Slide 1
... Any two unrelated individuals differ by one base pair every 1,000 or so, referred to as SNPs. Many SNPs have no effect on cell function and therefore can be used as molecular markers. ...
... Any two unrelated individuals differ by one base pair every 1,000 or so, referred to as SNPs. Many SNPs have no effect on cell function and therefore can be used as molecular markers. ...
Analysis of genes using RT-PCR
... Transcriptase enzyme binds to the double stranded DNA, separates strands and the DNA 'eye' opens. ...
... Transcriptase enzyme binds to the double stranded DNA, separates strands and the DNA 'eye' opens. ...
Crash Course Biology Notes on: DNA Structure and Replication
... 21. What links the two chains of DNA together? What type of bond do they have? 22. Can any pair of nitrogenous bases be linked? 23. What bases can be linked together? 24. What do we call bonded nitrogenous bases? 25. Which pairing is stronger and why? 26. What allows DNA to create you or any other o ...
... 21. What links the two chains of DNA together? What type of bond do they have? 22. Can any pair of nitrogenous bases be linked? 23. What bases can be linked together? 24. What do we call bonded nitrogenous bases? 25. Which pairing is stronger and why? 26. What allows DNA to create you or any other o ...
Transcription
... 1. Instead of copy the whole DNA strand, only a selected gene within the DNA is copied. 2. Instead of DNA polymerase attaching free nucleotides, it is RNA polymerase. 3. At the end of transcription there is a single, free strand of RNA nucleotides, not a double ...
... 1. Instead of copy the whole DNA strand, only a selected gene within the DNA is copied. 2. Instead of DNA polymerase attaching free nucleotides, it is RNA polymerase. 3. At the end of transcription there is a single, free strand of RNA nucleotides, not a double ...
Human Mitochondrial DNA
... • Transformation – the uptake and expression of foreign DNA by a cell • Transduction – the use of viruses to transform or genetically engineer cells • Competent/competency – the ability of cells to take up DNA • Selection – the process of screening potential clones for the expression of a particular ...
... • Transformation – the uptake and expression of foreign DNA by a cell • Transduction – the use of viruses to transform or genetically engineer cells • Competent/competency – the ability of cells to take up DNA • Selection – the process of screening potential clones for the expression of a particular ...
Biotechnology
... 2. A DNA fingerprint is produced using a gel electrophoresis. A gel electrophoresis is a tool that separates pieces of DNA based on size (the number of base pairs in each piece). ...
... 2. A DNA fingerprint is produced using a gel electrophoresis. A gel electrophoresis is a tool that separates pieces of DNA based on size (the number of base pairs in each piece). ...
b8 nucleic acids
... [Nucleic acids are polymers made up of nucleotides. A nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a pentose sugar and an organic nitrogenous base. Students should recognize, but do not need to recall, the structures of the five bases: adenine(A), cytosine(C), guanine(G), thymine(T) and uracil (U). Nuclei ...
... [Nucleic acids are polymers made up of nucleotides. A nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a pentose sugar and an organic nitrogenous base. Students should recognize, but do not need to recall, the structures of the five bases: adenine(A), cytosine(C), guanine(G), thymine(T) and uracil (U). Nuclei ...
Slide 1
... • A prokaryotic chromosome is typically a circular chain of DNA – Prokaryotic cells also often have smaller circles of DNA called plasmids E. coli bacteria cell ...
... • A prokaryotic chromosome is typically a circular chain of DNA – Prokaryotic cells also often have smaller circles of DNA called plasmids E. coli bacteria cell ...
DNA barcoding and DNA taxonomy
... rearrangements and nucleotide substitutions (Pons et al. submitted). Most of the major species-specific satellites of Pimelia species can be, in some cases, found in low copy number in other Pimelia taxa as predicted in the library hypothesis (Salser et al., 1977, Mestrovic et al., 1998). Low copy n ...
