INTRODUCTION TO OHM`S LAW
... changing. From zero, current and voltage builds up and reach its max peak in the positive value at 90 degrees and then back to zero and again to the negative peak value. In this regard, Its only possible to calculate instantaneous values of voltage and current throughout its cycle. For AC Ohms law c ...
... changing. From zero, current and voltage builds up and reach its max peak in the positive value at 90 degrees and then back to zero and again to the negative peak value. In this regard, Its only possible to calculate instantaneous values of voltage and current throughout its cycle. For AC Ohms law c ...
POWER QUALITY -- An Indian Perspective
... fluctuations in Earth’s magnetic field (geomagnetic storms) --- potential difference between different points on Earth’s surface --- DC enters one transformer neutral and exits at another -half-cycle saturation of transformer cores ...
... fluctuations in Earth’s magnetic field (geomagnetic storms) --- potential difference between different points on Earth’s surface --- DC enters one transformer neutral and exits at another -half-cycle saturation of transformer cores ...
What does the “PASSIVE” device mean
... it can be just resistor, capacitor or inductor, no other devices, device, where output power (Pout) is lower (or equal) than the input power (Pin), device, where input power (Pin) is lower (or equal) than the output power (Pout), all the semiconductor devices, e.g. LED, thyristors etc. 2. Wh ...
... it can be just resistor, capacitor or inductor, no other devices, device, where output power (Pout) is lower (or equal) than the input power (Pin), device, where input power (Pin) is lower (or equal) than the output power (Pout), all the semiconductor devices, e.g. LED, thyristors etc. 2. Wh ...
FIGURE 4.2-1 Circuit with an independent voltage source and an
... FIGURE 4.5-4 Mesh currents, i1 and i2, and element current, i1 – i2, of a (a) generic circuit element, (b) current source, and (c) resistor. ...
... FIGURE 4.5-4 Mesh currents, i1 and i2, and element current, i1 – i2, of a (a) generic circuit element, (b) current source, and (c) resistor. ...
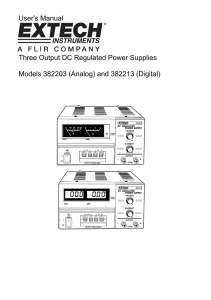
User`s Manual Three Output DC Regulated Power Supplies Models
... Power Supply. The 382203 and 382213 are solid state, compact, well regulated supplies suitable for many applications including bench testing, field service, hobby and telecommunication equipment use. ...
... Power Supply. The 382203 and 382213 are solid state, compact, well regulated supplies suitable for many applications including bench testing, field service, hobby and telecommunication equipment use. ...
Exam questions
... 3. Draw a simple labelled diagram to show the structure of a P-N junction diode. 4. Explain the meaning of the terms forward bias and reverse bias in relation to the operation of a diode. Illustrate each of these terms using a simple circuit diagram. 5. Explain in one sentence the difference in the ...
... 3. Draw a simple labelled diagram to show the structure of a P-N junction diode. 4. Explain the meaning of the terms forward bias and reverse bias in relation to the operation of a diode. Illustrate each of these terms using a simple circuit diagram. 5. Explain in one sentence the difference in the ...
tender notice for laboratory equipment in electrical
... One no. of digital MC based digital speed indicator for motor speed measurement 3 phase input, all are mounted on a nice cabinet ...
... One no. of digital MC based digital speed indicator for motor speed measurement 3 phase input, all are mounted on a nice cabinet ...
Rev. 0
... High-Side (Control) MOSFETs The high-side MOSFET is usually selected to be high speed to minimize switching losses (see any ADI Flex-Mode™ controller data sheet for more details on MOSFET losses). This usually implies a low gate resistance and low input capacitance/charge device. Yet, there is also ...
... High-Side (Control) MOSFETs The high-side MOSFET is usually selected to be high speed to minimize switching losses (see any ADI Flex-Mode™ controller data sheet for more details on MOSFET losses). This usually implies a low gate resistance and low input capacitance/charge device. Yet, there is also ...
fateme km proposed ece1250 2240 project
... We propose having a plastic crate of demos to be given to the instructor of ECE1250 and another for ECE2240 that particular semester. Each demo will be numbered/correlated to the textbook chapters it is associated with. Proposed graduate TA: Fateme Km. Fateme is working on her MS degree with Dr. Nei ...
... We propose having a plastic crate of demos to be given to the instructor of ECE1250 and another for ECE2240 that particular semester. Each demo will be numbered/correlated to the textbook chapters it is associated with. Proposed graduate TA: Fateme Km. Fateme is working on her MS degree with Dr. Nei ...
6 - 10.5 CYU Suggested Answers - Tse
... (c) The total resistance is 22 Ω x 4 = 88 Ω. 3. (a) The voltage of each resistor is 120 V. (b) The current in each resistor is 0.6 A. (c) The resistance of each resistor is 200 Ω. (d) The total resistance is 100 Ω. 4. (a) The current in the second light bulb is 280 mA. (b) The light bulbs are not id ...
... (c) The total resistance is 22 Ω x 4 = 88 Ω. 3. (a) The voltage of each resistor is 120 V. (b) The current in each resistor is 0.6 A. (c) The resistance of each resistor is 200 Ω. (d) The total resistance is 100 Ω. 4. (a) The current in the second light bulb is 280 mA. (b) The light bulbs are not id ...
BE LAB
... There are 2 types of transistor NPN and PNP. Emitter is the terminal which emitts charge carriers,heavily doped region collector is the terminal which collects the charge carries and moderately doped region or terminal. Base is the region through which charge carriers passes and thinly doped region. ...
... There are 2 types of transistor NPN and PNP. Emitter is the terminal which emitts charge carriers,heavily doped region collector is the terminal which collects the charge carries and moderately doped region or terminal. Base is the region through which charge carriers passes and thinly doped region. ...
L 27 - University of Iowa Physics
... • on some circuits (kitchens and bathrooms) there is additional protection GFCI ground fault circuit interrupt. If current accidentally flows through anything other than the hot or neutral it interrupts the circuit very quickly ...
... • on some circuits (kitchens and bathrooms) there is additional protection GFCI ground fault circuit interrupt. If current accidentally flows through anything other than the hot or neutral it interrupts the circuit very quickly ...
Power MOSFET
A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels.Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, for example an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.The design of power MOSFETs was made possible by the evolution of CMOS technology, developed for manufacturing integrated circuits in the late 1970s. The power MOSFET shares its operating principle with its low-power counterpart, the lateral MOSFET.The power MOSFET is the most widely used low-voltage (that is, less than 200 V) switch. It can be found in most power supplies, DC to DC converters, and low voltage motor controllers.