Prevention of DNA Rereplication Through a Meiotic Recombination
... kinase inhibitor Sic1 during meiosis can trigger extra rounds of DNA replication. When programmed DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are generated but not repaired due to absence of DMC1, a pathway involving the checkpoint gene RAD17 prevents this DNA rereplication. Further genetic analysis has now rev ...
... kinase inhibitor Sic1 during meiosis can trigger extra rounds of DNA replication. When programmed DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are generated but not repaired due to absence of DMC1, a pathway involving the checkpoint gene RAD17 prevents this DNA rereplication. Further genetic analysis has now rev ...
Variable effects of DNA-synthesis inhibitors upon DNA methylation
... clearly also other requirements which are necessary to ensure that active transcription occurs (8). Studies of the relationship between DNA methylation and gene expression have been aided by use of drugs capable of inducing DNA bypomethylation. ...
... clearly also other requirements which are necessary to ensure that active transcription occurs (8). Studies of the relationship between DNA methylation and gene expression have been aided by use of drugs capable of inducing DNA bypomethylation. ...
Microsoft Word
... the design, synthesis and DNA binding affinity of novel chrysin-pyrrolo[2,1c][1,4]benzodiazepine hybrids and their activity. While section B consists of the design, synthesis and DNA binding affinity of novel quinazolinone-PBD hybrids and their activity on nine human tumour cell lines. The section C ...
... the design, synthesis and DNA binding affinity of novel chrysin-pyrrolo[2,1c][1,4]benzodiazepine hybrids and their activity. While section B consists of the design, synthesis and DNA binding affinity of novel quinazolinone-PBD hybrids and their activity on nine human tumour cell lines. The section C ...
lecture_23 - supporting lehigh cse
... However, if the error occurs in one of the strands of double stranded DNA, repair enzymes can restore the proper DNA sequence by using the complement strand as a reference. RAID 1 array ...
... However, if the error occurs in one of the strands of double stranded DNA, repair enzymes can restore the proper DNA sequence by using the complement strand as a reference. RAID 1 array ...
DNA Tribes Digest for October 28, 2010
... parts of the world, including a predominant Mesopotamian contribution (49.9%) as well as smaller contributions from several European sub-regions (totaling 45.2%). The largest single genetic contribution of 49.9% identified was from the Mesopotamian region that characterizes populations of eastern An ...
... parts of the world, including a predominant Mesopotamian contribution (49.9%) as well as smaller contributions from several European sub-regions (totaling 45.2%). The largest single genetic contribution of 49.9% identified was from the Mesopotamian region that characterizes populations of eastern An ...
Forever 100bp Ladder Personalizer
... equal intensities, with a couple at higher concentration for orientation. This can be done to generate a quick ladder, albeit without accurately knowing amount of each band as is obtained when the mix is generated after quantitation of each PCR product. Simply amplify each of 12 differently sized fr ...
... equal intensities, with a couple at higher concentration for orientation. This can be done to generate a quick ladder, albeit without accurately knowing amount of each band as is obtained when the mix is generated after quantitation of each PCR product. Simply amplify each of 12 differently sized fr ...
RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY: APPLICATIONS IN THE
... fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs), short tandem repeats (STRs) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). All three can occur within genes as well as in intergenic regions, and altogether there are several million of these polymeric sites I the human genome, with SNPs being the most common. Gen ...
... fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs), short tandem repeats (STRs) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). All three can occur within genes as well as in intergenic regions, and altogether there are several million of these polymeric sites I the human genome, with SNPs being the most common. Gen ...
template strand
... occurs at a rate of one error per 10,000 base pairs. DNA polymerase proofreads each new nucleotide against the template nucleotide as soon as it is added. If there is an incorrect pairing, the enzyme removes the wrong nucleotide and then resumes synthesis. The final error rate is only one per billio ...
... occurs at a rate of one error per 10,000 base pairs. DNA polymerase proofreads each new nucleotide against the template nucleotide as soon as it is added. If there is an incorrect pairing, the enzyme removes the wrong nucleotide and then resumes synthesis. The final error rate is only one per billio ...
