Stress Responses and Checkpoints for DNA Damage
... Double-strand breaks Double-strand breaks (DSBs), in which both strands in the double helix are severed, are particularly hazardous to the cell because they can lead to genome rearrangements. Various mechanisms exist to repair DSBs: non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), recombinational repair (also k ...
... Double-strand breaks Double-strand breaks (DSBs), in which both strands in the double helix are severed, are particularly hazardous to the cell because they can lead to genome rearrangements. Various mechanisms exist to repair DSBs: non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), recombinational repair (also k ...
LET*S DO IT THE HARD WAY
... oxygen from sugar molecules may combine with other elements to form amino acids and/or other large carbon-based molecules. ...
... oxygen from sugar molecules may combine with other elements to form amino acids and/or other large carbon-based molecules. ...
Chapter 16 PPT
... • In mismatch repair of DNA, repair enzymes correct errors in base pairing • DNA can be damaged by chemicals, radioactive emissions, X-rays, UV light, and certain molecules (in cigarette smoke for example) • In nucleotide excision repair, a nuclease cuts out and replaces damaged stretches of DNA Cop ...
... • In mismatch repair of DNA, repair enzymes correct errors in base pairing • DNA can be damaged by chemicals, radioactive emissions, X-rays, UV light, and certain molecules (in cigarette smoke for example) • In nucleotide excision repair, a nuclease cuts out and replaces damaged stretches of DNA Cop ...
DNA RNA PS PPT
... nucleotides into complementary strands…“semi-conservative” (Meselson & Stahl 1958) • Portions to be replicated must untwist first ...
... nucleotides into complementary strands…“semi-conservative” (Meselson & Stahl 1958) • Portions to be replicated must untwist first ...
Identification ofStreptococcus parasanguinisDNA contamination in
... (Figure 1), and agarose gel analysis showed the presence of two bands in matching samples (Figure 2). Sanger sequence analysis showed that the 153 bp fragment did not align with any human sequence. Alignment with other organisms showed 98% identity with Streptococcus parasanguinis plasmid pFW213 [Ge ...
... (Figure 1), and agarose gel analysis showed the presence of two bands in matching samples (Figure 2). Sanger sequence analysis showed that the 153 bp fragment did not align with any human sequence. Alignment with other organisms showed 98% identity with Streptococcus parasanguinis plasmid pFW213 [Ge ...
Damage Control: The Pleiotropy of DNA Repair Genes
... cells. This result has been confirmed and extended to cells in the eye imaginal disc (M. Brodsky and G. M. Rubin, personal communication). Thus the function of the MEI-41 protein may not be in the repair of damage per se, but in triggering a DNA damage-dependent cellcycle checkpoint. Activation of t ...
... cells. This result has been confirmed and extended to cells in the eye imaginal disc (M. Brodsky and G. M. Rubin, personal communication). Thus the function of the MEI-41 protein may not be in the repair of damage per se, but in triggering a DNA damage-dependent cellcycle checkpoint. Activation of t ...
Chapter 10
... short tandem repeat (STR)—short segment of DNA in which the same sequence of two to six base pairs is repeated many times; varying numbers of repeats found among individuals ...
... short tandem repeat (STR)—short segment of DNA in which the same sequence of two to six base pairs is repeated many times; varying numbers of repeats found among individuals ...
Exam III
... B) The chromosome number is conserved. C) Sister chromatids are separated. D) Four daughter cells are formed. E) The sperm cells elongate to form a head and a tail end. Question 49 DNA is replicated during this phase of the cell cycle A) B) C) D) E) ...
... B) The chromosome number is conserved. C) Sister chromatids are separated. D) Four daughter cells are formed. E) The sperm cells elongate to form a head and a tail end. Question 49 DNA is replicated during this phase of the cell cycle A) B) C) D) E) ...
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady
... responsible for majority of replication DNA polymerase I has a single subunit whose job is to rapidly remove RNA primers and fill in DNA DNA polymerases II, IV and V are involved in DNA repair and replicating damaged DNA DNA polymerases I and III stall at DNA damage DNA polymerases II, IV and ...
