Worksheet – Structure of DNA and Replication
... _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 21. Why is DNA replication important to the growth and development of a multi-cellular organism? _______________________________________________________ ...
... _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 21. Why is DNA replication important to the growth and development of a multi-cellular organism? _______________________________________________________ ...
Nucleotides
... form the “backbone” of RNA and DNA • RNAs are far less stable than DNA • Polynucleotides Are Directional Macromolecule – “5′- end” or the “3′- end” – the 5′- end is at the left ...
... form the “backbone” of RNA and DNA • RNAs are far less stable than DNA • Polynucleotides Are Directional Macromolecule – “5′- end” or the “3′- end” – the 5′- end is at the left ...
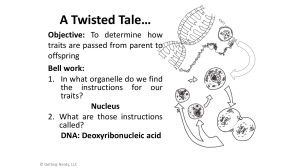
A Twisted Tale…
... the instructions for our traits? Nucleus 2. What are those instructions called? DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid ...
... the instructions for our traits? Nucleus 2. What are those instructions called? DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid ...
The Double Helix video notes
... ☐All organisms contain about the same amounts of adenine and thymine in their DNA. ☐The proportions of adenine + thymine and guanine + cytosine are the same in all organisms. ☐Larger organisms have greater amounts of each nitrogenous base than smaller organisms have. ☐The total length of DNA molecul ...
... ☐All organisms contain about the same amounts of adenine and thymine in their DNA. ☐The proportions of adenine + thymine and guanine + cytosine are the same in all organisms. ☐Larger organisms have greater amounts of each nitrogenous base than smaller organisms have. ☐The total length of DNA molecul ...
DNA Powerpoint - Year 10 Life Science
... The phosphate and sugar form the backbone of the DNA molecule The bases form the “rungs” There are four types of nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Each base will only bond with one other specific base (Nitrogenous base pairing) C and G always pair ...
... The phosphate and sugar form the backbone of the DNA molecule The bases form the “rungs” There are four types of nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Each base will only bond with one other specific base (Nitrogenous base pairing) C and G always pair ...
DNA Notes Review
... ______________23. Amino Acids are the monomers of DNA ______________24. The sides of the DNA double helix are made of the Nitrogenous bases ______________25. The enzyme that pairs up the nucleotides to their complementary pairs is the DNA Ligase ______________26. The process of DNA replication is ho ...
... ______________23. Amino Acids are the monomers of DNA ______________24. The sides of the DNA double helix are made of the Nitrogenous bases ______________25. The enzyme that pairs up the nucleotides to their complementary pairs is the DNA Ligase ______________26. The process of DNA replication is ho ...
RNA Synthesis
... 2. What is the mRNA if the complementary DNA is TCTGAG? 3. What does a cell copy in DNA replication? 4. How many strands of DNA are used to make complementary strands of DNA? 5. How does the cell make RNA? ...
... 2. What is the mRNA if the complementary DNA is TCTGAG? 3. What does a cell copy in DNA replication? 4. How many strands of DNA are used to make complementary strands of DNA? 5. How does the cell make RNA? ...
Genomic sequencing
... Comparing the sequenced genomes of: Members of different disease causing micro-organisms – do they have important genetic sequences in common? Member s of the same species, e.g. ...
... Comparing the sequenced genomes of: Members of different disease causing micro-organisms – do they have important genetic sequences in common? Member s of the same species, e.g. ...
Ch08
... 1. This is not a trivial question! Check out Fig 8-11 which shows the H-bonding between A-T and G-C base pairs. Those “Watson-Crick” H-bonds that are part of holding the two DNA strands together which along with hydrophobic stacking allows DNA to form stable double stranded structure. But consider t ...
... 1. This is not a trivial question! Check out Fig 8-11 which shows the H-bonding between A-T and G-C base pairs. Those “Watson-Crick” H-bonds that are part of holding the two DNA strands together which along with hydrophobic stacking allows DNA to form stable double stranded structure. But consider t ...
Laboratory #1 Lecture Guide: Forensic DNA Fingerprinting
... 3. Why might it be evolutionary advantageous for bacteria to evolve to produce restriction enzymes? ...
... 3. Why might it be evolutionary advantageous for bacteria to evolve to produce restriction enzymes? ...
Chapter 12 Review PPT
... The Watson and Crick model of DNA is a(an) ____________________, in which two strands are wound around each other. double helix ...
... The Watson and Crick model of DNA is a(an) ____________________, in which two strands are wound around each other. double helix ...
point of view that is personal rather than scientific
... The Watson and Crick model of DNA is a(an) ____________________, in which two strands are wound around each other. double helix ...
... The Watson and Crick model of DNA is a(an) ____________________, in which two strands are wound around each other. double helix ...
GEL ELECTROPHORESIS LAB READING: Read the explanation of
... their rate of movement through a gel under the influence of an electrical field. The direction of movement is affected by the charge of the molecules, and the rate of movement is affected by their size and shape, the density of the gel, and the strength of the electrical field. DNA is a negatively c ...
... their rate of movement through a gel under the influence of an electrical field. The direction of movement is affected by the charge of the molecules, and the rate of movement is affected by their size and shape, the density of the gel, and the strength of the electrical field. DNA is a negatively c ...
My CHXE Carrot BAC Research Poster
... extracted from the E. coli when necessary. This is done so that the segments of DNA from the same sample can be easily and continuously extracted and used to perform tests and experiments. The bacteria are able to replicate themselves and ...
... extracted from the E. coli when necessary. This is done so that the segments of DNA from the same sample can be easily and continuously extracted and used to perform tests and experiments. The bacteria are able to replicate themselves and ...
DNA
... • 1944- Avery identified DNA as the transforming factor • 1952- Hershey and Chase confirmed Avery’s results by radioactive tagging ...
... • 1944- Avery identified DNA as the transforming factor • 1952- Hershey and Chase confirmed Avery’s results by radioactive tagging ...
DNA sequencing

DNA sequencing is the process of determining the precise order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a strand of DNA. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery.Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with modern DNA sequencing technology has been instrumental in the sequencing of complete DNA sequences, or genomes of numerous types and species of life, including the human genome and other complete DNA sequences of many animal, plant, and microbial species.The first DNA sequences were obtained in the early 1970s by academic researchers using laborious methods based on two-dimensional chromatography. Following the development of fluorescence-based sequencing methods with a DNA sequencer, DNA sequencing has become easier and orders of magnitude faster.