RNA
... The Genetic Code Is Nearly Universal • The codon usage is almost invariant throughout the evolution. • Translation of mRNAs from foreign species is usually successful. • BUT, codon preference differs quite a bit between organisms. ...
... The Genetic Code Is Nearly Universal • The codon usage is almost invariant throughout the evolution. • Translation of mRNAs from foreign species is usually successful. • BUT, codon preference differs quite a bit between organisms. ...
Designing Molecular Machines·
... with each other in a very specific way-a secret handshake, if you will, that allows each letter to recognize its partner. To carry the anatomical analogy further, this handshake is a very specific interaction-we don't shake shoulders-and it's strong enough that, if I have you by the hand, I could pu ...
... with each other in a very specific way-a secret handshake, if you will, that allows each letter to recognize its partner. To carry the anatomical analogy further, this handshake is a very specific interaction-we don't shake shoulders-and it's strong enough that, if I have you by the hand, I could pu ...
DNA Replication - cloudfront.net
... from the last section of Lagging strand • DNA polymerase cannot seal the gap • The end of the parental strand is not replicated • These non coding DNA sequences called telomeres • As a result part of telomere is removed in every subsequent replication • Enzymes like nucleases fix the possible errors ...
... from the last section of Lagging strand • DNA polymerase cannot seal the gap • The end of the parental strand is not replicated • These non coding DNA sequences called telomeres • As a result part of telomere is removed in every subsequent replication • Enzymes like nucleases fix the possible errors ...
What is DNA sequencing
... Steps for Manual Sequencing using ddNTPs (Sanger's method): 1) Anneal primer to ssDNA template, (use high temp. or NaOH to denature template DNA) 2) separate into four different tubes "A", "G", "C", "T", each having all four dNTPs (standard deoxy) and ONE of the four dideoxy (ddNTP). for example, tu ...
... Steps for Manual Sequencing using ddNTPs (Sanger's method): 1) Anneal primer to ssDNA template, (use high temp. or NaOH to denature template DNA) 2) separate into four different tubes "A", "G", "C", "T", each having all four dNTPs (standard deoxy) and ONE of the four dideoxy (ddNTP). for example, tu ...
DNA_to_Proteins.ver6 - RI
... Can mutations be good? Think about it from an evolutionary point of view. What role can mutations play in adaptations? Why do some mutations result in small changes? Large changes? No changes? Why can a substitution mutation be considered silent? How could environmental factors affect altera ...
... Can mutations be good? Think about it from an evolutionary point of view. What role can mutations play in adaptations? Why do some mutations result in small changes? Large changes? No changes? Why can a substitution mutation be considered silent? How could environmental factors affect altera ...
DNA extraction from cheek cells protocol I mailed to you
... 6. Complete the following sentences to describe the structure of DNA. In the backbone of each strand in the DNA double helix molecule, the sugar of one nucleotide is bonded to the __________________ in the next nucleotide. The ________________ of the nucleotides in each strand of DNA extend toward e ...
... 6. Complete the following sentences to describe the structure of DNA. In the backbone of each strand in the DNA double helix molecule, the sugar of one nucleotide is bonded to the __________________ in the next nucleotide. The ________________ of the nucleotides in each strand of DNA extend toward e ...
DNA - Gene - Website Staff UI
... Is the heritable changes in the genetic material. The term mutation refers to (1) change in the genetic material, (2) the process by which the change occurs. Mutation provides the raw material for evolution. Without mutation, all of genes would exist in only one form and alleles would not exis. Orga ...
... Is the heritable changes in the genetic material. The term mutation refers to (1) change in the genetic material, (2) the process by which the change occurs. Mutation provides the raw material for evolution. Without mutation, all of genes would exist in only one form and alleles would not exis. Orga ...
Fall06MicrobGenetExamI
... Luria and Delbrück were trying to come up with an experiment to differentiate between the random-mutation hypothesis and the directed-change hypothesis in bacteria. In the experiment they came up with, they utilized the generation of resistance in E.coli to infection by phage T1 as their assay. The ...