... responsible for majority of replication DNA polymerase I has a single subunit whose job is to rapidly remove RNA primers and fill in DNA DNA polymerases II, IV and V are involved in DNA repair and replicating damaged DNA DNA polymerases I and III stall at DNA damage DNA polymerases II, IV and ...
Study Questions 2
... 6. Describe reasons why the major groove is more often used by proteins to recognize specific DNA sequences than the minor groove. Consider the sequence AATCGG; what information, in terms of hydrogen bond donors, hydrogen bond acceptors, nonpolar hydrogen, and methyl groups, are provided by the maj ...
... 6. Describe reasons why the major groove is more often used by proteins to recognize specific DNA sequences than the minor groove. Consider the sequence AATCGG; what information, in terms of hydrogen bond donors, hydrogen bond acceptors, nonpolar hydrogen, and methyl groups, are provided by the maj ...
DNA Technology
... translation. Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers the amino acids in the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. •The amino acids are lined up in the coded sequence to form a specific protein. ...
... translation. Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers the amino acids in the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. •The amino acids are lined up in the coded sequence to form a specific protein. ...
Meaning and Molecular Data - Circle
... with C and A with T In short DNA sequences, imprecise base pairing will not be tolerated Long sequences can tolerate some mispairing only if -G of the majority of bases in a sequence exceeds the energy required to keep mispaired bases together Because the source of any single strand of DNA is irrel ...
... with C and A with T In short DNA sequences, imprecise base pairing will not be tolerated Long sequences can tolerate some mispairing only if -G of the majority of bases in a sequence exceeds the energy required to keep mispaired bases together Because the source of any single strand of DNA is irrel ...
ch. 16 Molecular Basis of Inheritance-2009
... • The nitrogenous bases are paired in specific combinations: adenine with thymine and guanine with cytosine. • Pairing like nucleotides did not fit the uniform diameter indicated by the X-ray data. – A purine-purine pair would be too wide and a pyrimidine-pyrimidine pairing would be too short. – On ...
... • The nitrogenous bases are paired in specific combinations: adenine with thymine and guanine with cytosine. • Pairing like nucleotides did not fit the uniform diameter indicated by the X-ray data. – A purine-purine pair would be too wide and a pyrimidine-pyrimidine pairing would be too short. – On ...
Isolating DNA from Fruits
... received the Nobel Prize for their determination of the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). In the years since the structure of DNA was first unraveled, it has become the most significant biological topic of the century. Understanding the structure of DNA helps to explain many life processes a ...
... received the Nobel Prize for their determination of the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). In the years since the structure of DNA was first unraveled, it has become the most significant biological topic of the century. Understanding the structure of DNA helps to explain many life processes a ...
BASIS: A Genesis in Musical Interfaces
... character. A personality consists of seven sets of five parameters each. The sets are labeled as INBORN, GROWTH1 thru GROWTH5, and OVERALL GROWTH. Paging through the sets moves the faders to the stored values for that set and shows the names of the parameters on the lcds. On the INBORN page the para ...
... character. A personality consists of seven sets of five parameters each. The sets are labeled as INBORN, GROWTH1 thru GROWTH5, and OVERALL GROWTH. Paging through the sets moves the faders to the stored values for that set and shows the names of the parameters on the lcds. On the INBORN page the para ...
DNA Replication
... Primase is the enzyme that synthesizes the RNA Primer DNA polymerase III can then add the new nucleotides ...
... Primase is the enzyme that synthesizes the RNA Primer DNA polymerase III can then add the new nucleotides ...
DNA to Protein
... • Objective: Students will understand the structure of DNA and the preliminaries of DNA replication. – Complete Recycled Model of DNA (Due at the end of the period) ...
... • Objective: Students will understand the structure of DNA and the preliminaries of DNA replication. – Complete Recycled Model of DNA (Due at the end of the period) ...