... rearrangements and nucleotide substitutions (Pons et al. submitted). Most of the major species-specific satellites of Pimelia species can be, in some cases, found in low copy number in other Pimelia taxa as predicted in the library hypothesis (Salser et al., 1977, Mestrovic et al., 1998). Low copy n ...
Nucleic Acids PP
... RNA Structure • Because RNA molecules are single stranded, they can have a great variety of shapes and structures. • These shapes are formed by the single stranded molecule hydrogen bonding to itself in different ways ...
... RNA Structure • Because RNA molecules are single stranded, they can have a great variety of shapes and structures. • These shapes are formed by the single stranded molecule hydrogen bonding to itself in different ways ...
basic genetics for the clinical neurologist
... with the same genetic disease can be clinically affected to dramatically different extents, a phenomenon known as variability of expression. Penetrance refers to the fact that not all individuals who inherit the mutant gene develop the clinical phenotype. This is often age related. In autosomal domi ...
... with the same genetic disease can be clinically affected to dramatically different extents, a phenomenon known as variability of expression. Penetrance refers to the fact that not all individuals who inherit the mutant gene develop the clinical phenotype. This is often age related. In autosomal domi ...
Biotechnology Labs Makeup Assignment
... 2) Write a one page paper (one page per lab you’re making up) describing the following: DNA Extraction Only: -describe the technique used to purify and extract DNA from cells. What reagents (i.e. chemicals) are needed and what is the function of each reagent? (1 page) Dye/Indicator Lab Only: -how do ...
... 2) Write a one page paper (one page per lab you’re making up) describing the following: DNA Extraction Only: -describe the technique used to purify and extract DNA from cells. What reagents (i.e. chemicals) are needed and what is the function of each reagent? (1 page) Dye/Indicator Lab Only: -how do ...
BioE/MCB/PMB C146/246, Spring 2005 Problem Set 1
... to think that the similarity is due to convergent evolution rather than shared ancestry. Statistical tests are necessary to determine if the similarity is more or less than expected. Note that Fitch’s method relies on being able to group the sequences into subsets based on known homology. The metho ...
... to think that the similarity is due to convergent evolution rather than shared ancestry. Statistical tests are necessary to determine if the similarity is more or less than expected. Note that Fitch’s method relies on being able to group the sequences into subsets based on known homology. The metho ...
Honors DNA Review What are bacteriophages? Virus that infects
... DNA (Hershey and Chase experiment: This is why we knew that DNA was the hereditary material) 4. What part of T2 is not injected into the bacterium? protein 5. What happens to the cell at the end of a phage reproductive cycle? Lyses (burst) and the new viruses are released to infect other cells 6. Wh ...
... DNA (Hershey and Chase experiment: This is why we knew that DNA was the hereditary material) 4. What part of T2 is not injected into the bacterium? protein 5. What happens to the cell at the end of a phage reproductive cycle? Lyses (burst) and the new viruses are released to infect other cells 6. Wh ...
Document
... a timer so that they are on during the day and turn off at night, mimicking the conditions in the field. ...
... a timer so that they are on during the day and turn off at night, mimicking the conditions in the field. ...
Chpt. 10- Molecular Biology of the Gene - TJ
... DNA 2. What are the differences? a. Instead of the sugar deoxyribose, RNA has the sugar ribose b. The base thymine is replaced with the base uracil (U) 1. DNA A T C G T G T RNA A U C G U G U III. The importance of nucleotide sequences A. An elm, an elk, and an eel 1. All different organisms with t ...
... DNA 2. What are the differences? a. Instead of the sugar deoxyribose, RNA has the sugar ribose b. The base thymine is replaced with the base uracil (U) 1. DNA A T C G T G T RNA A U C G U G U III. The importance of nucleotide sequences A. An elm, an elk, and an eel 1. All different organisms with t ...
