HMIVT
... chromatids. Non-sister chromatids exchange segments at cross over site. Crossing over breaks up old combinations of alleles and puts new ones together in homologous chromosomes, mixes up maternal and paternal information about traits. ...
... chromatids. Non-sister chromatids exchange segments at cross over site. Crossing over breaks up old combinations of alleles and puts new ones together in homologous chromosomes, mixes up maternal and paternal information about traits. ...
Section 10-1
... 3. Semi-conservative replication produces a new DNA molecule with one original strand and one new strand. MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. b 2. a 3. b 4. d 5. c SHORT ANSWER 1. Replication occurs simultaneously at many origins along the DNA. 2. Producing exact copies ensures that when a cell divides, the offsprin ...
... 3. Semi-conservative replication produces a new DNA molecule with one original strand and one new strand. MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. b 2. a 3. b 4. d 5. c SHORT ANSWER 1. Replication occurs simultaneously at many origins along the DNA. 2. Producing exact copies ensures that when a cell divides, the offsprin ...
Molecular Genetics Review Worksheet File
... information about the DNA structure Their experiment involved infecting bacteria with viruses. Their work showed that DNA and not proteins were the genetic material In his experiment with mice and bacteria he discovered what he described as a “transforming principle These scientists first described ...
... information about the DNA structure Their experiment involved infecting bacteria with viruses. Their work showed that DNA and not proteins were the genetic material In his experiment with mice and bacteria he discovered what he described as a “transforming principle These scientists first described ...
DNA
... Hershey and Chase tagged the DNA in a virus with a radioactive isotope, and traced it into the cell. They also tagged the protein that makes up the virus, just to make sure it was the DNA that was passing on genetic information, not the protein. ...
... Hershey and Chase tagged the DNA in a virus with a radioactive isotope, and traced it into the cell. They also tagged the protein that makes up the virus, just to make sure it was the DNA that was passing on genetic information, not the protein. ...
Biology\DNA, Mitosis, Meiosis
... (group of 2 chromosomes which means 4 sister chromatids are present) This allows for crossing-over of chromatids with genes (pieces of chromosomes) being exchanged. (more genetic variability). Sexual reproduction produces offspring unlike either parent due to new combinations of genes. ...
... (group of 2 chromosomes which means 4 sister chromatids are present) This allows for crossing-over of chromatids with genes (pieces of chromosomes) being exchanged. (more genetic variability). Sexual reproduction produces offspring unlike either parent due to new combinations of genes. ...
Name
... 4) What are the 3 common components of plasmids used in DNA cloning? 1) Origin [OriC] of replication 2) Selectable marker [I.e. Kan Resistance Gene/Amp Resistance Gene 3) Multiple Cloning Site [MCS] ...
... 4) What are the 3 common components of plasmids used in DNA cloning? 1) Origin [OriC] of replication 2) Selectable marker [I.e. Kan Resistance Gene/Amp Resistance Gene 3) Multiple Cloning Site [MCS] ...
DNA Structure and Replication
... Deciphering the Structure • Chargaff showed that equal numbers of the bases adenine and thymine were always present; and that guanine and cytosine were always present in equal numbers. • Wilkins and Franklin X rayed DNA and revealed a pattern of repeating building ...
... Deciphering the Structure • Chargaff showed that equal numbers of the bases adenine and thymine were always present; and that guanine and cytosine were always present in equal numbers. • Wilkins and Franklin X rayed DNA and revealed a pattern of repeating building ...
2_Notes_DNA Structure and Replication
... • Discovered by Watson and Crick • Double: _______ __________ ____ _____ connected by nitrogen bases (hydrogen bonds) • Helix: Nucleotides _________ together • Always an ___________ ______________ of A and T • Always an equal number of ____ and ____ Review Questions 1. What two parts of a nucleoti ...
... • Discovered by Watson and Crick • Double: _______ __________ ____ _____ connected by nitrogen bases (hydrogen bonds) • Helix: Nucleotides _________ together • Always an ___________ ______________ of A and T • Always an equal number of ____ and ____ Review Questions 1. What two parts of a nucleoti ...
Biology Name: Jacob Smith DNA: Interactive Simulation I: DNA
... ● Click on “Play Game”; Click “Next” and reading each page, continue to click next until you come to the game.; Click on organism #1 and match the base pairs as fast as you can! It is hard. ● Click “Next” and then click on each organism until you identify the one that belongs to chromosome #1; Recor ...