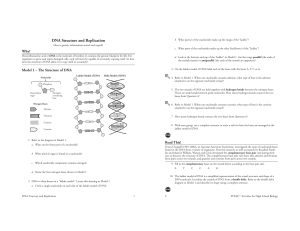
Section 1: The Structure of DNA
... • The instructions for inherited traits are called genes. A gene is a small segment of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, that is located in a chromosome. • DNA is the primary material that causes inheritable characteristics in related groups of organisms. • DNA is a simple molecule, composed of only fo ...
... • The instructions for inherited traits are called genes. A gene is a small segment of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, that is located in a chromosome. • DNA is the primary material that causes inheritable characteristics in related groups of organisms. • DNA is a simple molecule, composed of only fo ...
DNA - Cloudfront.net
... – DNA is contained in the nucleus. – Every cell in an organism has identical DNA organized into linear chromosomes. – Different organisms have different numbers of chromosomes – Humans 46, Drosophila 8, Sequoia Tree 22 • On chromosome 1 of human DNA there are 249 million base pairs coding for approx ...
... – DNA is contained in the nucleus. – Every cell in an organism has identical DNA organized into linear chromosomes. – Different organisms have different numbers of chromosomes – Humans 46, Drosophila 8, Sequoia Tree 22 • On chromosome 1 of human DNA there are 249 million base pairs coding for approx ...
Mitochondrial Deoxyribonucleic Acids in a Range of
... shaken vigorously for 10 min and centrifuged at 2,500g for 10 min, and the top aqueous layer was removed. This initial deproteinization with chloroform increases the yield of DNA from some tissues, at the same time decreasing the amount of RNA released into the aqueous phase. With certain plants suc ...
... shaken vigorously for 10 min and centrifuged at 2,500g for 10 min, and the top aqueous layer was removed. This initial deproteinization with chloroform increases the yield of DNA from some tissues, at the same time decreasing the amount of RNA released into the aqueous phase. With certain plants suc ...
DNA! - Chapter 10
... • DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins • Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes • The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictate the order of amino acids that make up a protein Nucleotide sequence of His gene ...
... • DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins • Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes • The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictate the order of amino acids that make up a protein Nucleotide sequence of His gene ...
DNA polymerase
... resulting in the DNA becoming denatured, this causes the doubled stranded molecule to separate giving 2 single strands which act as templates from which copies can be made. The second stage requires the use of oligonucleotides called DNA primers, which are simply short sections of single stranded ...
... resulting in the DNA becoming denatured, this causes the doubled stranded molecule to separate giving 2 single strands which act as templates from which copies can be made. The second stage requires the use of oligonucleotides called DNA primers, which are simply short sections of single stranded ...
18 DNA Structure and Replication-S
... species. Using the base-pair rules, complete the following table to show the percentage of each type of base in the five different organisms. ...
... species. Using the base-pair rules, complete the following table to show the percentage of each type of base in the five different organisms. ...
Homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of DNA. It is most widely used by cells to accurately repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks. Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species of bacteria and viruses.Although homologous recombination varies widely among different organisms and cell types, most forms involve the same basic steps. After a double-strand break occurs, sections of DNA around the 5' ends of the break are cut away in a process called resection. In the strand invasion step that follows, an overhanging 3' end of the broken DNA molecule then ""invades"" a similar or identical DNA molecule that is not broken. After strand invasion, the further sequence of events may follow either of two main pathways discussed below (see Models); the DSBR (double-strand break repair) pathway or the SDSA (synthesis-dependent strand annealing) pathway. Homologous recombination that occurs during DNA repair tends to result in non-crossover products, in effect restoring the damaged DNA molecule as it existed before the double-strand break.Homologous recombination is conserved across all three domains of life as well as viruses, suggesting that it is a nearly universal biological mechanism. The discovery of genes for homologous recombination in protists—a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms—has been interpreted as evidence that meiosis emerged early in the evolution of eukaryotes. Since their dysfunction has been strongly associated with increased susceptibility to several types of cancer, the proteins that facilitate homologous recombination are topics of active research. Homologous recombination is also used in gene targeting, a technique for introducing genetic changes into target organisms. For their development of this technique, Mario Capecchi, Martin Evans and Oliver Smithies were awarded the 2007 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine.