THE DNA OF CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS HE small
... content and the value derived from the study of renaturation. This may be taken as evidence that the unit genome (LAIRD 1971) in C. elegans is contained in the haploid set of chromatids and that the slowly renaturing sequences are represented uniquely in this genome. Our results are very similar to ...
... content and the value derived from the study of renaturation. This may be taken as evidence that the unit genome (LAIRD 1971) in C. elegans is contained in the haploid set of chromatids and that the slowly renaturing sequences are represented uniquely in this genome. Our results are very similar to ...
CHAPTER 16 THE MOLECULE BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... Each cell continually monitors and repairs its genetic material, with 100 repair enzymes known in E. coli and more than 130 repair enzymes identified in humans. A hereditary defect in one of these enzymes is associated with a form of colon cancer. ...
... Each cell continually monitors and repairs its genetic material, with 100 repair enzymes known in E. coli and more than 130 repair enzymes identified in humans. A hereditary defect in one of these enzymes is associated with a form of colon cancer. ...
S1 Supporting Information
... MU412 has replaced 1.3 kb of the r3b2 coding region by the pyrG gene. The mutant alleles in MU450 and MU451 have completely eliminated the 136157 coding region and replaced it by the pyrG gene. All those mutant strains were considered null mutants. Transformants harboring mutant alleles were also o ...
... MU412 has replaced 1.3 kb of the r3b2 coding region by the pyrG gene. The mutant alleles in MU450 and MU451 have completely eliminated the 136157 coding region and replaced it by the pyrG gene. All those mutant strains were considered null mutants. Transformants harboring mutant alleles were also o ...
Duplication of Small Segments Within the Major
... occurred 258 bp downstream from the 9q M-bcr breakpoint. It is concluded that a duplication of small segments within the M-bcr occurs in a small group of patients with CML, which may lead t o pseudogermline patterns on Southern blot. Such a duplication may provide insight into the mechanism of some ...
... occurred 258 bp downstream from the 9q M-bcr breakpoint. It is concluded that a duplication of small segments within the M-bcr occurs in a small group of patients with CML, which may lead t o pseudogermline patterns on Southern blot. Such a duplication may provide insight into the mechanism of some ...
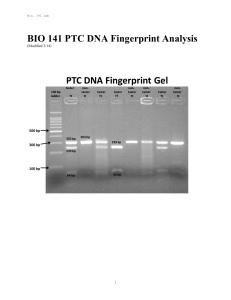
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... DNA’s structure resembles a twisted ladder called the double helix. DNA in all organisms consists of four bases called guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. The unique order or sequence of these bases in an individual’s cells serves as the blueprint for that individual. Of the approximately 3.3 b ...
... DNA’s structure resembles a twisted ladder called the double helix. DNA in all organisms consists of four bases called guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. The unique order or sequence of these bases in an individual’s cells serves as the blueprint for that individual. Of the approximately 3.3 b ...
Codon table worksheet
... Use your codon table to determine the amino acid sequence. Remember to read through the strand and ONLY start on AUG and STOP when it tells you to stop. Follow example below: DNA ...
... Use your codon table to determine the amino acid sequence. Remember to read through the strand and ONLY start on AUG and STOP when it tells you to stop. Follow example below: DNA ...
the role of germline polymorphisms in the t-cell
... complex, are encoded by genes on chromosomes 14 ( TCRA at 14q11.2) and 7 ( TCRB at 7q35), respectively. The TCRD locus, which codes for the d chain of cd T cells, also lies within the TCRA locus. The germline code of the TCRA and B loci consists of V (variable), J ( junctional ) and C (constant) reg ...
... complex, are encoded by genes on chromosomes 14 ( TCRA at 14q11.2) and 7 ( TCRB at 7q35), respectively. The TCRD locus, which codes for the d chain of cd T cells, also lies within the TCRA locus. The germline code of the TCRA and B loci consists of V (variable), J ( junctional ) and C (constant) reg ...