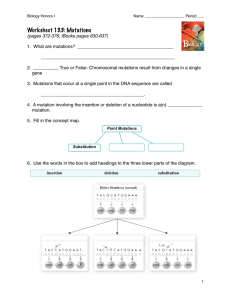
Worksheet 13.3
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
Name AP EXAM REVIEW SESSION II ASSESSMENT QUIZ Use the
... d. Sample 2 was cut at more restriction sites than was sample 4. e. Sample 4 was cut at more restriction sites than was sample 2. 6. Once a plasmid has incorporated specific genes, such as the gene coding for ampicillin resistance, the plasmid may be cloned by a. inserting it into a virus to generat ...
... d. Sample 2 was cut at more restriction sites than was sample 4. e. Sample 4 was cut at more restriction sites than was sample 2. 6. Once a plasmid has incorporated specific genes, such as the gene coding for ampicillin resistance, the plasmid may be cloned by a. inserting it into a virus to generat ...
Study Guide for the Genetics: Structure of DNA, Replication
... you did for homework. (The answer key is online.) ...
... you did for homework. (The answer key is online.) ...
Document
... Tri- and tetranucleotide repeats are gradually replacing dinucleotide repeats as the markers of choice because they give cleaner results dinucleotide repeat sequences are peculiarly prone to replication slippage during PCR amplification. Much effort has been devoted to producing compatible sets of m ...
... Tri- and tetranucleotide repeats are gradually replacing dinucleotide repeats as the markers of choice because they give cleaner results dinucleotide repeat sequences are peculiarly prone to replication slippage during PCR amplification. Much effort has been devoted to producing compatible sets of m ...
DNA PowerPoint Slides
... Using the genetic code, RNA strands are translated to specific sequences of amino acids which are the building blocks of proteins. These RNA strands are created using DNA strands as the template (a process called “transcription”) ...
... Using the genetic code, RNA strands are translated to specific sequences of amino acids which are the building blocks of proteins. These RNA strands are created using DNA strands as the template (a process called “transcription”) ...
DNA Replication and Repair
... To keep it apart, single-stranded binding proteins (SSBP) bind to the strands to prevent base pairs from re-annealing (pairing of complimentary strands of DNA through hydrogen bonding) DNA gyrase relieves tension from unwinding When an enzyme reaches a point of untwisted, singlestranded DNA, we call ...
... To keep it apart, single-stranded binding proteins (SSBP) bind to the strands to prevent base pairs from re-annealing (pairing of complimentary strands of DNA through hydrogen bonding) DNA gyrase relieves tension from unwinding When an enzyme reaches a point of untwisted, singlestranded DNA, we call ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis Review Questions
... 7. What is the shape of DNA called? 8. When DNA unzips, what bonds are being broken? 9. What is the end product of DNA replication? 10. After the DNA is unzipped, how does the DNA form two new strands? 11. DNA contains the instructions on how to make __________ 12. A section of DNA that codes for a ...
... 7. What is the shape of DNA called? 8. When DNA unzips, what bonds are being broken? 9. What is the end product of DNA replication? 10. After the DNA is unzipped, how does the DNA form two new strands? 11. DNA contains the instructions on how to make __________ 12. A section of DNA that codes for a ...
chapter 14 15 16 study guide
... trisomy 21 (down’s syndrome) occurs when a cell gets an extra copy of cs 21; mental retardation; only autosomal nondisjunction that can survive past a few months Turner’s syndrome: only known viable monosomy that can survive in humans; XO genotype (nondisjunction of the sex cs); female, sterile, sho ...
... trisomy 21 (down’s syndrome) occurs when a cell gets an extra copy of cs 21; mental retardation; only autosomal nondisjunction that can survive past a few months Turner’s syndrome: only known viable monosomy that can survive in humans; XO genotype (nondisjunction of the sex cs); female, sterile, sho ...
Microsatellite

A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from 2–5 base pairs) are repeated, typically 5-50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations in the human genome and they are notable for their high mutation rate and high diversity in the population. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name ""satellite"" refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying ""satellite"" layers of repetitive DNA. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.They are widely used for DNA profiling in kinship analysis and in forensic identification. They are also used in genetic linkage analysis/marker assisted selection to locate a gene or a mutation responsible for a given trait or disease.