DNA - Miss Schwippert
... DNA is needed in each cell to make necessary proteins. Because DNA is so important, when a cell divides, it must pass on an exact copy of the DNA to function correctly. ...
... DNA is needed in each cell to make necessary proteins. Because DNA is so important, when a cell divides, it must pass on an exact copy of the DNA to function correctly. ...
Lesson Plan - beyond benign
... identical on both strands (the 5’ and 3’ ends refers to the chemical structure of the DNA). Each of the double strands of the DNA molecule is complimentary to the other; thus adenine pairs with thymine, and guanine with cytosine. Restriction enzymes (also known as restriction endonucleases) recogniz ...
... identical on both strands (the 5’ and 3’ ends refers to the chemical structure of the DNA). Each of the double strands of the DNA molecule is complimentary to the other; thus adenine pairs with thymine, and guanine with cytosine. Restriction enzymes (also known as restriction endonucleases) recogniz ...
Laboratory of Insect Genetics and Biosciences (IGB) Dept. Biology
... R: This is true and this is why we decided to compare just the amount of 5mC to distinguish highly and poorly methylated genomes (with insects in the second category) without focussing on conservation of methylated sites. This analysis could be very difficult in aphids and honey bees since the diffe ...
... R: This is true and this is why we decided to compare just the amount of 5mC to distinguish highly and poorly methylated genomes (with insects in the second category) without focussing on conservation of methylated sites. This analysis could be very difficult in aphids and honey bees since the diffe ...
Preparation and analysis of environmental DNA: optimisation of
... to which interfering organic and inorganic impurities are present pose a problem for molecular analyses. These issues are important as subsequent analysis by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) may be problematic with sheared DNA or may not occur at all in the presence of certain impurities. Any loss of ...
... to which interfering organic and inorganic impurities are present pose a problem for molecular analyses. These issues are important as subsequent analysis by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) may be problematic with sheared DNA or may not occur at all in the presence of certain impurities. Any loss of ...
Lecture 6 DNA structure replication DNA structure, replication, and
... • Precision in the exchange g ((no g gain or loss of nucleotide pairs) prevents mutations from occurring • Gene conversion can give rise to an unequal yield of ...
... • Precision in the exchange g ((no g gain or loss of nucleotide pairs) prevents mutations from occurring • Gene conversion can give rise to an unequal yield of ...
C - MCC Year 12 Biology
... Replication of DNA can occur only in the 5´ to 3´ direction. This is no problem with the so-called leading strand because its new complementary strand can be built continuously in the 5´ to 3´ direction. The other strand, known as the lagging strand, can be built only backwards and in short disconti ...
... Replication of DNA can occur only in the 5´ to 3´ direction. This is no problem with the so-called leading strand because its new complementary strand can be built continuously in the 5´ to 3´ direction. The other strand, known as the lagging strand, can be built only backwards and in short disconti ...
Applications of Recombinant DNA to Pathologic Diagnosis
... is joined to a different chromosome. Cosmid: Plasmids into which the “cos” site of bacteriophage lambda has been inserted. A cosmid also allows plasmid molecules to be inserted into viral coat particles in vitro. DNA ligase: An enzyme capable of covalently joining two ends of DNA molecules. DNA prob ...
... is joined to a different chromosome. Cosmid: Plasmids into which the “cos” site of bacteriophage lambda has been inserted. A cosmid also allows plasmid molecules to be inserted into viral coat particles in vitro. DNA ligase: An enzyme capable of covalently joining two ends of DNA molecules. DNA prob ...
Introduction Kit components
... The GF-1 AmbiClean Kit ( Gel & PCR ) is a system designed for DNA recovery from agorose gel and rapid PCR clean-up of DNA bands ranging from 100bp to 20kb. The GF-1 AmbiClean Kit ( Gel & PCR ) contains special buffers to provide the correct salt concentration and pH for efficient recovery (80 - 90%) ...
... The GF-1 AmbiClean Kit ( Gel & PCR ) is a system designed for DNA recovery from agorose gel and rapid PCR clean-up of DNA bands ranging from 100bp to 20kb. The GF-1 AmbiClean Kit ( Gel & PCR ) contains special buffers to provide the correct salt concentration and pH for efficient recovery (80 - 90%) ...
