Lab - EMF and Terminal Voltage
... Materials: 3 D-cells, 4 light bulbs, 8 wire leads, multimeter Procedure: 1) Working in a group of 2 collect material from the front of the room 2) Use the multimeter to measure the voltage across each cell. Each one should have a voltage of approximately 1.50 V - if not see the instructor. 3) Connec ...
... Materials: 3 D-cells, 4 light bulbs, 8 wire leads, multimeter Procedure: 1) Working in a group of 2 collect material from the front of the room 2) Use the multimeter to measure the voltage across each cell. Each one should have a voltage of approximately 1.50 V - if not see the instructor. 3) Connec ...
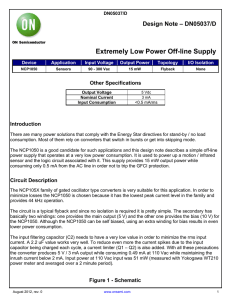
Electric Current
... With the current moving counter clockwise because of the direction of the voltage sources. Now in order to calculate the potential difference between B and A, all we have to do is calculate the voltage between these points: VBA = ε1 − I(R1 + R2 ) = 1 − I = 0.515 V ...
... With the current moving counter clockwise because of the direction of the voltage sources. Now in order to calculate the potential difference between B and A, all we have to do is calculate the voltage between these points: VBA = ε1 − I(R1 + R2 ) = 1 − I = 0.515 V ...
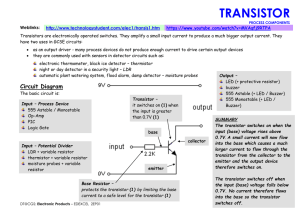
[2] block diagram of dstatcom
... low efficiency and if the voltage supplied is above the rated windings get damaged. Hence in order to provide reliable uniform, power modern method of mitigation is use of STATCOM. A battery energy system is used to supply the reactive power which is connected shunt with capacitor bank. The STATCOMs ...
... low efficiency and if the voltage supplied is above the rated windings get damaged. Hence in order to provide reliable uniform, power modern method of mitigation is use of STATCOM. A battery energy system is used to supply the reactive power which is connected shunt with capacitor bank. The STATCOMs ...
Lab 1
... (1-1) Refer to your measurements from In-Lab Exercise 1-2; note that these measurements are the Thevenin equivalent voltage and Norton equivalent current of the network in Figure 4. From these measurements, compute the Thevenin/Norton equivalent resistance of the network. Compare the experimental Th ...
... (1-1) Refer to your measurements from In-Lab Exercise 1-2; note that these measurements are the Thevenin equivalent voltage and Norton equivalent current of the network in Figure 4. From these measurements, compute the Thevenin/Norton equivalent resistance of the network. Compare the experimental Th ...
ideal voltage and current sources
... For example, an ideal 5 V source has a voltage of 5 V across its terminals, for currents of 1 mA, 1 A or 1000 A. This behaviour contrasts with a real source, in which the terminal voltage reduces as the current drawn increases. The current drawn from an ideal voltage source depends only on the circu ...
... For example, an ideal 5 V source has a voltage of 5 V across its terminals, for currents of 1 mA, 1 A or 1000 A. This behaviour contrasts with a real source, in which the terminal voltage reduces as the current drawn increases. The current drawn from an ideal voltage source depends only on the circu ...
Signal-strength display to an FM
... The Philips (www.semiconductors.philips.com) TDA7000 integrates a Tmonaural FM-radio receiver from the antenna connection to the audio out-put. External components include one tunable LC circuit for the local oscillator,a few capacitors,two resistors,and a potentiometer to control the variable-capac ...
... The Philips (www.semiconductors.philips.com) TDA7000 integrates a Tmonaural FM-radio receiver from the antenna connection to the audio out-put. External components include one tunable LC circuit for the local oscillator,a few capacitors,two resistors,and a potentiometer to control the variable-capac ...
BSNL JTO Question Paper 2 2014
... holes b) Diffusion of majority carriers across the junction c) Migration of minority carriers across the junction d) Flow of drift current 13. 14. The polarity of VGS for E-only MOSFET is a) positive b) negative c) zero d) depends on P or N channel BSNL JTO Recruitment Question Paper previous years ...
... holes b) Diffusion of majority carriers across the junction c) Migration of minority carriers across the junction d) Flow of drift current 13. 14. The polarity of VGS for E-only MOSFET is a) positive b) negative c) zero d) depends on P or N channel BSNL JTO Recruitment Question Paper previous years ...
1270 HOMEWORK #2 solution EX: Find the total power dissipated
... multiplied by the current flowing into the box. p = iv ...
... multiplied by the current flowing into the box. p = iv ...
DN426 - 6-Channel SAR ADCs for Industrial
... monitoring applications such as 3-phase power line monitoring to ensure line voltage compliance, portable power line instrumentation, power factor correction, motor control, and data acquisition. These applications may be battery powered, and it is here that the LTC2351-14’s ...
... monitoring applications such as 3-phase power line monitoring to ensure line voltage compliance, portable power line instrumentation, power factor correction, motor control, and data acquisition. These applications may be battery powered, and it is here that the LTC2351-14’s ...
Document
... drain-source voltage VDSS of related transistors are reduced to one-half of the input VDD voltage. This is allowed by the internally generated and accurately balanced middle-node voltage VDD/2. Consequently, advantageous rDS(on) of the low voltage transistors, along with reduced switching PWM voltag ...
... drain-source voltage VDSS of related transistors are reduced to one-half of the input VDD voltage. This is allowed by the internally generated and accurately balanced middle-node voltage VDD/2. Consequently, advantageous rDS(on) of the low voltage transistors, along with reduced switching PWM voltag ...
EX: In the circuit shown below, the switch closes at time t = 0. a) Find
... Write a numerical expression for vC(t) for t > 0 in the above circuit. Note: vC(t = 0) = 0 V. ...
... Write a numerical expression for vC(t) for t > 0 in the above circuit. Note: vC(t = 0) = 0 V. ...
Solid State Physics
... builds up on one side, there must be an equal and opposite charge on the other side. This charge must come from the substrate. Since it is P-type there are not many electrons but those that are present are all sucked up to the gate oxide. This creates a region that is very thin, but very rich in ele ...
... builds up on one side, there must be an equal and opposite charge on the other side. This charge must come from the substrate. Since it is P-type there are not many electrons but those that are present are all sucked up to the gate oxide. This creates a region that is very thin, but very rich in ele ...
Two-Switch Voltage Equalizer Using an LLC Resonant
... The existence of multiple MPPs confuses and hinders the conventional MPP tracking (MPPT) algorithm to extract maximum power. Although advanced MPPT algorithms have been proposed, with which a global MPP can be found by sweeping operation voltage over a wide range and tracked even under partially sha ...
... The existence of multiple MPPs confuses and hinders the conventional MPP tracking (MPPT) algorithm to extract maximum power. Although advanced MPPT algorithms have been proposed, with which a global MPP can be found by sweeping operation voltage over a wide range and tracked even under partially sha ...
Power MOSFET
A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels.Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, for example an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.The design of power MOSFETs was made possible by the evolution of CMOS technology, developed for manufacturing integrated circuits in the late 1970s. The power MOSFET shares its operating principle with its low-power counterpart, the lateral MOSFET.The power MOSFET is the most widely used low-voltage (that is, less than 200 V) switch. It can be found in most power supplies, DC to DC converters, and low voltage motor controllers.

![[2] block diagram of dstatcom](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003075383_1-88764035adc0591a25e323f598661b3a-300x300.png)