TAP 109- 1: Electrical characteristics
... Set up the basic circuit but using the bulb in a holder instead of the carbon resistor. This time the bulb can be left on between measurements. Repeat/check readings can be obtained by repeating the whole experiment but you will need to take care to reproduce (exactly) the voltage reading across the ...
... Set up the basic circuit but using the bulb in a holder instead of the carbon resistor. This time the bulb can be left on between measurements. Repeat/check readings can be obtained by repeating the whole experiment but you will need to take care to reproduce (exactly) the voltage reading across the ...
Regulated Power Supplies Objective
... Measure the DC voltage and current. If the measured value of current is greater than the rated current, quickly turn off the power and remove one of the resistors. If the measured value of current is significantly less than the rated value, add an additional parallel resistor. After making any such ...
... Measure the DC voltage and current. If the measured value of current is greater than the rated current, quickly turn off the power and remove one of the resistors. If the measured value of current is significantly less than the rated value, add an additional parallel resistor. After making any such ...
Electric Circuits - Greater Philadelphia Sea Perch Challenge
... As a ball falls to the earth it loses potential energy due to gravity and gains kinetic energy. This can be related to the earth doing work on the ball. Remember work is defined as a force that causes displacement. As the force of gravity pulls on the ball it is being displaced therefore work is don ...
... As a ball falls to the earth it loses potential energy due to gravity and gains kinetic energy. This can be related to the earth doing work on the ball. Remember work is defined as a force that causes displacement. As the force of gravity pulls on the ball it is being displaced therefore work is don ...
MCH6124 数据资料DataSheet下载
... customer' s products or equipment. To verify symptoms and states that cannot be evaluated in an independent device, the customer should always evaluate and test devices mounted in the customer' s products or equipment. SANYO Semiconductor Co.,Ltd. assumes no responsibility for equipment failures tha ...
... customer' s products or equipment. To verify symptoms and states that cannot be evaluated in an independent device, the customer should always evaluate and test devices mounted in the customer' s products or equipment. SANYO Semiconductor Co.,Ltd. assumes no responsibility for equipment failures tha ...
CEDMCS ACTM 10V Current Sensor Nuclear Automation Background Description
... provides calibration for offset, span and temperature compensation. The output signal is tailored to duplicate the original mV output levels based on the relationship of the DC current sensed through the main conductor. The unit operates from the original DC supply being delivered in the cable from ...
... provides calibration for offset, span and temperature compensation. The output signal is tailored to duplicate the original mV output levels based on the relationship of the DC current sensed through the main conductor. The unit operates from the original DC supply being delivered in the cable from ...
AN-7019 Limiting Cross-Conduction Current in Synchronous Buck Converter Designs
... Figure 9 shows the gate-ground voltage in the case of 10nS rise time. When compared to Figure 5 (left) showing the gate-source voltage under identical conditions, it becomes evident that measuring the gate-ground voltage of 2.5 Volt and predicting the existence of shoot through based on the fact tha ...
... Figure 9 shows the gate-ground voltage in the case of 10nS rise time. When compared to Figure 5 (left) showing the gate-source voltage under identical conditions, it becomes evident that measuring the gate-ground voltage of 2.5 Volt and predicting the existence of shoot through based on the fact tha ...
Selection Guide to Clamp-On Current Probes
... other diverse instruments. The probe is “clamped” around the current carrying conductor to perform non-contact current measurements and without interrupting the circuit under test. The probe outputs current or voltage signal directly proportional to the measured current, thereby providing current me ...
... other diverse instruments. The probe is “clamped” around the current carrying conductor to perform non-contact current measurements and without interrupting the circuit under test. The probe outputs current or voltage signal directly proportional to the measured current, thereby providing current me ...
A Sub kBT/q Semimetal Nanowire Field Effect
... Applying the gate electric field modifies the channel band structure such that positive gate bias builds up the transmission due to self-consistent change in the channel’s charge density. Fig. S1 shows the transmission characteristics of the TFET device at different gate bias voltages corresponding ...
... Applying the gate electric field modifies the channel band structure such that positive gate bias builds up the transmission due to self-consistent change in the channel’s charge density. Fig. S1 shows the transmission characteristics of the TFET device at different gate bias voltages corresponding ...
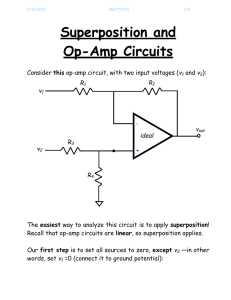
Superposition and
... Superposition and Op-Amp Circuits Consider this op-amp circuit, with two input voltages (v1 and v2): R2 ...
... Superposition and Op-Amp Circuits Consider this op-amp circuit, with two input voltages (v1 and v2): R2 ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.