DNA and Gene Expression (chaps 12-15)
... 26 The main reason scientists thought that proteins, rather than DNA, were the carriers of genetic material in the cell was: A. their abundance within the cell. B. their presence within the nucleus. C. the large number of possible amino acid combinations. D. their ability to be exported from the cel ...
... 26 The main reason scientists thought that proteins, rather than DNA, were the carriers of genetic material in the cell was: A. their abundance within the cell. B. their presence within the nucleus. C. the large number of possible amino acid combinations. D. their ability to be exported from the cel ...
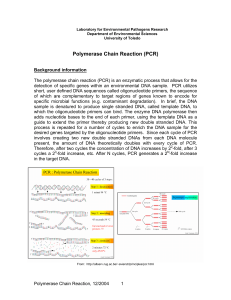
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - Department of Environmental
... Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Background information The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an enzymatic process that allows for the detection of specific genes within an environmental DNA sample. PCR utilizes short, user defined DNA sequences called oligonucleotide primers, the sequence of which ...
... Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Background information The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an enzymatic process that allows for the detection of specific genes within an environmental DNA sample. PCR utilizes short, user defined DNA sequences called oligonucleotide primers, the sequence of which ...
Simple and inexpensive DNA extraction protocol for - Funpec-RP
... Ariefdjohan et al., 2010). The procedure must extract DNA from a large number of different bacteria, and the recovered nucleic acid must be suitable for subsequent molecular techniques, such as endonuclease restriction or Taq polymerase amplification. In this report, several protocols for obtaining ...
... Ariefdjohan et al., 2010). The procedure must extract DNA from a large number of different bacteria, and the recovered nucleic acid must be suitable for subsequent molecular techniques, such as endonuclease restriction or Taq polymerase amplification. In this report, several protocols for obtaining ...
Electroosmotic screening of the DNA charge in a
... sium ions attracted to the negatively charged phosphate groups of the DNA backbone. The average residence time of potassium ions at the DNA surface was found to be just several picoseconds, close to the average residence time of water. This indicates that ions are not bound to DNA. The chloride ions ...
... sium ions attracted to the negatively charged phosphate groups of the DNA backbone. The average residence time of potassium ions at the DNA surface was found to be just several picoseconds, close to the average residence time of water. This indicates that ions are not bound to DNA. The chloride ions ...
myDNA
... 2. Cut out your traits along the heavy black lines and then tape them together end to end. You should have one long strip with all your trait words in a row, no spaces between any letters. Cut off and discard any empty boxes at the end. 3. Now, cut your traits between the following letters.Cut only ...
... 2. Cut out your traits along the heavy black lines and then tape them together end to end. You should have one long strip with all your trait words in a row, no spaces between any letters. Cut off and discard any empty boxes at the end. 3. Now, cut your traits between the following letters.Cut only ...
DNA insertion mutations can be predicted by a periodic
... Here, I(Δx) signifies the prospective number of mice that harbor the inserted viral DNA at the Δx-nucleotide position from the cytosine (position r) at which the insertion occurred most frequently. For example, when Δx = 10 (bp), i.e., the q and s positions in the segment, I(Δx) was close to 21, whi ...
... Here, I(Δx) signifies the prospective number of mice that harbor the inserted viral DNA at the Δx-nucleotide position from the cytosine (position r) at which the insertion occurred most frequently. For example, when Δx = 10 (bp), i.e., the q and s positions in the segment, I(Δx) was close to 21, whi ...
DNA repair

DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1 million individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs).The rate of DNA repair is dependent on many factors, including the cell type, the age of the cell, and the extracellular environment. A cell that has accumulated a large amount of DNA damage, or one that no longer effectively repairs damage incurred to its DNA, can enter one of three possible states: an irreversible state of dormancy, known as senescence cell suicide, also known as apoptosis or programmed cell death unregulated cell division, which can lead to the formation of a tumor that is cancerousThe DNA repair ability of a cell is vital to the integrity of its genome and thus to the normal functionality of that organism. Many genes that were initially shown to influence life span have turned out to be involved in DNA damage repair and protection.