24 October - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... posted on the course website. PRINT it out and turn it in either on your discussion sections or on next Monday's class no later than 12:00PM. Email attachments and late delivery are not acceptable. 1. What factors ensure the fidelity of replication during DNA synthesis? 2. Define “promoter” and disc ...
... posted on the course website. PRINT it out and turn it in either on your discussion sections or on next Monday's class no later than 12:00PM. Email attachments and late delivery are not acceptable. 1. What factors ensure the fidelity of replication during DNA synthesis? 2. Define “promoter” and disc ...
A1981LX51500001
... characteristics. XP studies have become a starting point and justification for many experiments investigating carcinogen action on DNA The role of DNA repair mechanisms in carcinogenesis is a currently active field of research. "A wide range of human diseases have now been identified that exhibit in ...
... characteristics. XP studies have become a starting point and justification for many experiments investigating carcinogen action on DNA The role of DNA repair mechanisms in carcinogenesis is a currently active field of research. "A wide range of human diseases have now been identified that exhibit in ...
12.2 DNA Replication ppt
... bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
... bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
Unit: DNA and Human Heredity (Ch. 12-14)
... (substitutions) and frameshift mutations (deletions, insertions, and translocations). ...
... (substitutions) and frameshift mutations (deletions, insertions, and translocations). ...
Section 4.2 - Cells and DNA
... 7. This organelle is like a manufacturing plant that makes proteins. 8. Organelle that controls all the activities within the cell. 13. X-shaped structure that holds genetic information. 14. Nitrogen base of DNA, starts with the letter "G". 15. Nitrogen base of DNA, starts with the letter "A". 16. S ...
... 7. This organelle is like a manufacturing plant that makes proteins. 8. Organelle that controls all the activities within the cell. 13. X-shaped structure that holds genetic information. 14. Nitrogen base of DNA, starts with the letter "G". 15. Nitrogen base of DNA, starts with the letter "A". 16. S ...
Slide
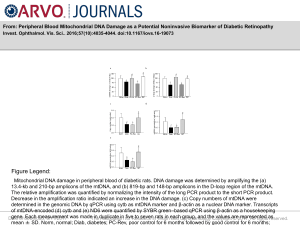
... 13.4-kb and 210-bp amplicons of the mtDNA, and (b) 819-bp and 148-bp amplicons in the D-loop region of the mtDNA. The relative amplification was quantified by normalizing the intensity of the long PCR product to the short PCR product. Decrease in the amplification ratio indicated an increase in the ...
... 13.4-kb and 210-bp amplicons of the mtDNA, and (b) 819-bp and 148-bp amplicons in the D-loop region of the mtDNA. The relative amplification was quantified by normalizing the intensity of the long PCR product to the short PCR product. Decrease in the amplification ratio indicated an increase in the ...
Biotech
... technique to multiply a sample of DNA many times in a short period of time. It supplies the scientist with sufficient DNA for further testing. http://www.dnalc.org/resources/animations/pcr.html ...
... technique to multiply a sample of DNA many times in a short period of time. It supplies the scientist with sufficient DNA for further testing. http://www.dnalc.org/resources/animations/pcr.html ...
1 - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... d. degradation of the transposon while it is moving 7. Oxidative stress can damage DNA by a. causing single-strand breaks b, causing double-strand breaks c. oxidation of guanine to 8-oxo-guanine d. b and c e. all of the above 8. Which of the following is not true regarding DNA photolyases a. repair ...
... d. degradation of the transposon while it is moving 7. Oxidative stress can damage DNA by a. causing single-strand breaks b, causing double-strand breaks c. oxidation of guanine to 8-oxo-guanine d. b and c e. all of the above 8. Which of the following is not true regarding DNA photolyases a. repair ...
dr. jayil lee _apr. 26, 2016
... collision of FtsK with other DNA binding proteins. This study gives us an insight into how proteins cope with the crowded environments of DNA inside cells. On the other hand, using the single-stranded DNA curtain technique, we investigated the homologous recombination that is a repair pathway of DNA ...
... collision of FtsK with other DNA binding proteins. This study gives us an insight into how proteins cope with the crowded environments of DNA inside cells. On the other hand, using the single-stranded DNA curtain technique, we investigated the homologous recombination that is a repair pathway of DNA ...
REPLICATION, TRANSCRIPTION, TRANSLATION TAKS
... 14 Part of a DNA strand is represented in the diagram above. In order for DNA to replicate, the strand must separate at which of the following locations? F Between every phosphate-sugar pair G Between the eight sugar-base pairs H* Between the four nitrogenous base pairs J Between any two chemical bo ...