... ● Click on “Play Game”; Click “Next” and reading each page, continue to click next until you come to the game.; Click on organism #1 and match the base pairs as fast as you can! It is hard. ● Click “Next” and then click on each organism until you identify the one that belongs to chromosome #1; Recor ...
FREE Sample Here
... 20. You could label a different part of the DNA molecule, as suggested in question 16, and see if the density results are the same. You could repeat these tests with another species of bacteria or with cells from a eukaryotic organism to see if the results can be generalized to all cells. ...
... 20. You could label a different part of the DNA molecule, as suggested in question 16, and see if the density results are the same. You could repeat these tests with another species of bacteria or with cells from a eukaryotic organism to see if the results can be generalized to all cells. ...
You Light Up My Life
... Each old strand serves as the template for complementary new strand Figure 13.10 Page 223 ...
... Each old strand serves as the template for complementary new strand Figure 13.10 Page 223 ...
Chapter 9: DNA - Elmwood Park Memorial High School
... 1. In 1928, Frederick Griffith found that the capsule that enclosed one strain of Streptococcus pneumonia caused the microorganism’s _____________________________________. 2. Avery’s experiment demonstrated that DNA is the ___________________________ material. 3. After infecting E. coli bacter ...
... 1. In 1928, Frederick Griffith found that the capsule that enclosed one strain of Streptococcus pneumonia caused the microorganism’s _____________________________________. 2. Avery’s experiment demonstrated that DNA is the ___________________________ material. 3. After infecting E. coli bacter ...
Document
... 15. The figure below shows DNA replicating. In the space provided, describe what is occurring. ...
... 15. The figure below shows DNA replicating. In the space provided, describe what is occurring. ...
1415 Protein Synthesis Review Game
... the exact same enzyme working within their cells, then which of the following statements has to be true? A. They have at least one gene in their DNA that has the exact same sequence. ...
... the exact same enzyme working within their cells, then which of the following statements has to be true? A. They have at least one gene in their DNA that has the exact same sequence. ...
(KEY).
... 6. Create a template strand of 5 codons. Next replicate them to make a new strand. Be sure to follow the proper DNA-DNA “base pair rules”. Template strand: AAA TTT GGG CCC ACT New strand: TTT AAA CCC GGG TGA DNA VS. RNA 7. Describe the differences and characteristics of DNA vs. RNA using the table b ...
... 6. Create a template strand of 5 codons. Next replicate them to make a new strand. Be sure to follow the proper DNA-DNA “base pair rules”. Template strand: AAA TTT GGG CCC ACT New strand: TTT AAA CCC GGG TGA DNA VS. RNA 7. Describe the differences and characteristics of DNA vs. RNA using the table b ...
DNA discovery and Structure PowerPoint
... • Proteins make up the structures of cells. • Proteins, in the form of enzymes, also control all cell processes. • DNA carries the instructions from mother to daughter cells, from parents to children. Therefore it is the molecule of heredity. ...
... • Proteins make up the structures of cells. • Proteins, in the form of enzymes, also control all cell processes. • DNA carries the instructions from mother to daughter cells, from parents to children. Therefore it is the molecule of heredity. ...
DNA Slides - U3A in Kennet
... BUT ALSO ¬ In parasitic association with organisms they become pathogens and are implicated in most diseses and causes of death ...
... BUT ALSO ¬ In parasitic association with organisms they become pathogens and are implicated in most diseses and causes of death ...
Document
... a. harmless bacteria into disease-causing bacteria. b. disease-causing bacteria into harmless bacteria. c. heat-killed S bacteria into R bacteria. d. S bacteria into heat-killed R bacteria. _____ 2. In 1952, Hershey and Chase used a bacteriophage to determine that genetic material is made of which o ...
... a. harmless bacteria into disease-causing bacteria. b. disease-causing bacteria into harmless bacteria. c. heat-killed S bacteria into R bacteria. d. S bacteria into heat-killed R bacteria. _____ 2. In 1952, Hershey and Chase used a bacteriophage to determine that genetic material is made of which o ...
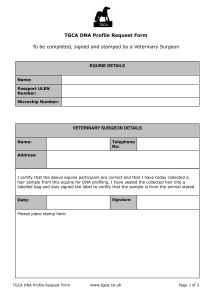
DNA Collection Veterinary Form10 December
... Upon completion the DNA profile results will be uploaded to the TGCA database. If you make a specific request then the TGCA will email you with a copy of the results. Please note that it may take up to three weeks for the laboratory to return your results to the TGCA. ...
