AP BIOLOGY - Bremen High School District 228
... Helicases separate the two strands of the double helix, and DNA polymerases then construct two new strands using each of the original strands as templates. Ligase assembles single-stranded codons, then polymerase knits these codons together into a DNA strand. The two strands of DNA separate, and res ...
... Helicases separate the two strands of the double helix, and DNA polymerases then construct two new strands using each of the original strands as templates. Ligase assembles single-stranded codons, then polymerase knits these codons together into a DNA strand. The two strands of DNA separate, and res ...
Individual nucleosomes are released by digestion of chromatin with
... • Nucleosomes may form at specific positions as the result either of the local structure of DNA or of proteins that interact with specific sequences. • The most common cause of nucleosome positioning is the binding of proteins to DNA to establish a boundary. • Nucleosome positioning describes the pl ...
... • Nucleosomes may form at specific positions as the result either of the local structure of DNA or of proteins that interact with specific sequences. • The most common cause of nucleosome positioning is the binding of proteins to DNA to establish a boundary. • Nucleosome positioning describes the pl ...
Document
... • In 1928, Griffith was a British microbiologist who was studying the bacterium that causes pneumonia ...
... • In 1928, Griffith was a British microbiologist who was studying the bacterium that causes pneumonia ...
The effect of DNA phase structure on DNA walks
... obvious that these walks do not distinguish between coding and non-coding strands. Both strands have exactly the same composition and the results don’t depend on the direction of the walk. Nevertheless, it was observed in several genomes that coding regions have higher (G + C)/(A + T ) ratio than th ...
... obvious that these walks do not distinguish between coding and non-coding strands. Both strands have exactly the same composition and the results don’t depend on the direction of the walk. Nevertheless, it was observed in several genomes that coding regions have higher (G + C)/(A + T ) ratio than th ...
Making the connection: DNA to Protein Engagement Exploration
... • Students will link the function of the protein to the amino acid sequence. • Student will look indepth at a specific genetic disorder to determine the (symptoms, possible treatments, nucleotide and corresponding amino acid sequences, associations, etc.) Concept(s) learned in this module: • Genetic ...
... • Students will link the function of the protein to the amino acid sequence. • Student will look indepth at a specific genetic disorder to determine the (symptoms, possible treatments, nucleotide and corresponding amino acid sequences, associations, etc.) Concept(s) learned in this module: • Genetic ...
Unit 2 Review (B5-B8)
... of radioactivity? Explain. DNA would not be radioactive because DNA is not make with uracil ...
... of radioactivity? Explain. DNA would not be radioactive because DNA is not make with uracil ...
Disclaimer:
... were only 20 amino acids to code for each amino acid, that would lead to 44 stop codons – if a mistake was made, the degenerate code allows for the chance that the mistake would still lead to the same amino acid (or maybe even a different one). However, without a degenerate code, a mistake would mos ...
... were only 20 amino acids to code for each amino acid, that would lead to 44 stop codons – if a mistake was made, the degenerate code allows for the chance that the mistake would still lead to the same amino acid (or maybe even a different one). However, without a degenerate code, a mistake would mos ...
Significance of multiple mutations in cancer
... extensive heterogeneity of cancer cells within each tumor. In addition, tumors invariably develop resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. Each of the tumor phenotypes involves, or can be mimicked by, specific mutations introduced in critical genes. These mutations either arise from copying unrepaired ...
... extensive heterogeneity of cancer cells within each tumor. In addition, tumors invariably develop resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. Each of the tumor phenotypes involves, or can be mimicked by, specific mutations introduced in critical genes. These mutations either arise from copying unrepaired ...
Cats and You: DNA Doubles?
... Deriving meaningful knowledge from the DNA sequence will define research through the coming decades to inform our understanding of biological systems. This enormous task will require the expertise and creativity of tens of thousands of scientists from varied disciplines in both the public and privat ...
... Deriving meaningful knowledge from the DNA sequence will define research through the coming decades to inform our understanding of biological systems. This enormous task will require the expertise and creativity of tens of thousands of scientists from varied disciplines in both the public and privat ...
