34.1 Flow of Charge
... • Power transmission more efficient at higher V • Transfer of energy quietly from 1 place to another ...
... • Power transmission more efficient at higher V • Transfer of energy quietly from 1 place to another ...
– Simple turn-off description of Trench- Field-stop IGBT IGBT
... current. This leads to the equivalent circuit of Fig. 2, which represents the switching of a Trench-Field-stop IGBT by the output characteristics to describe the static characteristics, a collector-gate-voltage dependent capacitance a constant gate emitter capacitance and an additional output capaci ...
... current. This leads to the equivalent circuit of Fig. 2, which represents the switching of a Trench-Field-stop IGBT by the output characteristics to describe the static characteristics, a collector-gate-voltage dependent capacitance a constant gate emitter capacitance and an additional output capaci ...
Basic Ciruits
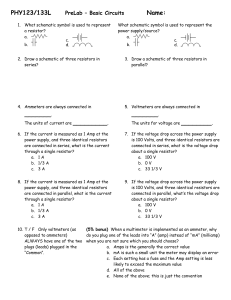
... 9. If the voltage drop across the power supply is 100 Volts, and three identical resistors are connected in parallel, what’s the voltage drop about a single resistor? a. 100 V b. 0 V c. 33 1/3 V ...
... 9. If the voltage drop across the power supply is 100 Volts, and three identical resistors are connected in parallel, what’s the voltage drop about a single resistor? a. 100 V b. 0 V c. 33 1/3 V ...
tic226 series silicon triacs
... 2. This value applies for 50-Hz full-sine-wave operation with resistive load. Above 85°C derate linearly to 110°C case temperature at the rate of 320 mA/°C. 3. This value applies for one 50-Hz full-sine-wave when the device is operating at (or below) the rated value of on-state current. Surge may be ...
... 2. This value applies for 50-Hz full-sine-wave operation with resistive load. Above 85°C derate linearly to 110°C case temperature at the rate of 320 mA/°C. 3. This value applies for one 50-Hz full-sine-wave when the device is operating at (or below) the rated value of on-state current. Surge may be ...
Current and Voltage part 2
... One amp is a flow of a certain quantity of electricity in one second. The amount of electric current entering a circuit always equals the amount exiting the circuit. ...
... One amp is a flow of a certain quantity of electricity in one second. The amount of electric current entering a circuit always equals the amount exiting the circuit. ...
CLASS XII EMI and AC Sure shot Questions 2015-16
... 10. Give the principle , construction ,theory and working of an A.C. Generator. What is the source of energy generation in this device? 11. Define mutual induction. Derive an expression for the mutual inductance of two long co-axial solenoids having different number of turns. 12. Explain the underly ...
... 10. Give the principle , construction ,theory and working of an A.C. Generator. What is the source of energy generation in this device? 11. Define mutual induction. Derive an expression for the mutual inductance of two long co-axial solenoids having different number of turns. 12. Explain the underly ...
ENERGY AND THE ENVIRONMENT Photovoltaic Cells Take
... Indoors, the peak power output was102.7 mW, at a resistance of 11.45 kΩ Outdoors, the peak power output was 1.541 W at a resistance of 29.13 Ω There is a noticeably large difference between the maximum power obtained indoors and that obtained outdoors - the power available under a cloudy sky is 15 t ...
... Indoors, the peak power output was102.7 mW, at a resistance of 11.45 kΩ Outdoors, the peak power output was 1.541 W at a resistance of 29.13 Ω There is a noticeably large difference between the maximum power obtained indoors and that obtained outdoors - the power available under a cloudy sky is 15 t ...
Voltage Transducer LV 100-100 VPN = 100 V
... This transducer must be used in electric/electronic equipment with respect to applicable standards and safety requirements in accordance with the manufacturer’s operating instructions. ...
... This transducer must be used in electric/electronic equipment with respect to applicable standards and safety requirements in accordance with the manufacturer’s operating instructions. ...
Power MOSFET
A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels.Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, for example an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.The design of power MOSFETs was made possible by the evolution of CMOS technology, developed for manufacturing integrated circuits in the late 1970s. The power MOSFET shares its operating principle with its low-power counterpart, the lateral MOSFET.The power MOSFET is the most widely used low-voltage (that is, less than 200 V) switch. It can be found in most power supplies, DC to DC converters, and low voltage motor controllers.