Document
... 10. Two separate circuits wrap around a metal bar. Just after the switch is closed, how do the currents I1 and I2 flow through the resistors R1 and R2? a. I1 flows to the left, I2 flows to the left b. I1 flows to the left, I2 flows to the right c. I1 flows to the left, I2 is zero d. I1 flows to the ...
... 10. Two separate circuits wrap around a metal bar. Just after the switch is closed, how do the currents I1 and I2 flow through the resistors R1 and R2? a. I1 flows to the left, I2 flows to the left b. I1 flows to the left, I2 flows to the right c. I1 flows to the left, I2 is zero d. I1 flows to the ...
AC Power: A Worked Example
... where X is the total reactance of the circuit. N.B. be careful of the signs as X and Q can be positive or negative. The sign of the reactive power should be the same as that of the circuit reactance. Therefore, lagging power factors are caused by positive reactive power and leading power factors by ...
... where X is the total reactance of the circuit. N.B. be careful of the signs as X and Q can be positive or negative. The sign of the reactive power should be the same as that of the circuit reactance. Therefore, lagging power factors are caused by positive reactive power and leading power factors by ...
Sample-and-Hold Design Eric Sorensen March 16, 2012
... compensating for this, a large portion of the input signal will couple into the output during the hold phase. This is called feedthrough. During the hold phase, a very small amount of current is being drawn from the holding capacitor (on the order of a few nA). Even a small amount of feedthrough ha ...
... compensating for this, a large portion of the input signal will couple into the output during the hold phase. This is called feedthrough. During the hold phase, a very small amount of current is being drawn from the holding capacitor (on the order of a few nA). Even a small amount of feedthrough ha ...
Name
... 3. The current in the heating element of an electric iron is 5.0 A. If the iron dissipates 590 W of power, what is the voltage across it? Asnwer: V = P/I = 590 W/5A = 120 V ...
... 3. The current in the heating element of an electric iron is 5.0 A. If the iron dissipates 590 W of power, what is the voltage across it? Asnwer: V = P/I = 590 W/5A = 120 V ...
TIP120/TIP121/TIP122 NPN Epitaxial Darlington Transistor T IP
... A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. ...
... A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. ...
Bus Edison Short Circuit Currents Current Limiting
... Any potentially damaging arcing at the fault location will also be reduced. Specifying EDISON current limiting fuses provides excellent protection by reducing short-circuit current energy allowed to flow to a fault. Thus, the requirements of NEC 110.10 and article 240 can be met. UL provides a servi ...
... Any potentially damaging arcing at the fault location will also be reduced. Specifying EDISON current limiting fuses provides excellent protection by reducing short-circuit current energy allowed to flow to a fault. Thus, the requirements of NEC 110.10 and article 240 can be met. UL provides a servi ...
DM5426/DM7426 Quad 2-Input NAND Gates with High Voltage
... National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications. ...
... National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications. ...
Using the TPS61040 in High Voltage Applications
... and to the inductor. The IC turns on its internal MOSFET, Q1, and current starts to flow from Vin through L1, the SW pin of the IC, Q1, and an internal sense resistor. The control portion of the IC monitors the current flowing through the internal sense resistor, R1, and when this current reaches 40 ...
... and to the inductor. The IC turns on its internal MOSFET, Q1, and current starts to flow from Vin through L1, the SW pin of the IC, Q1, and an internal sense resistor. The control portion of the IC monitors the current flowing through the internal sense resistor, R1, and when this current reaches 40 ...
Power MultiMeter PMM-1 Version 2.5 Multi
... single or three-phase electrical system. In the single-phase mode, the PMM-1 is easily configured to measure the amplitude and phase angle between any two voltages and current inputs. These measured quantities are then displayed in an enlarged font size for easier reading on a graphic display. In th ...
... single or three-phase electrical system. In the single-phase mode, the PMM-1 is easily configured to measure the amplitude and phase angle between any two voltages and current inputs. These measured quantities are then displayed in an enlarged font size for easier reading on a graphic display. In th ...
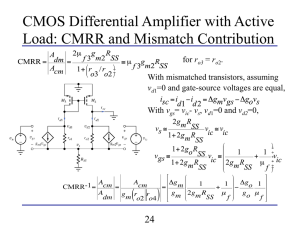
CMOS Differential Amplifier with Active Load: CMRR and Mismatch
... MOSFETs and the reference current. BJTs can’t similarly be connected in series due to small fixed voltage developed across each diode and exponential relationship between voltage and current. ...
... MOSFETs and the reference current. BJTs can’t similarly be connected in series due to small fixed voltage developed across each diode and exponential relationship between voltage and current. ...
Series and parallel circuits
... containing 2.5 mm2 copper wires. Most electrical appliances are connected to the mains electricity supply by plugging them into a standard power socket. It would not be safe to connect the electric cooker hob to the mains electricity supply by plugging it into a standard power socket. Why? ...
... containing 2.5 mm2 copper wires. Most electrical appliances are connected to the mains electricity supply by plugging them into a standard power socket. It would not be safe to connect the electric cooker hob to the mains electricity supply by plugging it into a standard power socket. Why? ...
Lecture Slides
... No current flows when reverse biased (b). No internal resistance to limit current when forward biased (c). ...
... No current flows when reverse biased (b). No internal resistance to limit current when forward biased (c). ...
Information contained herein is proprietary information of the
... fire later in each half cycle, allowing current to flow through the control windings for a shorter period of time; hence, less d-c current flows in the control windings. To become more familiar with this operation lets take the case in which the generator line voltage increases. The sequence of even ...
... fire later in each half cycle, allowing current to flow through the control windings for a shorter period of time; hence, less d-c current flows in the control windings. To become more familiar with this operation lets take the case in which the generator line voltage increases. The sequence of even ...
Fairchild Semiconductors
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.