Beliefs of Judaism
... – God promised that Abraham’s people would be kings and build nations. – In return, the Israelites had to believe in and obey only Him. ...
... – God promised that Abraham’s people would be kings and build nations. – In return, the Israelites had to believe in and obey only Him. ...
Judaism and Chrisitanity
... In prophets of old – especially Moses, through whom Torah was revealed to the Hebrew people In Torah (first five books of the Bible), containing religious, moral and social law which guides the life of a Jew ...
... In prophets of old – especially Moses, through whom Torah was revealed to the Hebrew people In Torah (first five books of the Bible), containing religious, moral and social law which guides the life of a Jew ...
Judaism by Philip Neal3 - The Bible Sabbath Association
... “wow” in the column. From the fact that the vast majority of Jews in first century Palestine were not interested in religion to the fact that in rabbinical Judaism, the Talmud rules over the Torah, I found myself surprised often. Neil does a fantastic job of sharing key elements of the Talmud, the “ ...
... “wow” in the column. From the fact that the vast majority of Jews in first century Palestine were not interested in religion to the fact that in rabbinical Judaism, the Talmud rules over the Torah, I found myself surprised often. Neil does a fantastic job of sharing key elements of the Talmud, the “ ...
the PowerPoint slides.
... know I will never give a d’var Torah basing my ideas on this premise, I know I will never teach this hypothesis, and I know that when I teach my children the Torah, I will tell them all of the stories that I learned as a child about Torah Misinai and the authority of the Torah. As much as the logica ...
... know I will never give a d’var Torah basing my ideas on this premise, I know I will never teach this hypothesis, and I know that when I teach my children the Torah, I will tell them all of the stories that I learned as a child about Torah Misinai and the authority of the Torah. As much as the logica ...
Chapter 6 Lesson 3 The Development of Judaism Return to Judah
... -‐king Cyrus II let Jews return to Judah -‐constructed new temple, the Second Temple -‐Persians did not allow Jews to have own government or king ...
... -‐king Cyrus II let Jews return to Judah -‐constructed new temple, the Second Temple -‐Persians did not allow Jews to have own government or king ...
What is Judaism
... 4. The ________ is the story of the Jewish people’s journey. Places of Worship 5. The __________ has 3 purposes as a place of study, assembly and prayer. 6. Sabbath worship occurs every ________ night and _________ morning. 7. The job of the _________ is to teach the word of the Torah. 8. The prayer ...
... 4. The ________ is the story of the Jewish people’s journey. Places of Worship 5. The __________ has 3 purposes as a place of study, assembly and prayer. 6. Sabbath worship occurs every ________ night and _________ morning. 7. The job of the _________ is to teach the word of the Torah. 8. The prayer ...
What is Judaism?
... that elaborates on how to apply God’s Law in everyday life through: Dietary rules (Kashrut/Kosher) Dress and other symbols Prayer and devotion to the one God The synagogue and rites Proper social relations between male and female, in ...
... that elaborates on how to apply God’s Law in everyday life through: Dietary rules (Kashrut/Kosher) Dress and other symbols Prayer and devotion to the one God The synagogue and rites Proper social relations between male and female, in ...
What is Judaism?
... • Enslaved in ancient Egypt and freed by Moses (more than 3300 years ago) • Hebrew monarchy in the “Promised Land” (The Land of Israel), ends 6th century BCE ...
... • Enslaved in ancient Egypt and freed by Moses (more than 3300 years ago) • Hebrew monarchy in the “Promised Land” (The Land of Israel), ends 6th century BCE ...
Slide 1
... The Jewish ritual of preparing the dead for burial is called Taharah. The Jewish community has a voluntary burial society called the Chevra Kadisha. They believe that performing a Taharah is the ultimate mitzvah or worthy deed. A group of three or four people (usually women), prepares the body with ...
... The Jewish ritual of preparing the dead for burial is called Taharah. The Jewish community has a voluntary burial society called the Chevra Kadisha. They believe that performing a Taharah is the ultimate mitzvah or worthy deed. A group of three or four people (usually women), prepares the body with ...
1. Scripture in Judaism
... What was it about the destruction of the Temple by the Romans in 70 CE that most affected Judaism? What had been the principal means of drawing down divine blessing? What were the most important blessings? In the revised variant of post-Temple Judaism, ...
... What was it about the destruction of the Temple by the Romans in 70 CE that most affected Judaism? What had been the principal means of drawing down divine blessing? What were the most important blessings? In the revised variant of post-Temple Judaism, ...
Followers of Judaism believe in one, all
... through various prophets. Some of these prophets include Abraham, Isaac, and Moses. ...
... through various prophets. Some of these prophets include Abraham, Isaac, and Moses. ...