... Luria and Delbrück were trying to come up with an experiment to differentiate between the random-mutation hypothesis and the directed-change hypothesis in bacteria. In the experiment they came up with, they utilized the generation of resistance in E.coli to infection by phage T1 as their assay. The ...
DNA
... controls all the activities of the cell including cell reproduction, and heredity. How does it do this? The nucleus controls these activities by the chromosomes. Chromosomes are microscopic, threadlike strands composed of the chemical DNA (short for deoxyribonucleic acid). In simple terms, DNA contr ...
... controls all the activities of the cell including cell reproduction, and heredity. How does it do this? The nucleus controls these activities by the chromosomes. Chromosomes are microscopic, threadlike strands composed of the chemical DNA (short for deoxyribonucleic acid). In simple terms, DNA contr ...
Biology 202
... the bases are adenine. What are the percentages of thymine, cytosine and guanine? 1 pt ...
... the bases are adenine. What are the percentages of thymine, cytosine and guanine? 1 pt ...
8-DNA
... 21. The relationship between the sequences of bases in DNA and amino acids in protein would be best stated as: A. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA is determined by the amino acid sequence of DNA polymerase. B. The sequence of nucleotides in a DNA is determined by the amino acids in proteins. C. Th ...
... 21. The relationship between the sequences of bases in DNA and amino acids in protein would be best stated as: A. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA is determined by the amino acid sequence of DNA polymerase. B. The sequence of nucleotides in a DNA is determined by the amino acids in proteins. C. Th ...
Lecture 1 09-23-2016
... VNTR = Variable number of tandem repeats Tandem = In a line AGGCTAGGCTAGGCTA GGCT Multiple repeats of same sequence; number of repeats is variable = allele! ...
... VNTR = Variable number of tandem repeats Tandem = In a line AGGCTAGGCTAGGCTA GGCT Multiple repeats of same sequence; number of repeats is variable = allele! ...
GEP Implementation * First Year
... Pick one of the two genes in the contig and compare the gene structure of the query BLASTX track and the reference D. melanogaster annotation ...
... Pick one of the two genes in the contig and compare the gene structure of the query BLASTX track and the reference D. melanogaster annotation ...
DNA Function in Heredity Chapter 11
... – primers are already there – dNTPs are already there – DNA polymerase is already there – get - four copies of DNA between primers – …8 copies, 16 copies, 32 copies… – >1 million/20 cycles; >1 billion/30 cycles ...
... – primers are already there – dNTPs are already there – DNA polymerase is already there – get - four copies of DNA between primers – …8 copies, 16 copies, 32 copies… – >1 million/20 cycles; >1 billion/30 cycles ...
ch10 GN
... • RNA ______________________________attaches to a special place (certain base sequence called ____________________________) on the DNA molecule and moves along the strand, unwinding and separating the strands. • The RNA polymerase then begins reading and copying the DNA as it goes along. “zips up” a ...
... • RNA ______________________________attaches to a special place (certain base sequence called ____________________________) on the DNA molecule and moves along the strand, unwinding and separating the strands. • The RNA polymerase then begins reading and copying the DNA as it goes along. “zips up” a ...
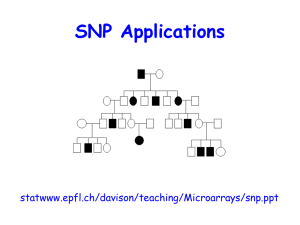
SNP Applications
... • Immediate goals: – Detection/identification of … – The hundreds of thousands of SNPs estimated to be present in the human genome – Interest also in other organisms, e.g. potatoes(!) – Establishment of SNP Database(s) ...
... • Immediate goals: – Detection/identification of … – The hundreds of thousands of SNPs estimated to be present in the human genome – Interest also in other organisms, e.g. potatoes(!) – Establishment of SNP Database(s) ...