Proceedings - Applied Reproductive Strategies in Beef Cattle
... Animal Science Department South Dakota State University Introduction Genetic selection tools have advanced substantially during the last decade. Ten years ago, DNA testing was not widely available. Today, several breed associations have started incorporating genomic information into their EPDs. Nume ...
... Animal Science Department South Dakota State University Introduction Genetic selection tools have advanced substantially during the last decade. Ten years ago, DNA testing was not widely available. Today, several breed associations have started incorporating genomic information into their EPDs. Nume ...
Standard Mutation Nomenclature in Molecular Diagnostics
... As shown in Table 1, genetic sequence changes occur at the DNA level, and we usually identify mutations at the DNA level in a clinical genetic testing. Descriptions at the amino acid level are usually inferred with no experimental proof and are not unequivocal because amino acid codes are degenerate ...
... As shown in Table 1, genetic sequence changes occur at the DNA level, and we usually identify mutations at the DNA level in a clinical genetic testing. Descriptions at the amino acid level are usually inferred with no experimental proof and are not unequivocal because amino acid codes are degenerate ...
Practice test 2
... 3. The DNA fragment is recombined into a vector. 4. The DNA fragment to be inserted is isolated. a. 1, 2, 3, 4 c. 2, 4, 3, 1 b. 2, 3, 1, 4 d. 4, 1, 2, 3 10. The process used to separate DNA segments of different lengths is _____. a. PCR c. gene amplification b. gel electrophoresis d. all of these 11 ...
... 3. The DNA fragment is recombined into a vector. 4. The DNA fragment to be inserted is isolated. a. 1, 2, 3, 4 c. 2, 4, 3, 1 b. 2, 3, 1, 4 d. 4, 1, 2, 3 10. The process used to separate DNA segments of different lengths is _____. a. PCR c. gene amplification b. gel electrophoresis d. all of these 11 ...
ppt
... DNA which will give rise to a mature messenger RNA that will be translated into the specific amino acids of the protein product ...
... DNA which will give rise to a mature messenger RNA that will be translated into the specific amino acids of the protein product ...
12.2 Powerpoint
... Concluded that when the S cells were killed, DNA was released R bacteria incorporated this DNA into their cells and changed into S cells. Many people did not believe that it was DNA, not protein that transformed genes ...
... Concluded that when the S cells were killed, DNA was released R bacteria incorporated this DNA into their cells and changed into S cells. Many people did not believe that it was DNA, not protein that transformed genes ...
Overcoming constraints of genomic DNA isolated from
... Abstract: The worldwide archives of paraffin-embedded tissue represent a valuable and extensive source of material for biomedical research, including molecular analysis of genomes and transcriptomes. However, the fixation and embedding procedures affect the integrity of genomic DNA. The challenge is ...
... Abstract: The worldwide archives of paraffin-embedded tissue represent a valuable and extensive source of material for biomedical research, including molecular analysis of genomes and transcriptomes. However, the fixation and embedding procedures affect the integrity of genomic DNA. The challenge is ...
Diapositiva 1 - Curso de Sistemática IB 2010
... If most DNA changes were due to adaptive evolution than one would imagine that most changes would occur in the first and ...
... If most DNA changes were due to adaptive evolution than one would imagine that most changes would occur in the first and ...
(DNA).
... enzymes and binding proteins. A growing body of evidence indicates that these enzymes assemble their products in “factories” through which the DNA moves. Such factories may be bound to membranes in bacteria. In higher organisms, the replication factories are not permanent ...
... enzymes and binding proteins. A growing body of evidence indicates that these enzymes assemble their products in “factories” through which the DNA moves. Such factories may be bound to membranes in bacteria. In higher organisms, the replication factories are not permanent ...
Genetic mapping of Theobroma cacao (Malvaceae - Funpec-RP
... alleles, probably deriving from specific individual mutations that are characterized by nonpigmentation of the leaves (Bartley, 2005). A similar effect was observed in F2 progenies, resulting from self-fertilization of F1 plants from Pa 121 x SIC 802 and Pa 121 x Pa 169 (Yamada et al., 1982). One fo ...
