CHANGES IN DNA CAN PRODUCE VARIATIONS
... people to survive with it and pass it on (occurs in Africa, parts of India and Middle East). • A PEDIGREE (diagram of family relationships that include 2 or more generations) can show how the sickle cell allele is passed on through generations of a family. ...
... people to survive with it and pass it on (occurs in Africa, parts of India and Middle East). • A PEDIGREE (diagram of family relationships that include 2 or more generations) can show how the sickle cell allele is passed on through generations of a family. ...
DNA Profiles
... rare and fatal disorder, started a foundation to obtain tissue samples and funding for research The research hospital patented the gene and charged participating families for the test After a lawsuit, the hospital was allowed to continue to license the test and collect royalties ...
... rare and fatal disorder, started a foundation to obtain tissue samples and funding for research The research hospital patented the gene and charged participating families for the test After a lawsuit, the hospital was allowed to continue to license the test and collect royalties ...
Understanding DNA
... 2. Draw the cell and label the ff structures: a. cell membrane Note: Follow guidelines on b. chromosomes Making Diagrams ...
... 2. Draw the cell and label the ff structures: a. cell membrane Note: Follow guidelines on b. chromosomes Making Diagrams ...
Review Questions - effinghamschools.com
... What is NOT true of DNA a) It is located in the nucleus b) It delivers information for making proteins to the ribosome. c) It provides instructions for controling cell activities d) It is found in all living organisms e) All of these are true ...
... What is NOT true of DNA a) It is located in the nucleus b) It delivers information for making proteins to the ribosome. c) It provides instructions for controling cell activities d) It is found in all living organisms e) All of these are true ...
1 Genetics (BIL-250) Review Questions #1 (2
... (3-1) Draw a DNA replication fork and identify and label the locations of the following major components: (1) 5’ and 3’ ends of each strand, (2) leading strand, (3) lagging strand, (4) single-stranded binding proteins, (5) DNA polymerase, (6)Okazaki fragments, (7) RNA primer, (8) DNA helicase, (9) D ...
... (3-1) Draw a DNA replication fork and identify and label the locations of the following major components: (1) 5’ and 3’ ends of each strand, (2) leading strand, (3) lagging strand, (4) single-stranded binding proteins, (5) DNA polymerase, (6)Okazaki fragments, (7) RNA primer, (8) DNA helicase, (9) D ...
DNA functions worksheet
... When would DNA be found as chromatin? When would it be found as chromosomes? 3. One nucleotide of DNA is made of three smaller parts. What are these parts? ...
... When would DNA be found as chromatin? When would it be found as chromosomes? 3. One nucleotide of DNA is made of three smaller parts. What are these parts? ...
Quiz 3 review sheet
... • Describe the conditions that, if they change, will have an impact on allele frequencies over time (Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium) • Explain how and why non-coding regions are used for DNA profiling • Interpret data from genome screening • Describe the conditions that are important for the “Hardy Wein ...
... • Describe the conditions that, if they change, will have an impact on allele frequencies over time (Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium) • Explain how and why non-coding regions are used for DNA profiling • Interpret data from genome screening • Describe the conditions that are important for the “Hardy Wein ...
assignment DNA - UniMAP Portal
... 4. Why are mutation and recombination important in the process of natural selection and the evolution of organisms? ...
... 4. Why are mutation and recombination important in the process of natural selection and the evolution of organisms? ...
Extranuclear Inheritance
... mitochondria or chloroplasts determines phenotype of offspring • Infectious heredity – comes about from the symbiotic (parasitic) relationship associated with a microorganism; inherited phenotype is affected by the presence of the microorganism living in the cell’s cytoplasm • Maternal effect – nucl ...
... mitochondria or chloroplasts determines phenotype of offspring • Infectious heredity – comes about from the symbiotic (parasitic) relationship associated with a microorganism; inherited phenotype is affected by the presence of the microorganism living in the cell’s cytoplasm • Maternal effect – nucl ...
chapter 19_updates
... DNA at specific nucleotide sequences • Type II restriction enzyme: most useful enzyme • By adding methyl groups to the recognition sequence to protect itself from being digested by its own enzyme in bacteria ...
... DNA at specific nucleotide sequences • Type II restriction enzyme: most useful enzyme • By adding methyl groups to the recognition sequence to protect itself from being digested by its own enzyme in bacteria ...
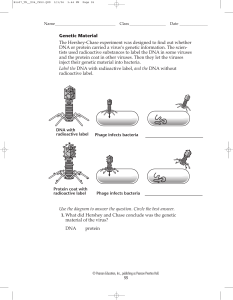
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
SNC2D Genes - Malvern Science
... Food for thought.. (don’t write) • How do we communicate to each other? • What does each of the following mean? – kobo – meti – etwar ...