PDF
... (note that I/J are assigned to one cell). The letters we need to fill are (B, O, U , X, Z). So we will make these characters share some amino acids their codons. The start codon is repeated with amino acid (M) so we will not use it. (B) will be assigned 3 stop codons. (L, R, S) are three amino acids ...
... (note that I/J are assigned to one cell). The letters we need to fill are (B, O, U , X, Z). So we will make these characters share some amino acids their codons. The start codon is repeated with amino acid (M) so we will not use it. (B) will be assigned 3 stop codons. (L, R, S) are three amino acids ...
Document
... the most successful and widely used DNA profiling procedure. STRs are locations on the chromosome that contain short sequences that repeat themselves within the DNA molecule. They serve as useful markers for identification because they are found in great abundance throughout the human genome. ...
... the most successful and widely used DNA profiling procedure. STRs are locations on the chromosome that contain short sequences that repeat themselves within the DNA molecule. They serve as useful markers for identification because they are found in great abundance throughout the human genome. ...
File
... In gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments are placed at one end of a porous gel, and an electric voltage is applied to the gel. When the power is turned on, the negatively charged DNA molecules move toward the positive end of the gel. ...
... In gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments are placed at one end of a porous gel, and an electric voltage is applied to the gel. When the power is turned on, the negatively charged DNA molecules move toward the positive end of the gel. ...
Information. How to bring your samples
... Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is commonly used in molecular biology to detect RNA expression levels. In RT-PCR, the RNA template is first converted into complementary DNA (cDNA) using a reverse transcriptase. The cDNA is then used as a template for exponential amplificatio ...
... Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is commonly used in molecular biology to detect RNA expression levels. In RT-PCR, the RNA template is first converted into complementary DNA (cDNA) using a reverse transcriptase. The cDNA is then used as a template for exponential amplificatio ...
DNA Replication Practice Test Answer Section
... a. cells missing protein and RNA were able to transform R cells into S cells and kill mice, but cells missing DNA could not. b. cells missing DNA were able to transform R cells into S cells and kill mice, but cells missing protein and RNA could not. c. cells missing DNA, protein, and RNA were able t ...
... a. cells missing protein and RNA were able to transform R cells into S cells and kill mice, but cells missing DNA could not. b. cells missing DNA were able to transform R cells into S cells and kill mice, but cells missing protein and RNA could not. c. cells missing DNA, protein, and RNA were able t ...
DNA Technology Notes
... Biologists use DNA technology to produce plants with many desirable traits. Genetically engineered cotton resists insect infestation of the bolls. Sweet-potato plants are resistant to a virus that could kill most of the African harvest. Rice plants with increased iron and vitamins ...
... Biologists use DNA technology to produce plants with many desirable traits. Genetically engineered cotton resists insect infestation of the bolls. Sweet-potato plants are resistant to a virus that could kill most of the African harvest. Rice plants with increased iron and vitamins ...
DNA Technology Notes (13.1 &13.2)
... Biologists use DNA technology to produce plants with many desirable traits. Genetically engineered cotton resists insect infestation of the bolls. Sweet-potato plants are resistant to a virus that could kill most of the African harvest. Rice plants with increased iron and vitamins ...
... Biologists use DNA technology to produce plants with many desirable traits. Genetically engineered cotton resists insect infestation of the bolls. Sweet-potato plants are resistant to a virus that could kill most of the African harvest. Rice plants with increased iron and vitamins ...
A Recipe for Traits.indd
... determined by that organism’s DNA. DNA is made of smaller units. Differences in the sequence of these smaller units are what create differences in traits. More advanced information: The DNA molecule contains a sequence of four chemical bases, each represented by the first letter of its name: Guanine ...
... determined by that organism’s DNA. DNA is made of smaller units. Differences in the sequence of these smaller units are what create differences in traits. More advanced information: The DNA molecule contains a sequence of four chemical bases, each represented by the first letter of its name: Guanine ...
SCIENCE AS A PROCESS
... Images from: http://instruct1.cit.cornell.edu/courses/biog105/pages/demos/106/unit01/6.dnareplicationmodels.html ...