... alleles, probably deriving from specific individual mutations that are characterized by nonpigmentation of the leaves (Bartley, 2005). A similar effect was observed in F2 progenies, resulting from self-fertilization of F1 plants from Pa 121 x SIC 802 and Pa 121 x Pa 169 (Yamada et al., 1982). One fo ...
Activity 19.4, DNA Sequencing
... “DNA Sequencing is a laboratory method of determining the nucleotide sequence of a DNA fragment. The most popular method, sometimes called dideoxysequencing, was worked out by Frederick Sanger in 1974, and so is also called Sanger sequencing. The method utilizes DNA polymerase in vitro to perform a ...
... “DNA Sequencing is a laboratory method of determining the nucleotide sequence of a DNA fragment. The most popular method, sometimes called dideoxysequencing, was worked out by Frederick Sanger in 1974, and so is also called Sanger sequencing. The method utilizes DNA polymerase in vitro to perform a ...
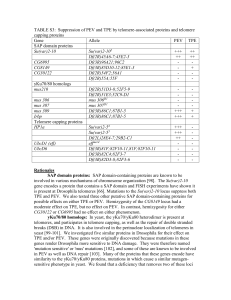
TABLE S3: Suppression of PEV and TPE by telomere
... genes render Drosophila more sensitive to DNA damage. They were therefore named 'mutation sensitive' or 'mus' mutations [102], and some of these are known to be involved in PEV as well as DNA repair [103]. Many of the proteins that these genes encode have similarity to the yKu70/yKu80 proteins, muta ...
... genes render Drosophila more sensitive to DNA damage. They were therefore named 'mutation sensitive' or 'mus' mutations [102], and some of these are known to be involved in PEV as well as DNA repair [103]. Many of the proteins that these genes encode have similarity to the yKu70/yKu80 proteins, muta ...
power pack 5 dna replication
... 10. In proof reading during DNA replication a. wrong nucleotides are inserted b. wrong nucleotides are taken out c. wrong nucleotides are removed and correct ones are inserted d. mutations are prevented 11. E.coli fully labeled with N15 is allowed to grow in N14 medium. The two strands of DNA molecu ...
... 10. In proof reading during DNA replication a. wrong nucleotides are inserted b. wrong nucleotides are taken out c. wrong nucleotides are removed and correct ones are inserted d. mutations are prevented 11. E.coli fully labeled with N15 is allowed to grow in N14 medium. The two strands of DNA molecu ...
CXA 300 Human Molecular Biology Laboratory Manual Semester 1
... CXA 300 Human Molecular Biology Laboratory Manual ...
... CXA 300 Human Molecular Biology Laboratory Manual ...
Activity 16.1 Is the Hereditary Material DNA or Protein?
... Meselson and Stahl grew bacteria in a culture medium that contained nucleotides labeled with heavy nitrogen (one extra neutron added), or 15N. After many generations, the DNA in the bacteria was completely labeled with 15N nucleotides. They grew other bacteria in only 14N-labeled nucleotides. If the ...
... Meselson and Stahl grew bacteria in a culture medium that contained nucleotides labeled with heavy nitrogen (one extra neutron added), or 15N. After many generations, the DNA in the bacteria was completely labeled with 15N nucleotides. They grew other bacteria in only 14N-labeled nucleotides. If the ...
Missense mutation in the ligand-binding domain of the horse
... Androgenic functions lead to the development of a male phenotype during gestation of the mammalian XY embryo, in addition to the secondary sexual characteristics that appear after puberty in an individual [Dohle et al., 2003]. Androgen hormones elicit their effects on target cells by binding a cytos ...
... Androgenic functions lead to the development of a male phenotype during gestation of the mammalian XY embryo, in addition to the secondary sexual characteristics that appear after puberty in an individual [Dohle et al., 2003]. Androgen hormones elicit their effects on target cells by binding a cytos ...
Microsatellite

A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from 2–5 base pairs) are repeated, typically 5-50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations in the human genome and they are notable for their high mutation rate and high diversity in the population. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name ""satellite"" refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying ""satellite"" layers of repetitive DNA. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.They are widely used for DNA profiling in kinship analysis and in forensic identification. They are also used in genetic linkage analysis/marker assisted selection to locate a gene or a mutation responsible for a given trait or disease.