... Food for thought.. (don’t write) • How do we communicate to each other? • What does each of the following mean? – kobo – meti – etwar ...
The Human Genome
... • The DNA fragment containing the replacement gene is spliced to viral DNA and the patient is infected with the modified virus particles, that carry the gene into the cells to correct genetic defects. ...
... • The DNA fragment containing the replacement gene is spliced to viral DNA and the patient is infected with the modified virus particles, that carry the gene into the cells to correct genetic defects. ...
BSC 219
... Egg provides majority of cytoplasm Paternal inheritance of organelles is common in gymnosperms. Heteroplasmy Distinctive DNA within the cytoplasm of a single cell The Genetics of Organelle-Encoded Traits Homoplasmy All wild-type or all mutant-type DNA are in the cytoplasm of a single cell. May be se ...
... Egg provides majority of cytoplasm Paternal inheritance of organelles is common in gymnosperms. Heteroplasmy Distinctive DNA within the cytoplasm of a single cell The Genetics of Organelle-Encoded Traits Homoplasmy All wild-type or all mutant-type DNA are in the cytoplasm of a single cell. May be se ...
BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.McDermid Lecture #1: DNA is the Genetic Material
... Figure 8-3 Bacteriophage (bacterial virus) T2 Radioisotope 32P to follow DNA; P not found in protein 35S labels protein; S not found in DNA Results 35S protein -> 32P DNA -> Conclusion: If DNA is the hereditary material then: 1) How do cells replicate their DNA? 2) How is genetic information stored? ...
... Figure 8-3 Bacteriophage (bacterial virus) T2 Radioisotope 32P to follow DNA; P not found in protein 35S labels protein; S not found in DNA Results 35S protein -> 32P DNA -> Conclusion: If DNA is the hereditary material then: 1) How do cells replicate their DNA? 2) How is genetic information stored? ...
DNA NOTES
... 19. In the cytoplasm, mRNA attaches to a ________________. The ________________, with its attached mRNA, is now ready to synthesize a __________________. 20. During Translation, a __________ molecule transfers an _____________________to the ribosome. Each new ______________________links with the pre ...
... 19. In the cytoplasm, mRNA attaches to a ________________. The ________________, with its attached mRNA, is now ready to synthesize a __________________. 20. During Translation, a __________ molecule transfers an _____________________to the ribosome. Each new ______________________links with the pre ...
Handout 2: Glossary
... chromosomes Long thread-like structures made of DNA and protein that are the gene-bearing structures of eukaryotic cells. codon A three-nucleotide sequence that codes for a specific amino acid or a stop signal in protein synthesis. denaturation A process in which a protein's structure is altered, ca ...
... chromosomes Long thread-like structures made of DNA and protein that are the gene-bearing structures of eukaryotic cells. codon A three-nucleotide sequence that codes for a specific amino acid or a stop signal in protein synthesis. denaturation A process in which a protein's structure is altered, ca ...
Dna: Hereditary molecules of life
... Every time a cell divides, an exact copy of its genetic information must be passed on to each of the two new cells produced. This is a huge task. Copies of molecules that consist of 6 billion base pairs (the diploid set) must be made, and each base pair must be “matched”. At the rate of one base pe ...
... Every time a cell divides, an exact copy of its genetic information must be passed on to each of the two new cells produced. This is a huge task. Copies of molecules that consist of 6 billion base pairs (the diploid set) must be made, and each base pair must be “matched”. At the rate of one base pe ...
BUILDING THE LIFE MOLECULES: DNA AND RNA The
... developing a program of new tools to help teaching and learning of structural molecular biology area at all levels, from elementary to graduate schools. In this way, we have developed a kit denoted Building the life molecules: DNA and RNA. The kit is composed by: (1) an interactive software called T ...
... developing a program of new tools to help teaching and learning of structural molecular biology area at all levels, from elementary to graduate schools. In this way, we have developed a kit denoted Building the life molecules: DNA and RNA. The kit is composed by: (1) an interactive software called T ...
Electrophoresis literally means “the condition of
... The type and number of bonds that join a cytosine to a guanine base ...
... The type and number of bonds that join a cytosine to a guanine base ...
Genealogical DNA test

A genealogical DNA test looks at a person's genome at specific locations. Results give information about genealogy or personal ancestry. In general, these tests compare the results of an individual to others from the same lineage or to current and historic ethnic groups. The test results are not meant for medical use, where different types of genetic testing are needed. They do not determine specific genetic diseases or disorders (see possible exceptions in Medical information below). They are intended only to give genealogical information.