Tiny boost converter with adjustable input current limit
... application the frequency will be 3.5 MHz and is defined by the input to output voltage ratio and does not vary from moderate to heavy load currents. At light load the converter will automatically enter Power Save Mode and operates in PFM (Pulse Frequency Modulation) mode. During PWM operation the c ...
... application the frequency will be 3.5 MHz and is defined by the input to output voltage ratio and does not vary from moderate to heavy load currents. At light load the converter will automatically enter Power Save Mode and operates in PFM (Pulse Frequency Modulation) mode. During PWM operation the c ...
Small Signal * Low Frequency Transistor amplifier Circuits
... Consider a general amplifier as shown below. In this amplifier, the resistance R is common to the input and output circuits do not have a common resistance. The purpose of the following analysis is to remove the inter dependence of input and output circuits. So that either input circuits or outpu ...
... Consider a general amplifier as shown below. In this amplifier, the resistance R is common to the input and output circuits do not have a common resistance. The purpose of the following analysis is to remove the inter dependence of input and output circuits. So that either input circuits or outpu ...
Document
... Resistors are rated in watts. A resistor is rated as a 1-W resistor if its resistance equals 1,000,000 ohms and its current-carrying capacity equals 1/1,000,000 amp, since P = E x I = IR x I = I2R where P — power — is given in watts, R — resistance is given in ohms and I — current — is given in ampe ...
... Resistors are rated in watts. A resistor is rated as a 1-W resistor if its resistance equals 1,000,000 ohms and its current-carrying capacity equals 1/1,000,000 amp, since P = E x I = IR x I = I2R where P — power — is given in watts, R — resistance is given in ohms and I — current — is given in ampe ...
(1) - Gateforum
... In Fig.2.3, A = 1 and B =1, the input B is now replaced by a sequence 101010…. the outputs x and y will be (a) fixed at 0 and 1, respectively ...
... In Fig.2.3, A = 1 and B =1, the input B is now replaced by a sequence 101010…. the outputs x and y will be (a) fixed at 0 and 1, respectively ...
A. current.
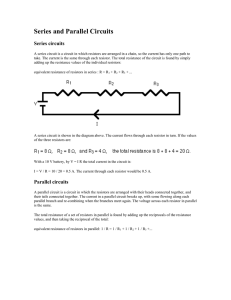
... Series circuits • Characteristics of series circuit (continued): 4. The total voltage impressed across a series circuit divides among the individual electrical devices in the circuit so that the sum of the “voltage drops” across the resistance of each individual device is equal to the total voltage ...
... Series circuits • Characteristics of series circuit (continued): 4. The total voltage impressed across a series circuit divides among the individual electrical devices in the circuit so that the sum of the “voltage drops” across the resistance of each individual device is equal to the total voltage ...
LM20146 6A, Adjustable Frequency Synchronous Buck Regulator
... The device can operate at high switching frequency allowing use of a small inductor while still achieving high efficiency. The precision internal voltage reference allows the output to be set as low as 0.8V. Fault protection features include: current limiting, thermal shutdown, over voltage protecti ...
... The device can operate at high switching frequency allowing use of a small inductor while still achieving high efficiency. The precision internal voltage reference allows the output to be set as low as 0.8V. Fault protection features include: current limiting, thermal shutdown, over voltage protecti ...
LP38841-ADJ - Texas Instruments
... ceramic which provides more phase margin to the loop, thereby allowing the use of a smaller output capacitor because adequate phase margin can be maintained out to a higher crossover frequency. The tantalum capacitor will typically also provide faster settling time on the output after a fast changin ...
... ceramic which provides more phase margin to the loop, thereby allowing the use of a smaller output capacitor because adequate phase margin can be maintained out to a higher crossover frequency. The tantalum capacitor will typically also provide faster settling time on the output after a fast changin ...
anushka singh
... In this method of commutation we use high electrical resistance brushes for getting spark less commutation. This can be obtained by replacing low resistance copper brushes with high resistance carbon brushes. We can clearly see from the picture that the current IC from the coil C may reach to ...
... In this method of commutation we use high electrical resistance brushes for getting spark less commutation. This can be obtained by replacing low resistance copper brushes with high resistance carbon brushes. We can clearly see from the picture that the current IC from the coil C may reach to ...
Forced Commutated HVDC Converters
... With a parallel-capacitor type circuit, a low dc voltage limit exists beyond which a commutation failure occurs due to insufficient charge on the capacitor (end of region Y2, alpha = 240 degrees). In quadrant Q2 this limit merges into LC inverter operation region X. With a series-capacitor type circ ...
... With a parallel-capacitor type circuit, a low dc voltage limit exists beyond which a commutation failure occurs due to insufficient charge on the capacitor (end of region Y2, alpha = 240 degrees). In quadrant Q2 this limit merges into LC inverter operation region X. With a series-capacitor type circ ...
12V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency, Low I , Step-Up DC-DC Controller Q
... Low IQ, Step-Up DC-DC Controller The control circuitry allows the IC to operate in continuous-conduction mode (CCM) while maintaining high efficiency with heavy loads. When the power switch is turned on, it stays on until either 1) the maximum ontime one-shot turns it off (typically 16µs later), or ...
... Low IQ, Step-Up DC-DC Controller The control circuitry allows the IC to operate in continuous-conduction mode (CCM) while maintaining high efficiency with heavy loads. When the power switch is turned on, it stays on until either 1) the maximum ontime one-shot turns it off (typically 16µs later), or ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... upside down, putting 1/5 of an ohm instead of 5 ohms, for instance. Here's a way to check your answer. If you have two or more resistors in parallel, look for the one with the smallest resistance. The equivalent resistance will always be between the smallest resistance divided by the number of resis ...
... upside down, putting 1/5 of an ohm instead of 5 ohms, for instance. Here's a way to check your answer. If you have two or more resistors in parallel, look for the one with the smallest resistance. The equivalent resistance will always be between the smallest resistance divided by the number of resis ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.