synapse? In the first cell, an electrical signal, or impulse, is initiated on the part of an axon closest to the cell body. The impulse travels down the axon to its terminals. At each terminal, as a result of the impulse, a ...
Neurons
... Dendrites are treelike extensions at the beginning of a neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body. These tiny protrusions receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma. Dendrites are also covered with synapses. Dendrite Characteristics ...
... Dendrites are treelike extensions at the beginning of a neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body. These tiny protrusions receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma. Dendrites are also covered with synapses. Dendrite Characteristics ...
Chapter 13: Peripheral Nervous System
... Motor functions include facial expression, and the transmittal of autonomic impulses to lacrimal and salivary glands Sensory function is taste from the anterior two-thirds of the ...
... Motor functions include facial expression, and the transmittal of autonomic impulses to lacrimal and salivary glands Sensory function is taste from the anterior two-thirds of the ...
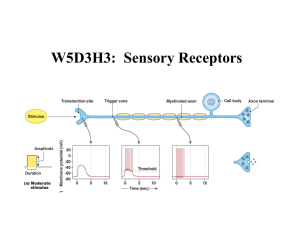
W5D3H3: Sensory Receptors
... In the somatosensory system, various different sensory receptors capture different stimuli and convey them to the sensory cortex. Each type of receptor is specialised, that is, receives the stimulus to which it is predetermined to receive. Immediately as it is stimulated, the receptor sends a signal ...
... In the somatosensory system, various different sensory receptors capture different stimuli and convey them to the sensory cortex. Each type of receptor is specialised, that is, receives the stimulus to which it is predetermined to receive. Immediately as it is stimulated, the receptor sends a signal ...
د. غسان The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): The ANS coordinates
... The “fight-or-flight” reaction elicited by the sympathetic system is essentially a whole body response. Changes in organ and tissue function throughout the body are coordinated so that there is an increase in the delivery of well-oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood to the working skeletal muscles. Both ...
... The “fight-or-flight” reaction elicited by the sympathetic system is essentially a whole body response. Changes in organ and tissue function throughout the body are coordinated so that there is an increase in the delivery of well-oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood to the working skeletal muscles. Both ...
NEUROBIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOR
... Three classes of neurons in CNS • Afferent (sensory) • Efferent (motor) • Interneurons ...
... Three classes of neurons in CNS • Afferent (sensory) • Efferent (motor) • Interneurons ...
Lecture CH18 chem131pikul partA
... • A neurotransmitter is a chemical messenger that transmits nerve impulses from one neuron to another. • The space between the two neurons is called a synapse. • The presynaptic neuron releases the neurotransmitter. • The postsynaptic neuron contains the receptors that bind the neurotransmitter. ...
... • A neurotransmitter is a chemical messenger that transmits nerve impulses from one neuron to another. • The space between the two neurons is called a synapse. • The presynaptic neuron releases the neurotransmitter. • The postsynaptic neuron contains the receptors that bind the neurotransmitter. ...
Action potential
... “Information” travels within the nervous system as propagated electrical signals (action potentials) The most important information (vision, balance, motor commands) is carried by large-diameter, ...
... “Information” travels within the nervous system as propagated electrical signals (action potentials) The most important information (vision, balance, motor commands) is carried by large-diameter, ...
Human Tissues IV
... XLIII. STRUCTURE OF THE INTERCALATED DISK a. picture highlighting intercalated disk c. A single neuromuscular junction tells each individual cell to contract in skeletal muscle via depolarization; but in cardiac cells we don’t want independent control of each fiber. Instead, we have a set of fibers/ ...
... XLIII. STRUCTURE OF THE INTERCALATED DISK a. picture highlighting intercalated disk c. A single neuromuscular junction tells each individual cell to contract in skeletal muscle via depolarization; but in cardiac cells we don’t want independent control of each fiber. Instead, we have a set of fibers/ ...
Molecular and Cellular aspects of a Sacred Disease `Epilepsy`
... induced (Roll and Szepetowski, 2002). Ion channels are the transmembrane proteins containing selective pores for different types. ligand binding, voltage, cell volume, intracellular ions or neucleotides are responsible for the activation of ion channels,. Ligand gated channels are activated by diffe ...
... induced (Roll and Szepetowski, 2002). Ion channels are the transmembrane proteins containing selective pores for different types. ligand binding, voltage, cell volume, intracellular ions or neucleotides are responsible for the activation of ion channels,. Ligand gated channels are activated by diffe ...
Somatosensory system
... • Action potential peripheral axon soma in dorsal root ganglion proximal axon in spinal cord via axons white matter brain • The diameter of the axons, the degree of axonal myelination, and the number of synapse in the pathway determine how quickly the information is processed ...
... • Action potential peripheral axon soma in dorsal root ganglion proximal axon in spinal cord via axons white matter brain • The diameter of the axons, the degree of axonal myelination, and the number of synapse in the pathway determine how quickly the information is processed ...
Figure 8.12
... ◦ White connective tissue layer ◦ Seen anteriorly as the “white of the eye” Cornea ◦ Transparent, central anterior portion ◦ Allows for light to pass through ◦ Repairs itself easily ◦ The only human tissue that can be transplanted without fear of rejection ...
... ◦ White connective tissue layer ◦ Seen anteriorly as the “white of the eye” Cornea ◦ Transparent, central anterior portion ◦ Allows for light to pass through ◦ Repairs itself easily ◦ The only human tissue that can be transplanted without fear of rejection ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.