File
... • Active region, middle region – normal operation of transistor Emitter diode – FB and Collector diode – RB • Breakdown region – transistor will be destroyed • Saturation region – rising part of curve, VCE between zero and few tenth of volt Collector diode has insufficient positive voltage to collec ...
... • Active region, middle region – normal operation of transistor Emitter diode – FB and Collector diode – RB • Breakdown region – transistor will be destroyed • Saturation region – rising part of curve, VCE between zero and few tenth of volt Collector diode has insufficient positive voltage to collec ...
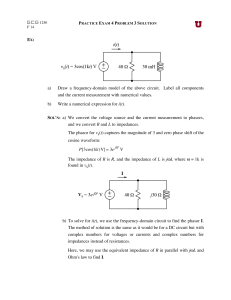
EX: a) Draw a frequency-domain model of the above circuit. Label
... SOL'N: a) We convert the voltage source and the current measurement to phasors, and we convert R and L to impedances. The phasor for vs(t) captures the magnitude of 3 and zero phase shift of the cosine waveform: P[3cos(1kt)V] = 3e j0° V ...
... SOL'N: a) We convert the voltage source and the current measurement to phasors, and we convert R and L to impedances. The phasor for vs(t) captures the magnitude of 3 and zero phase shift of the cosine waveform: P[3cos(1kt)V] = 3e j0° V ...
Ohm`s law - Websupport1
... is as shown in Fig. 4.2(a) for the indicated current direction. A reversal in current will reverse the polarity, as shown in Fig. 4.2(b). In general, the flow of charge is from a high (+) to a low (–) potential. ...
... is as shown in Fig. 4.2(a) for the indicated current direction. A reversal in current will reverse the polarity, as shown in Fig. 4.2(b). In general, the flow of charge is from a high (+) to a low (–) potential. ...
Sep 1999 Micropower, Precision Current Sense Amplifier Operates from 2.5V to 60V
... current sense amplifier designed for monitoring of the current either into or out of a battery or other element capable of sourcing or sinking current. The LT1787 features a miniscule 40µV (typical) input offset voltage with a 128mV full-scale input voltage. (The part is generally used at ±128mV ful ...
... current sense amplifier designed for monitoring of the current either into or out of a battery or other element capable of sourcing or sinking current. The LT1787 features a miniscule 40µV (typical) input offset voltage with a 128mV full-scale input voltage. (The part is generally used at ±128mV ful ...
FPGA board - ECE Users Pages
... transistor. It consists of a pFET transistor with the gate connected to a capacitor, hence this node does not have a dc path to ground. The primary characteristic of a floating-gate transistor is that it can store charge on the floating node. Charge can be removed or added via tunnelling and hot elect ...
... transistor. It consists of a pFET transistor with the gate connected to a capacitor, hence this node does not have a dc path to ground. The primary characteristic of a floating-gate transistor is that it can store charge on the floating node. Charge can be removed or added via tunnelling and hot elect ...
MJE5740 - NPN Silicon Power Darlington
... derated when TC ≥ 25_C. Second breakdown limitations do not derate the same as thermal limitations. Allowable current at the voltages shown on Figure 6 may be found at any case temperature by using the appropriate curve on Figure 1. ...
... derated when TC ≥ 25_C. Second breakdown limitations do not derate the same as thermal limitations. Allowable current at the voltages shown on Figure 6 may be found at any case temperature by using the appropriate curve on Figure 1. ...
Assembly Instruction
... There is one resistor, R1. It does not matter which way round it goes. Bend the legs the resistor near to the body at 90 degrees. ...
... There is one resistor, R1. It does not matter which way round it goes. Bend the legs the resistor near to the body at 90 degrees. ...
AD581 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The AD581 is ideal for application with the entire AD7533 series of 10- and 12-bit multiplying CMOS D/A converters, especially for low power applications. It is equally suitable for the AD7574 8-bit A/D converter. In the standard hook-up, as shown in Figure 14, the +10 volt reference is inverted by ...
... The AD581 is ideal for application with the entire AD7533 series of 10- and 12-bit multiplying CMOS D/A converters, especially for low power applications. It is equally suitable for the AD7574 8-bit A/D converter. In the standard hook-up, as shown in Figure 14, the +10 volt reference is inverted by ...
Basic Circuitry2 - Electro Tech Online
... What is electricity? (electron flow) Atoms have electrons orbiting the nucleus of the atom. Some electrons on the outer orbits can jump from one atom to the next atom When an electron moves, it leaves a ‘hole’ in the orbit for another electron to jump into That electron leaves another hole, ...
... What is electricity? (electron flow) Atoms have electrons orbiting the nucleus of the atom. Some electrons on the outer orbits can jump from one atom to the next atom When an electron moves, it leaves a ‘hole’ in the orbit for another electron to jump into That electron leaves another hole, ...
Document
... electromagnet rotates inside coils of wire. Describe how changing the speed of rotation of the electromagnet’s coil(s) affects the size and frequency of the voltage generated. Describe how changing the number of turns on the electromagnet’s coil(s) affects the size of the voltage generated. H.D. Whe ...
... electromagnet rotates inside coils of wire. Describe how changing the speed of rotation of the electromagnet’s coil(s) affects the size and frequency of the voltage generated. Describe how changing the number of turns on the electromagnet’s coil(s) affects the size of the voltage generated. H.D. Whe ...
Chapter 1 0 - RC Circuits
... • Total current in an RC circuit always leads the source voltage • The resistor voltage is always in phase with the current • The capacitor voltage always lags the current by ...
... • Total current in an RC circuit always leads the source voltage • The resistor voltage is always in phase with the current • The capacitor voltage always lags the current by ...
Limited Availability Product
... the IC varies in direct proportion to the primary current through its full-scale amplitude. Nonlinearity in the output can be attributed to the saturation of the flux concentrator approaching the full-scale current. The following equation is used to derive the ...
... the IC varies in direct proportion to the primary current through its full-scale amplitude. Nonlinearity in the output can be attributed to the saturation of the flux concentrator approaching the full-scale current. The following equation is used to derive the ...
Chapter 10
... • Describe the relationship between current and voltage in an RC circuit • Determine impedance and phase angle in a series RC circuit • Analyze a series RC circuit • Determine the impedance and phase angle in a parallel RC circuit ...
... • Describe the relationship between current and voltage in an RC circuit • Determine impedance and phase angle in a series RC circuit • Analyze a series RC circuit • Determine the impedance and phase angle in a parallel RC circuit ...
LectNotes4-MeshAnalysis
... Works on all circuits. No creative thinking needed. Computers don't like as much as nodal analysis. Once over lightly. Process: Write KVL for every mesh in terms of mesh currents. Special handling for current sources. What's a mesh? A loop that does not contain any other loops within it. In essence, ...
... Works on all circuits. No creative thinking needed. Computers don't like as much as nodal analysis. Once over lightly. Process: Write KVL for every mesh in terms of mesh currents. Special handling for current sources. What's a mesh? A loop that does not contain any other loops within it. In essence, ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.