07 Momentum - matermiddlehigh.org
... How long this force acts, it is also important. The quantity of force x time interval is called impulse impulse = F ∙ t impulse = change in momentum F ∙ t = m ∙ v F∙t =m∙v ...
... How long this force acts, it is also important. The quantity of force x time interval is called impulse impulse = F ∙ t impulse = change in momentum F ∙ t = m ∙ v F∙t =m∙v ...
Physics 218 - Purdue Physics
... what height you choose, as long as you are consistent with that choice through the whole problem. Usually it’s easiest to choose the lowest point in the problem as h=0. • Then, solve the problem! ...
... what height you choose, as long as you are consistent with that choice through the whole problem. Usually it’s easiest to choose the lowest point in the problem as h=0. • Then, solve the problem! ...
Part5-Electromagneti..
... Polarization A string can have transverse waves in the up-anddown (vertical) direction, or in the side-to-side (horizontal) direction. Waves that are only “waving” in one direction are said to be polarized. Up-and-down waves are vertically polarized. Side-to-side waves are horizontally polarized. If ...
... Polarization A string can have transverse waves in the up-anddown (vertical) direction, or in the side-to-side (horizontal) direction. Waves that are only “waving” in one direction are said to be polarized. Up-and-down waves are vertically polarized. Side-to-side waves are horizontally polarized. If ...
Lecture 3: Specific Intensity, Flux and Optical Depth
... Lecture 3: Specific Intensity, Flux and Optical Depth We begin a more detailed look at stellar atmospheres by defining the fundamental variable, which is called the Specific Intensity. It may be specified as a function of frequency, Iν, or of wavelength,Iλ . It is basically the same as flux except l ...
... Lecture 3: Specific Intensity, Flux and Optical Depth We begin a more detailed look at stellar atmospheres by defining the fundamental variable, which is called the Specific Intensity. It may be specified as a function of frequency, Iν, or of wavelength,Iλ . It is basically the same as flux except l ...
Rotational Doppler effect in left
... In the case of electromagnetic radiation this usually means that the subunits must be much smaller than the wavelength of radiation. Then the unit cells of metamaterials can be modeled as the atoms (or molecules) in ordinary materials. In particular, electric atoms with an electric-dipole moment lea ...
... In the case of electromagnetic radiation this usually means that the subunits must be much smaller than the wavelength of radiation. Then the unit cells of metamaterials can be modeled as the atoms (or molecules) in ordinary materials. In particular, electric atoms with an electric-dipole moment lea ...
Academic Physics Semester II Review Sheet
... 19. A 0.17 kg hockey puck slows down from 54 m/s to 35 m/s when it slides on horizontal ice surface. Find the change in momentum of the puck? 20. A 0.01 kg bullet is fired at 250 m/s into a wooden block that is fixed. The bullet emerges from the block with a speed of 120 m/s. What is the change in m ...
... 19. A 0.17 kg hockey puck slows down from 54 m/s to 35 m/s when it slides on horizontal ice surface. Find the change in momentum of the puck? 20. A 0.01 kg bullet is fired at 250 m/s into a wooden block that is fixed. The bullet emerges from the block with a speed of 120 m/s. What is the change in m ...
Happy/Sad Ball Lesson Plan
... larger total force to both stop the current motion and reverse it. ● Looking at each ball’s momentum before and after the collision will show this. Both balls have the same mass and were released from the same height, meaning that at the point just before impact they have the same momentum. After th ...
... larger total force to both stop the current motion and reverse it. ● Looking at each ball’s momentum before and after the collision will show this. Both balls have the same mass and were released from the same height, meaning that at the point just before impact they have the same momentum. After th ...
Obtaining Maxwell`s equations heuristically
... First, as already mentioned, there is no experimental evidence for magnetic charges so there cannot exist any fieldgenerating pseudoscalars. The only pseudoscalar [see Eq. (11)] that can be generated and obeys linearity is to take the first-order spatial derivative of an axial field vector. Thus, we ...
... First, as already mentioned, there is no experimental evidence for magnetic charges so there cannot exist any fieldgenerating pseudoscalars. The only pseudoscalar [see Eq. (11)] that can be generated and obeys linearity is to take the first-order spatial derivative of an axial field vector. Thus, we ...
Momentum - gandell
... • If forces come in equal and opposite pairs, what about Impulse? • If Impulses are equal what is the difference caused by a bigger mass? • Hint a 600 lb sumo wrestler and 90 lb nerd collide with equal Impulse. What difference would you observe????? Physics I Honors ...
... • If forces come in equal and opposite pairs, what about Impulse? • If Impulses are equal what is the difference caused by a bigger mass? • Hint a 600 lb sumo wrestler and 90 lb nerd collide with equal Impulse. What difference would you observe????? Physics I Honors ...
Bose-Einstein Condensates Bosons Liquid Helium
... 2.7 mK (1000 times smaller than 42 He ). How is this possible? Two atoms of 23 He align themselves to give an overall spin of s = 1 and angular momentum l = 1. The paired system becomes a boson! Thus, liquid 23 He can become a superfluid, but only when two atoms perform a complicated dance and act a ...
... 2.7 mK (1000 times smaller than 42 He ). How is this possible? Two atoms of 23 He align themselves to give an overall spin of s = 1 and angular momentum l = 1. The paired system becomes a boson! Thus, liquid 23 He can become a superfluid, but only when two atoms perform a complicated dance and act a ...
12.4 Momentum and Impulse
... Most often mass doesn’t change so velocity changes and this is acceleration. And then we get: p = mass x Δv (Don’t forget Δ is “change in”) p = mass x Acceleration p = force ...
... Most often mass doesn’t change so velocity changes and this is acceleration. And then we get: p = mass x Δv (Don’t forget Δ is “change in”) p = mass x Acceleration p = force ...
25_InstructorGuideWin
... induced emf. After all, most of the demonstrations of induction are concerned only with the direction of the induced current. An early statement of Lenz’s law also allows Faraday’s law to be stated without the troublesome minus sign. Many of the applications of magnetic induction, such as eddy curre ...
... induced emf. After all, most of the demonstrations of induction are concerned only with the direction of the induced current. An early statement of Lenz’s law also allows Faraday’s law to be stated without the troublesome minus sign. Many of the applications of magnetic induction, such as eddy curre ...
Rotational Motion - University of Colorado Boulder
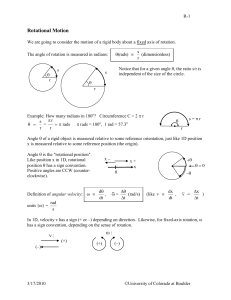
... Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The direction of A B is the direction perpendicular to the plane defined by th ...
... Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The direction of A B is the direction perpendicular to the plane defined by th ...