... 14 Part of a DNA strand is represented in the diagram above. In order for DNA to replicate, the strand must separate at which of the following locations? F Between every phosphate-sugar pair G Between the eight sugar-base pairs H* Between the four nitrogenous base pairs J Between any two chemical bo ...
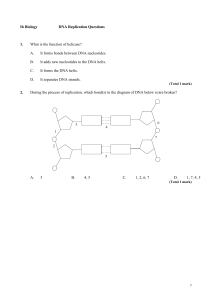
Ib Biology DNA Replication Questions 1. What is the function of
... [Freeman, Scott, Biological Science, 1st, 2002. Electronically reproduced by permission of Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, New Jersey] ...
... [Freeman, Scott, Biological Science, 1st, 2002. Electronically reproduced by permission of Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, New Jersey] ...
DNA Structure
... -What did she study? -What did the photos suggest? Watson and Crick (Last Paragraph) -What did Watson observe? -What did he immediately know? -What did Watson and Crick complete? What year? Chargaff (2nd Paragraph) -What did he find? -Give an example -What is Chargaff’s rule? ...
... -What did she study? -What did the photos suggest? Watson and Crick (Last Paragraph) -What did Watson observe? -What did he immediately know? -What did Watson and Crick complete? What year? Chargaff (2nd Paragraph) -What did he find? -Give an example -What is Chargaff’s rule? ...
Chapter 21
... 3’ to 5’ direction lagging strand. 5’ to 3’ direction is the leading strand. Okazaki fragments are made on the lagging strand. DNA returns to a coiled structure. Two identical DNA strands are made. • Takes about 8 hours to complete 3 billion base pairs. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dKubyIRiN84 ...
... 3’ to 5’ direction lagging strand. 5’ to 3’ direction is the leading strand. Okazaki fragments are made on the lagging strand. DNA returns to a coiled structure. Two identical DNA strands are made. • Takes about 8 hours to complete 3 billion base pairs. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dKubyIRiN84 ...
Modification of Genes and Proteins - sharonap-cellrepro-p3
... cytoplasm, and is “decoded” to create a chain of amino acids. ...
... cytoplasm, and is “decoded” to create a chain of amino acids. ...
Genetics – Part One - The Biology Corner
... 5. Describe the process of DNA replication. Know the players involved: DNA helicase, DNA polymerase, replication fork, leading strand, lagging strand, Okazaki fragments, DNA ligase, complimentary strand, base-pairing 6. Describe the process of transcription, including where it occurs and what compon ...
... 5. Describe the process of DNA replication. Know the players involved: DNA helicase, DNA polymerase, replication fork, leading strand, lagging strand, Okazaki fragments, DNA ligase, complimentary strand, base-pairing 6. Describe the process of transcription, including where it occurs and what compon ...
The discovery:DNA
... The discovery:DNA .The Swiss biochemist Friedrich Miescher (18441895) discovered the nucleic acids in 1868. His experiment: ...
... The discovery:DNA .The Swiss biochemist Friedrich Miescher (18441895) discovered the nucleic acids in 1868. His experiment: ...
Ch 16 homework
... Which enzyme functions here to deal with supercoils in DNA? What enzyme functions here to unwind the DNA? Which enzyme functions to synthesize these small RNA sequences? What are these ~1000 nucleotide long DNA fragments called? Is this strand the leading or lagging strand ...
... Which enzyme functions here to deal with supercoils in DNA? What enzyme functions here to unwind the DNA? Which enzyme functions to synthesize these small RNA sequences? What are these ~1000 nucleotide long DNA fragments called? Is this strand the leading or lagging strand ...
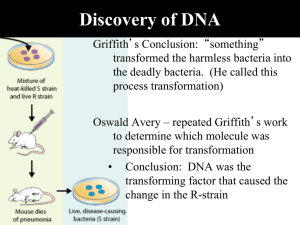
Discovery of DNA
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
DNA repair

DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1 million individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs).The rate of DNA repair is dependent on many factors, including the cell type, the age of the cell, and the extracellular environment. A cell that has accumulated a large amount of DNA damage, or one that no longer effectively repairs damage incurred to its DNA, can enter one of three possible states: an irreversible state of dormancy, known as senescence cell suicide, also known as apoptosis or programmed cell death unregulated cell division, which can lead to the formation of a tumor that is cancerousThe DNA repair ability of a cell is vital to the integrity of its genome and thus to the normal functionality of that organism. Many genes that were initially shown to influence life span have turned out to be involved in DNA damage repair and protection.