Detection of Large Expansions in SCA8 Using a Fluorescent Repeat
... We detected more than 73 repeats that covered a repeat range from 80 to 250, which is most often associated with ataxia. We therefore consider this method to be useful for detecting the presence of a pathogenic (CTG)n trinucleotide repeat expansion, especially for the screening of a large population ...
... We detected more than 73 repeats that covered a repeat range from 80 to 250, which is most often associated with ataxia. We therefore consider this method to be useful for detecting the presence of a pathogenic (CTG)n trinucleotide repeat expansion, especially for the screening of a large population ...
Review Sheet : DNA, RNA & Protein Synthesis
... Refer to the illustration. Suppose that you are given a protein containing the following sequence of amino acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic code given to determine which of the following contains a DNA sequence that codes for this amin ...
... Refer to the illustration. Suppose that you are given a protein containing the following sequence of amino acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic code given to determine which of the following contains a DNA sequence that codes for this amin ...
gene expression_hour 1 - study
... DNA Replication Model… DNA Replication Process of copying a double stranded DNA strand which is the two resulting double strands are identical and each of them consist of one original and one newly synthesize strand. ...
... DNA Replication Model… DNA Replication Process of copying a double stranded DNA strand which is the two resulting double strands are identical and each of them consist of one original and one newly synthesize strand. ...
Chapter 20 - Biotechnology
... – One challenge is the sheer number of proteins in humans and our close relatives because of alternative RNA splicing and post-translational modifications. – Collecting all the proteins will be difficult because a cell’s proteins differ with cell type and its state. – In addition, unlike DNA, protei ...
... – One challenge is the sheer number of proteins in humans and our close relatives because of alternative RNA splicing and post-translational modifications. – Collecting all the proteins will be difficult because a cell’s proteins differ with cell type and its state. – In addition, unlike DNA, protei ...
MCB 142 second midterm: Molecular Genetics
... strands of DNA is shown, but not the helical structure.) If the Holliday junctions are resolved by cutting the strands as shown by the thick black bars, will the result be crossing over or gene conversion? For full credit, explain your logic. For convenience, the rest of the maternal chromosome is s ...
... strands of DNA is shown, but not the helical structure.) If the Holliday junctions are resolved by cutting the strands as shown by the thick black bars, will the result be crossing over or gene conversion? For full credit, explain your logic. For convenience, the rest of the maternal chromosome is s ...
DNA notes 2015 - OG
... - DNA makes a copy of itself - Important during meiosis & mitosis – DNA gets passed on to daughter cells • DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the parent strands and checks the strand for errors • Each double helix now has 1 old strand & 1 new strand •This is called SEMI-CONSERVATIVE • If the origina ...
... - DNA makes a copy of itself - Important during meiosis & mitosis – DNA gets passed on to daughter cells • DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the parent strands and checks the strand for errors • Each double helix now has 1 old strand & 1 new strand •This is called SEMI-CONSERVATIVE • If the origina ...
DNA, the Genetic Material
... 3. a nitrogen-containing base. The only difference between each nucleotide is the identity of the base. There are only four possible bases that make up each DNA nucleotide: adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T), and cytosine (C). ...
... 3. a nitrogen-containing base. The only difference between each nucleotide is the identity of the base. There are only four possible bases that make up each DNA nucleotide: adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T), and cytosine (C). ...
Plasmid w/ kanamycin resistance (pKAN)
... – Plasmid fragments are loaded into a gel – Connected to a power supply ...
... – Plasmid fragments are loaded into a gel – Connected to a power supply ...
Microsatellite

A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from 2–5 base pairs) are repeated, typically 5-50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations in the human genome and they are notable for their high mutation rate and high diversity in the population. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name ""satellite"" refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying ""satellite"" layers of repetitive DNA. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.They are widely used for DNA profiling in kinship analysis and in forensic identification. They are also used in genetic linkage analysis/marker assisted selection to locate a gene or a mutation responsible for a given trait or disease.