The Torah
... The most important of these is the Torah (‘teaching’) which is made up of the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy – the five ‘Books of the Law’. These are handwritten on parchment scrolls for reading in the synagogue. In the synagogue the scrolls are kept in the Holy Ark. Th ...
... The most important of these is the Torah (‘teaching’) which is made up of the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy – the five ‘Books of the Law’. These are handwritten on parchment scrolls for reading in the synagogue. In the synagogue the scrolls are kept in the Holy Ark. Th ...
What is Judaism?
... In prophets of old – especially Moses, through whom Torah was revealed to the Hebrew people In Torah (first five books of the Bible), containing religious, moral and social law which guides the life of a Jew ...
... In prophets of old – especially Moses, through whom Torah was revealed to the Hebrew people In Torah (first five books of the Bible), containing religious, moral and social law which guides the life of a Jew ...
Abo lnformation ut Judaism
... East about 4,000 years ago at a time when most people believed in many gods. Abraham believed that only one all-powerful God had created the world. Jews believe God made a covenant (agreement) withAbraham thatAbraham's descendants would be God's chosen people, called Hebrews, and that they would dwe ...
... East about 4,000 years ago at a time when most people believed in many gods. Abraham believed that only one all-powerful God had created the world. Jews believe God made a covenant (agreement) withAbraham thatAbraham's descendants would be God's chosen people, called Hebrews, and that they would dwe ...
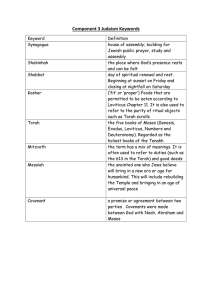
Judaism Key Words Document
... closing at nightfall on Saturday (‘fit’ or ‘proper’) Foods that are permitted to be eaten according to Leviticus Chapter 11. It is also used to refer to the purity of ritual objects such as Torah scrolls the five books of Moses (Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy). Regarded as the h ...
... closing at nightfall on Saturday (‘fit’ or ‘proper’) Foods that are permitted to be eaten according to Leviticus Chapter 11. It is also used to refer to the purity of ritual objects such as Torah scrolls the five books of Moses (Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy). Regarded as the h ...
Orthodox - emmausSOR2009
... and therefore binding. seek ways to fulfil the Torah in modern circumstances. high moral and ethical concern for the world’s well-being. observe strictly the Jewish Sabbath. strict dietary rules. (note: there are many varieties of Orthodoxy) 2005 Preliminary Course: Judaism. This sheet may be photoc ...
... and therefore binding. seek ways to fulfil the Torah in modern circumstances. high moral and ethical concern for the world’s well-being. observe strictly the Jewish Sabbath. strict dietary rules. (note: there are many varieties of Orthodoxy) 2005 Preliminary Course: Judaism. This sheet may be photoc ...
The Three Branches of Judaism
... following AD 90. The ______________ gave permission for this. The 39 books of the OT made this list. None of the Apocryphra made this list. Mishnah Once the canon was agreed upon, the time came to collect in writing the many interpretations of the law that had accrued over the centuries. Several dec ...
... following AD 90. The ______________ gave permission for this. The 39 books of the OT made this list. None of the Apocryphra made this list. Mishnah Once the canon was agreed upon, the time came to collect in writing the many interpretations of the law that had accrued over the centuries. Several dec ...
What is Judaism?
... In Torah (first five books of the Bible), containing religious, moral and social law which guides the life of a Jew ...
... In Torah (first five books of the Bible), containing religious, moral and social law which guides the life of a Jew ...
What is Judaism?
... • In prophets of old – especially Moses, through whom Torah was revealed to the Hebrew people • In Torah (first five books of the Bible), containing religious, moral and social law which guides the life of a Jew ...
... • In prophets of old – especially Moses, through whom Torah was revealed to the Hebrew people • In Torah (first five books of the Bible), containing religious, moral and social law which guides the life of a Jew ...
judaism
... The heart of Judaism is in the home and family, social responsibility and doing Mitzvot (“good deeds” based on God’s commandments) Through education and hard work we make our lives, the lives of others, and the world, what God intended it to be – Holy! ...
... The heart of Judaism is in the home and family, social responsibility and doing Mitzvot (“good deeds” based on God’s commandments) Through education and hard work we make our lives, the lives of others, and the world, what God intended it to be – Holy! ...
What is Judaism?
... In prophets of old – especially Moses, through whom Torah was revealed to the Hebrew people In Torah (first five books of the Bible), containing religious, moral and social law which guides the life of a Jew ...
... In prophets of old – especially Moses, through whom Torah was revealed to the Hebrew people In Torah (first five books of the Bible), containing religious, moral and social law which guides the life of a Jew ...