AND8093/D Current Sensing Power MOSFETs
... Particularly at high speeds, noise spikes at both turn–on and turn–off are a first order design consideration in SENSEFET circuits. These spikes are short, roughly the same duration as the switching transitions that produce them, and can be several times the value of the sense voltage that is being ...
... Particularly at high speeds, noise spikes at both turn–on and turn–off are a first order design consideration in SENSEFET circuits. These spikes are short, roughly the same duration as the switching transitions that produce them, and can be several times the value of the sense voltage that is being ...
150LECTURE14CHAPTER13 RCL CIRCUITS Lecture Notes Page
... At low frequencies the circuit is capacitive as XC > XL. At low frequencies the circuit is inductive as XL > XC. The high value of current at resonance produces very high values of voltage across the inductor and capacitor. Series resonance circuits are useful for constructing highly frequency selec ...
... At low frequencies the circuit is capacitive as XC > XL. At low frequencies the circuit is inductive as XL > XC. The high value of current at resonance produces very high values of voltage across the inductor and capacitor. Series resonance circuits are useful for constructing highly frequency selec ...
Exp_Ohmic Circuit Elements
... components are called electronic circuits. In a DC circuit, the direction of the electric currents in all of the components is constant in time. Any points where a given circuit connects to devices that are not considered to be part of the circuit itself are called terminals. A single-loop circuit i ...
... components are called electronic circuits. In a DC circuit, the direction of the electric currents in all of the components is constant in time. Any points where a given circuit connects to devices that are not considered to be part of the circuit itself are called terminals. A single-loop circuit i ...
Chapter 6 - Series-Parallel Circuits
... • A load resistor should be large compared to the resistance across which it is connected, in order that the loading effect may be minimized • A balanced Wheatstone bridge can be used to measure an unknown resistance • A bridge is balanced when the output voltage is zero. The balanced condition prod ...
... • A load resistor should be large compared to the resistance across which it is connected, in order that the loading effect may be minimized • A balanced Wheatstone bridge can be used to measure an unknown resistance • A bridge is balanced when the output voltage is zero. The balanced condition prod ...
Voltage Drops Around Closed Loops Select Resistors Build the
... a POWER SOURCE is a voltage RISE ...
... a POWER SOURCE is a voltage RISE ...
DATA SHEET BFQ18A NPN 4 GHz wideband transistor September 1995
... more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods ...
... more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods ...
AP 1 Quick Review on Electricity
... individual currents. The branch with the lowest resistance gets the most current. Adding resistors in parallel reduces the total resistance in the circuit and will increase the total current, but the individual currents will not change. The equivalent resistance of a parallel circuit will always be ...
... individual currents. The branch with the lowest resistance gets the most current. Adding resistors in parallel reduces the total resistance in the circuit and will increase the total current, but the individual currents will not change. The equivalent resistance of a parallel circuit will always be ...
Application Note Driving IGBTs with unipolar gate voltage
... Transistor to shunt the Miller current (active Miller clamping) An additional measure to prevent the unwanted turn-on is shorting the gate to emitter path. This can be achieved by an additional transistor between gate and emitter. This “switch” shorts the gate-emitter region after a time delay, as l ...
... Transistor to shunt the Miller current (active Miller clamping) An additional measure to prevent the unwanted turn-on is shorting the gate to emitter path. This can be achieved by an additional transistor between gate and emitter. This “switch” shorts the gate-emitter region after a time delay, as l ...
LED PAGE
... intensity fall to half its axial value. This is why LED shows more brightness in full on condition. High bright LEDs have narrow viewing angle so that light is focused into a beam. Forward voltage (Vf) is the voltage drop across the LED when it conducts. The forward voltage drop range from 1.8 V to ...
... intensity fall to half its axial value. This is why LED shows more brightness in full on condition. High bright LEDs have narrow viewing angle so that light is focused into a beam. Forward voltage (Vf) is the voltage drop across the LED when it conducts. The forward voltage drop range from 1.8 V to ...
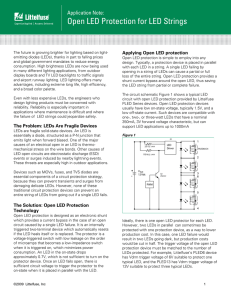
Open LED Protection for LED Strings
... Key parameters for the Littelfuse PLED device are VBR, IS, IH, IT, and VT, as shown in the V-I curve (Figure 2). VBR is the region from off-state voltage to breakdown voltage rating of the device. In the off-state, VBR is the continuous peak combination of AC and DC voltage that may be applied to th ...
... Key parameters for the Littelfuse PLED device are VBR, IS, IH, IT, and VT, as shown in the V-I curve (Figure 2). VBR is the region from off-state voltage to breakdown voltage rating of the device. In the off-state, VBR is the continuous peak combination of AC and DC voltage that may be applied to th ...
1 Figure 2. Equivalent circuit of figure 1 if RE= R1+
... For example, a lamp connected to a 6V RMS AC supply will light with the same brightness when connected to a steady 6V DC supply. However, the lamp will be dimmer if connected to a 6V peak AC supply because the RMS value of this is only 4.2V (it is equivalent to a steady 4.2V DC). In everyday use AC ...
... For example, a lamp connected to a 6V RMS AC supply will light with the same brightness when connected to a steady 6V DC supply. However, the lamp will be dimmer if connected to a 6V peak AC supply because the RMS value of this is only 4.2V (it is equivalent to a steady 4.2V DC). In everyday use AC ...
Document
... C) 2 Ω D) 4 Ω E) 8 Ω 10. Two 15-W and three 25-W light bulbs and a 24 V battery are connected in a series circuit. What is the current that passes through each bulb? A) 0.23 A B) 0.51 A C) 0.96 A D) 1.6 A E) 4.38 A 11. Complete the following statement: A simple series circuit contains a resistance R ...
... C) 2 Ω D) 4 Ω E) 8 Ω 10. Two 15-W and three 25-W light bulbs and a 24 V battery are connected in a series circuit. What is the current that passes through each bulb? A) 0.23 A B) 0.51 A C) 0.96 A D) 1.6 A E) 4.38 A 11. Complete the following statement: A simple series circuit contains a resistance R ...
Document
... C) 2 Ω D) 4 Ω E) 8 Ω 10. Two 15-W and three 25-W light bulbs and a 24 V battery are connected in a series circuit. What is the current that passes through each bulb? A) 0.23 A B) 0.51 A C) 0.96 A D) 1.6 A **E) 4.38 A 11. Complete the following statement: A simple series circuit contains a resistance ...
... C) 2 Ω D) 4 Ω E) 8 Ω 10. Two 15-W and three 25-W light bulbs and a 24 V battery are connected in a series circuit. What is the current that passes through each bulb? A) 0.23 A B) 0.51 A C) 0.96 A D) 1.6 A **E) 4.38 A 11. Complete the following statement: A simple series circuit contains a resistance ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.