SASO_GFCINov2014
... Ground Fault / Residual Current Electric current that flows from electrical equipment through a human to ground. ...
... Ground Fault / Residual Current Electric current that flows from electrical equipment through a human to ground. ...
Electric Components
... • A diode consists of a piece of n-type and a piece of p-type semiconductor joined together (a junction). • Electrons in the n-type half of the diode are repelled away from the junction by the negative ions in the p-type region, and holes in the p-type half are repelled by the positive ions in the n ...
... • A diode consists of a piece of n-type and a piece of p-type semiconductor joined together (a junction). • Electrons in the n-type half of the diode are repelled away from the junction by the negative ions in the p-type region, and holes in the p-type half are repelled by the positive ions in the n ...
Ohm`s Law - Physics Concepts Ltd
... 20 1(A)Yes Diode rectifies (allows current flow in one direction) Some web pages about electricity are available at: http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/physics/electricity/index.shtml Copyright-free from www.physconcepts.co.uk ...
... 20 1(A)Yes Diode rectifies (allows current flow in one direction) Some web pages about electricity are available at: http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/physics/electricity/index.shtml Copyright-free from www.physconcepts.co.uk ...
TYPES OF FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS
... Is a three terminal semi conductor device in which current conduction is by one type of carrier i.e electrons or holes. The output characteristics are controlled by input voltage and not by input current. ...
... Is a three terminal semi conductor device in which current conduction is by one type of carrier i.e electrons or holes. The output characteristics are controlled by input voltage and not by input current. ...
9 Electricity Notes
... • Can cause excess electrical energy to flow through parts of the circuit causing overheating of wires. ...
... • Can cause excess electrical energy to flow through parts of the circuit causing overheating of wires. ...
BA-E-TK-101--Draft A5 - ELB Füllstandsgeräte Bundschuh GmbH+Co
... Errorlimit = ±1%; FSO= ±0,2 mA; burden resistance 500 ΩFor an inverse display (100% indication = float, bottom position), the connection wires 0% and 100% have to be exchanged For an inverse display (100% indication = float, bottom position), the connection wires 0% (RED) and 100% (Yellow) have to b ...
... Errorlimit = ±1%; FSO= ±0,2 mA; burden resistance 500 ΩFor an inverse display (100% indication = float, bottom position), the connection wires 0% and 100% have to be exchanged For an inverse display (100% indication = float, bottom position), the connection wires 0% (RED) and 100% (Yellow) have to b ...
Inverse Transmission Parameter
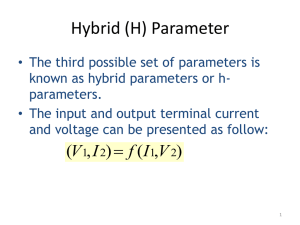
... • The third possible set of parameters is known as hybrid parameters or hparameters. • The input and output terminal current and voltage can be presented as follow: ...
... • The third possible set of parameters is known as hybrid parameters or hparameters. • The input and output terminal current and voltage can be presented as follow: ...
Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm`s Law
... are the power ratings for your resistors? Fit the DMM with alligator clips and wire leads to make a continuity checker. Use it to discover the pattern of electrical connections on a protoboard. Which holes are connected? You will rely on that pattern of connections in putting together circuits durin ...
... are the power ratings for your resistors? Fit the DMM with alligator clips and wire leads to make a continuity checker. Use it to discover the pattern of electrical connections on a protoboard. Which holes are connected? You will rely on that pattern of connections in putting together circuits durin ...
Protection Relay NJBK1 Series Motor Protector
... 5.2 LED displays the current value, setting state, fault code and other information about the maximum phase. 5.3 With overload inverse time-lag protection, open-phase protection, three-phase current unbalance protection and other functions. 5.4 5 optional built-in overload curves,meet the use at dif ...
... 5.2 LED displays the current value, setting state, fault code and other information about the maximum phase. 5.3 With overload inverse time-lag protection, open-phase protection, three-phase current unbalance protection and other functions. 5.4 5 optional built-in overload curves,meet the use at dif ...
Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm’s Law
... The power rating of a resistor depends on its size. Using the vernier calipers measure the length and diameter of one of your resistors. Compare your measurements with the data on the page from a component catalog at http://www.pa.msu.edu/courses/2013spring/PHY440/docs/DigiRes.pdf. What are the powe ...
... The power rating of a resistor depends on its size. Using the vernier calipers measure the length and diameter of one of your resistors. Compare your measurements with the data on the page from a component catalog at http://www.pa.msu.edu/courses/2013spring/PHY440/docs/DigiRes.pdf. What are the powe ...
ch13
... This is an experimental law, valid for both alternating current (ac) and direct current (dc) circuits. When you pass an electric current (I) through a resistance (R) there will be a potential difference or voltage (V) created across the resistance. Ohm’s law gives a relationship between the voltage ...
... This is an experimental law, valid for both alternating current (ac) and direct current (dc) circuits. When you pass an electric current (I) through a resistance (R) there will be a potential difference or voltage (V) created across the resistance. Ohm’s law gives a relationship between the voltage ...
Document
... Indicators and Objectives • PS-6.6: Explain the relationships among voltage, resistance, and current in Ohm’s law. • PS-6.9: Compare the functioning of simple series and parallel circuits. ...
... Indicators and Objectives • PS-6.6: Explain the relationships among voltage, resistance, and current in Ohm’s law. • PS-6.9: Compare the functioning of simple series and parallel circuits. ...
lec25
... where Q is the amount of charge passing the point. One ampere of current is one coulomb per second. ...
... where Q is the amount of charge passing the point. One ampere of current is one coulomb per second. ...
Ohm`s Law (and Circuit Theory) Tutorial
... ends are connected all together), but this does introduce the concept of branches. Since the resistors are no longer one right after the other, as is the case for series, when current gets to the two resistors, it has two ways it can go (either through one resistor or the other). This means that the ...
... ends are connected all together), but this does introduce the concept of branches. Since the resistors are no longer one right after the other, as is the case for series, when current gets to the two resistors, it has two ways it can go (either through one resistor or the other). This means that the ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.