... Images from: http://instruct1.cit.cornell.edu/courses/biog105/pages/demos/106/unit01/6.dnareplicationmodels.html ...
Lecture 17, Mar 3
... You should be able to draw the abbreviated structure of a nucleotide (as shown at right) from its name (as shown in the table). You should also be able to write the abbreviated name of a nucleotide as shown in the table from an illustration such as the one shown at right. ...
... You should be able to draw the abbreviated structure of a nucleotide (as shown at right) from its name (as shown in the table). You should also be able to write the abbreviated name of a nucleotide as shown in the table from an illustration such as the one shown at right. ...
Chapter 24 Genes and Chromosomes
... Where to start , where to stop, etc. How much DNA? 3 base pairs/amino acid Small peptide may be 50 AA (150 BP) Average protein 350 AA (1050 bp) Eukaryote and some prokaryote have noncoding DNA in middle to make even longer How many genes in a Chromosome? Ecoli genome is a single chromosome that has ...
... Where to start , where to stop, etc. How much DNA? 3 base pairs/amino acid Small peptide may be 50 AA (150 BP) Average protein 350 AA (1050 bp) Eukaryote and some prokaryote have noncoding DNA in middle to make even longer How many genes in a Chromosome? Ecoli genome is a single chromosome that has ...
gen-305-presentation-8-16
... Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display ...
... Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display ...
Molecular Basis
... Each cell continually monitors and repairs its genetic material, with 100 repair enzymes known in E. coli and more than 130 repair enzymes identified in humans. A hereditary defect in one of these enzymes is associated with a form of colon cancer. ...
... Each cell continually monitors and repairs its genetic material, with 100 repair enzymes known in E. coli and more than 130 repair enzymes identified in humans. A hereditary defect in one of these enzymes is associated with a form of colon cancer. ...
What is CODIS - DNA Registry
... CODIS is a computer software program that operates local, State, and national databases of DNA profiles from convicted offenders, unsolved crime scene evidence, and missing persons. Every State in the Nation has a statutory provision for the establishment of a DNA database that allows for the collec ...
... CODIS is a computer software program that operates local, State, and national databases of DNA profiles from convicted offenders, unsolved crime scene evidence, and missing persons. Every State in the Nation has a statutory provision for the establishment of a DNA database that allows for the collec ...
Exam 1 Key
... a) The base sequence of a region where DNA replication begins is shown. What is the sequence of the primer that is synthesized complementary to the underlined bases? Write the sequence below the underlined bases. Be sure to indicate the 5´ and 3´ ends. 5´- T C G A G A C G C A C A T C T G G C A G C G ...
... a) The base sequence of a region where DNA replication begins is shown. What is the sequence of the primer that is synthesized complementary to the underlined bases? Write the sequence below the underlined bases. Be sure to indicate the 5´ and 3´ ends. 5´- T C G A G A C G C A C A T C T G G C A G C G ...
Just One Nucleotide! Exploring the Effects of Random
... misconceptions and details that were unclear are: confusion between transcription and translation; assuming the Start and Stop codons relate to transcription and not translation; starting a new protein every time they see the codon for methionine (AUG); inability to differentiate between codons and ...
... misconceptions and details that were unclear are: confusion between transcription and translation; assuming the Start and Stop codons relate to transcription and not translation; starting a new protein every time they see the codon for methionine (AUG); inability to differentiate between codons and ...
AP Biology
... Genes for antibiotic resistance = R Plasmids Role in rapid evolution Method for spreading “antibiotic resistance” ...
... Genes for antibiotic resistance = R Plasmids Role in rapid evolution Method for spreading “antibiotic resistance” ...
Microsatellite

A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from 2–5 base pairs) are repeated, typically 5-50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations in the human genome and they are notable for their high mutation rate and high diversity in the population. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name ""satellite"" refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying ""satellite"" layers of repetitive DNA. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.They are widely used for DNA profiling in kinship analysis and in forensic identification. They are also used in genetic linkage analysis/marker assisted selection to locate a gene or a mutation responsible for a given trait or disease.