... Upon completion the DNA profile results will be uploaded to the TGCA database. If you make a specific request then the TGCA will email you with a copy of the results. Please note that it may take up to three weeks for the laboratory to return your results to the TGCA. ...
PDF
... previously identified. The authors showed that one such protein, Spo11p, which in other species cleaves doublestranded DNA as a prelude to meiotic recombination, was expressed in mitotically growing C. albicans. When the researchers deleted the gene, tetraploid cells could still reduce their chromos ...
... previously identified. The authors showed that one such protein, Spo11p, which in other species cleaves doublestranded DNA as a prelude to meiotic recombination, was expressed in mitotically growing C. albicans. When the researchers deleted the gene, tetraploid cells could still reduce their chromos ...
Nucleotides and DNA Structure
... binding to the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA. A) lysine and alanine B) lysine and arginine C) leucine and alanine D) leucine and arginine Which does not apply to most bacterial DNA? A) Circular. B) Relaxed. C) Not packed into nucleosomes. D) Supercoiled. Which best describes the structure of a nuc ...
... binding to the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA. A) lysine and alanine B) lysine and arginine C) leucine and alanine D) leucine and arginine Which does not apply to most bacterial DNA? A) Circular. B) Relaxed. C) Not packed into nucleosomes. D) Supercoiled. Which best describes the structure of a nuc ...
chapter 10 bio analysis
... 3. What is the name given to the point where replication starts on a DNA molecule? The Replication Fork is the point at which two chains of DNA start to separate. 4. How does the replicated model of DNA compare to the original model of DNA? The second part of the DNA is the complete opposite of the ...
... 3. What is the name given to the point where replication starts on a DNA molecule? The Replication Fork is the point at which two chains of DNA start to separate. 4. How does the replicated model of DNA compare to the original model of DNA? The second part of the DNA is the complete opposite of the ...
Science 9
... on the RNA and puts the small components of proteins, called amino acids, in the right order to make the __protein__ . 15. Proteins are very, very important and have many functions. Complete the table below. WARNING: These are NOT in order! ...
... on the RNA and puts the small components of proteins, called amino acids, in the right order to make the __protein__ . 15. Proteins are very, very important and have many functions. Complete the table below. WARNING: These are NOT in order! ...
What unique chromosomal events lead to the formation of a haploid
... subject to endogenous double-strand DNA breaks, mediated by the SPO11 enzyme, that initiate the molecular events of meiotic recombination. Also during the leptotene phase, homologous chromosomes find each other by homology searching mechanisms that are not well understood, but may be facilitated by ...
... subject to endogenous double-strand DNA breaks, mediated by the SPO11 enzyme, that initiate the molecular events of meiotic recombination. Also during the leptotene phase, homologous chromosomes find each other by homology searching mechanisms that are not well understood, but may be facilitated by ...
Homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of DNA. It is most widely used by cells to accurately repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks. Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species of bacteria and viruses.Although homologous recombination varies widely among different organisms and cell types, most forms involve the same basic steps. After a double-strand break occurs, sections of DNA around the 5' ends of the break are cut away in a process called resection. In the strand invasion step that follows, an overhanging 3' end of the broken DNA molecule then ""invades"" a similar or identical DNA molecule that is not broken. After strand invasion, the further sequence of events may follow either of two main pathways discussed below (see Models); the DSBR (double-strand break repair) pathway or the SDSA (synthesis-dependent strand annealing) pathway. Homologous recombination that occurs during DNA repair tends to result in non-crossover products, in effect restoring the damaged DNA molecule as it existed before the double-strand break.Homologous recombination is conserved across all three domains of life as well as viruses, suggesting that it is a nearly universal biological mechanism. The discovery of genes for homologous recombination in protists—a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms—has been interpreted as evidence that meiosis emerged early in the evolution of eukaryotes. Since their dysfunction has been strongly associated with increased susceptibility to several types of cancer, the proteins that facilitate homologous recombination are topics of active research. Homologous recombination is also used in gene targeting, a technique for introducing genetic changes into target organisms. For their development of this technique, Mario Capecchi, Martin Evans and Oliver Smithies were awarded the 2007 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine.