* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science 9 Review Quiz
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
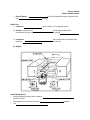
• Electric Motors – into Basic Parts: 1) Armature: Science 9 Notes Motors and Generators electricity flowing through an electric field energy. shaft with the coil wrapped around it. 2) Brushes: usually bars of pushed against the metal commutator springs. Make electrical contact with the moving 3) Commuter: and then that breaks the flow of electricity the connection of the coil 4) Magnet How a Motor Works: • Current flowing through a wire creates a around the wire • The magnetic field interacts with the • The magnets • • The brushes Reverses changes position so that its other half contacts the Direct and Alternating Current: • AC/DC: – Alternating Current – flows then (60 Hz) – Used in larger appliances Direct Current – flows in Transformers • AC transformers – change – can step-up( ) or step-down ( • Read page 329 voltage) Generating Electricity • Induced Current: – current can be generated in a circuit by The faster you move the magnet the more current is generated Generators • There are two types of generators: 1) AC generators - The most type - Central axis has a loop of wire that is attached to two 2) DC generators - spinning armature produces - If you run electricity through a DC generator it will spin like a motor Review: • • A motor converts energy A generator converts energy Your Task: • Check & Reflect page 331 # 1-8 energy into energy into Name: Science 9 Review Quiz 1. Which of the following statements is not true according to the Law of Electrical Charges? a. Positive charges repel neutral objects b. Positive charges repel positive charges c. Negative charges attract neutral objects d. Negative charges attract positive charges 2. The Van de Graff machine is frequently used during science experiments to demonstrate a. Magnetic field b. Current flow c. Superconducting material d. Static charge 3. A cell is connected by copper wire to a motor. The motor is connected in series to a lamp. The lamp is connected to a switch and the switch hooks back up to the cell. The “load” in this circuit is represented by the a. Cell and switch b. Motor and lamp c. Lamp and wire d. Wire and switch 4. Two definition relating to electrical measurement are written on the board: a. The quantity of electrons flowing pass a certain point b. The potential drop of flowing electrons Definitions A and B refer to, respectively a. b. c. d. Resistance and voltage Voltage and resistance Voltage and current Current and voltage 5. A current of 0.5A flows through a lamp that is connected to a 120V electrical power source. What is the resistance of the lamp? a. 60 Ω b. 120 Ω c. 240 Ω d. 360 Ω 6. Consider the following statements a student made about cells 1. Cells have two electrolytes and one electrode 2. Cells convert electrical energy into chemical energy 3. Cells connected together make a battery 4. Cells that cannot be recharged are primary cells Which pair of statements above best describes cells? a. b. c. d. 3 and 4 2 and 4 1 and 3 1 and 2 7. The element silver can be attached to a steel spoon to give it an expensive look. The process used is called a. Electrolysis b. Electro-refining c. Electron transfer d. Electroplating 8. When the temperature of a sample of mercury is brought down near Absolute Zero, the mercury becomes an excellent a. Insulator b. Superconductor c. Resistor d. Magnetic field 9. A science experiment to determine which materials complete a circuit and make a lamp work was performed by a group of grade 9 students. Their results determined that only two materials that they tried worked. The two materials could have been a. Aluminum foil and paper strip b. A carbon rod and a glass rod c. Aluminum foil and a carbon rod d. A carbon rod and a paper strip 10. A three way switch would most likely be used to operate a. A stove element b. A hallway light c. An oven element d. A laptop computer 11. Different combinations of electrodes and electrolytes are used in an experiment to determine which will produce a current. The combinations are listed in a chart below. Sample T U V W Electrode 1 Zinc Zinc Zinc Copper Electrode 2 Copper Zinc Carbon Copper Electrolyte Distilled Water Salt Water Salt Water Distilled Water a. Place a number 1 in the corresponding space if the electrode-electrolyte combination produces a current. Place a number 2 if the combination does not produce a current. T U V W b. Explain which sample produces the highest current. Explain why. 12. The scientist best known for their work related to magnetism and electricity are a. Watt and Chadwick b. Darwin and Mendel c. Volta and Ohm d. Faraday and Oersted 13. A kitchen appliance, plugged into a 120 V outlet uses 12 A of current. What is the resistance of the appliances? a. 0.1Ω b. 1 Ω c. 10Ω d. 100 Ω 14. Ohm’s Law explains the relationship between current, voltage and a. Energy b. Power c. Resistance d. Time 15. How does an increase in temperature affect the amount of resistance produced? The resistance a. Increases b. Decreases c. Increase, then decreases d. Remains unchanged 16. Draw the symbol for each of the following electrical components a. Battery of 3 cells b. Voltmeter c. Fuse d. Motor 17. Explain why a three-volt bulb would burn out if connected to a power supply for 1.5 V D cells hooked up in series 18. Draw a schematic diagram for a circuit consisting of a four cell battery connected to two lamps in parallel (each controlled by separate switches) to an ammeter. 19. Draw a diagram describing how protons and electrons behave in an insulator and a conductor. 20. An insulating material is one that a. Allows the free movement of current b. Limits the movement of current c. Prevents the movement of current d. Alters the movement of current 21. A conductor is made into a superconductor by a. Increasing the temperature b. Increasing the amount of material c. Decreasing the temperature d. Decreasing the amount of material 22. The main function of a switch is to a. Overload a circuit b. Interrupt a circuit c. Heat a circuit d. Change the direction of a circuit 23. The “potential drop” of a current in a circuit is measured in a. Amperes b. Volts c. Watts d. Ohms 24. What instrument is used to measure a current of 1 milliamp? a. Voltmeter b. Ohmmeter c. Galvanometer d. Ammeter 25. The metal conductor inside a cell is referred to as an a. Electron b. Electrolyte c. Electrode d. Electric charge 26. A battery is a device that converts a. Electrical energy into chemical energy b. Chemical energy to heat energy c. Electrical energy to heat energy d. Chemical energy to electrical energy 27. The basic differences between a “dry” cell and a “wet” cell is the a. State of the electrolyte b. Size of electrode c. Shape of container d. Location of poles 28. An electric current splits a water molecule into hydrogen and oxygen gas. This process is called a. Electro-refining b. Electroplating c. Electrolysis d. Electron analysis 29. What is the difference between a battery and a cell? 30. Which of the following terms describes what lightning rods do and completes the statement: lightning rods a current a. Generate b. Charge c. Ground d. Ignite 31. Explain why a balloon rubbed with fur sticks to a wall 32. A current of 0.687 A flows through a lamp that is connected to a 145 V electrical power source. What is the resistance of the lamp? 33. V = 3.5 V, I = 0.76 A; R= 34. I = 1,710,000 A, R = 0.002 Ω; V= 35. Draw a circuit with at least two different loads in parallel with a power supply of a five cell battery. With one switch that controls both loads and one switch that controls only one of the loads. As well as a voltmeter.( Be sure to indicate electron flow and the positive and negative terminals of the battery) 36. Draw a circuit that consists of a 9V battery, an ammeter and a 35Ω resistor in series. Include a voltmeter that is measuring the potential difference across the resistor. Remember to label the positive and negative terminals of the battery and indicate the direction of electron flow. b.What will the reading be on the ammeter in question 36? Be sure to show all of your calculations and formulas. 37. Draw a circuit consisting of a battery made up of four 1.5V cells, on switch, one lamp, two 0.50Ω resistors in series and a voltmeter. Indicate the direction in which current flows and the positive and negative terminals. 38. Draw a wet cell. Be sure to label all of the parts and indicate electron flow. Challenge Question: What is the value of this resistor, in ohms (Ω)?