Applied Genetics
... organism with the DNA of another organism. • Recombinant DNA technology was first used in the 1970’s with bacteria. ...
... organism with the DNA of another organism. • Recombinant DNA technology was first used in the 1970’s with bacteria. ...
DNA with Nitrogen Bases
... • Each triplet codes for a specific amino acid which transfer RNA (tRNA) provides. The amino acids link up at the ribosome until an amino acid (polypeptide) chain is created which builds up to make a protein. ...
... • Each triplet codes for a specific amino acid which transfer RNA (tRNA) provides. The amino acids link up at the ribosome until an amino acid (polypeptide) chain is created which builds up to make a protein. ...
Genes and DNA Chapter 6
... Any physical or chemical agent that can cause a mutation in DNA is called a mutagen. ...
... Any physical or chemical agent that can cause a mutation in DNA is called a mutagen. ...
DNA Webquest: A self guided introduction to basic genetics
... a cross bridge bond with ________________________ and cytosine will bond with ______________________. It is estimated that there are approximately six billion letter pairings in the DNA of a human cell! When a cell is preparing to divide, a double dose of DNA is prepared so that the “daughter cells” ...
... a cross bridge bond with ________________________ and cytosine will bond with ______________________. It is estimated that there are approximately six billion letter pairings in the DNA of a human cell! When a cell is preparing to divide, a double dose of DNA is prepared so that the “daughter cells” ...
DNA Unit
... model of shape proposed by Watson and Crick - Discovery made 1953 - won Nobel Prize in 1962 ...
... model of shape proposed by Watson and Crick - Discovery made 1953 - won Nobel Prize in 1962 ...
Slide 1
... Three forms of F: 1. F+ - F plasmid transferred to recipient cell recipient cell becomes F+ male 2. F’ – if fragment of chromosomal DNA is incorporated into the plasmid F’ male 3. Hfr – if F plasmid sequence is integrated into the bacterial chromosome cell called Hfr cell (high frequency of re ...
... Three forms of F: 1. F+ - F plasmid transferred to recipient cell recipient cell becomes F+ male 2. F’ – if fragment of chromosomal DNA is incorporated into the plasmid F’ male 3. Hfr – if F plasmid sequence is integrated into the bacterial chromosome cell called Hfr cell (high frequency of re ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Team – Game – Tournament
... Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Team – Game – Tournament Questions 1. What is the name of the molecule that stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation of organism to the next? 2. DNA is a polymer formed from subunits called …? 3. Name the three basic parts that make up a DN ...
... Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Team – Game – Tournament Questions 1. What is the name of the molecule that stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation of organism to the next? 2. DNA is a polymer formed from subunits called …? 3. Name the three basic parts that make up a DN ...
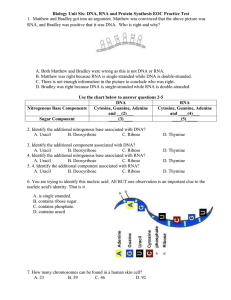
EOC Unit 6 Practice Test
... D. The amino acids will remain the same. 16. A strand of mRNA read GUU GCU CCU CUA GGU. What would the amino acid sequence be? A. Val-ALA-ASP-LEU-ARG B. VAL-ARG-ASP-LEU-ALA C. VAL-ALA-PRO-LEU-GLY D. GLY-ALA-PRO-VAL-LEU 17. If a dog has 39 pairs of chromosomes, how many of those pairs are considered ...
... D. The amino acids will remain the same. 16. A strand of mRNA read GUU GCU CCU CUA GGU. What would the amino acid sequence be? A. Val-ALA-ASP-LEU-ARG B. VAL-ARG-ASP-LEU-ALA C. VAL-ALA-PRO-LEU-GLY D. GLY-ALA-PRO-VAL-LEU 17. If a dog has 39 pairs of chromosomes, how many of those pairs are considered ...
Lecture 9 - Bacterial Genetics Chpt. 8
... –Create space between bases »Extra base is often added to fill space • Ethidium bromide is common intercalating agent –Potential carcinogen ...
... –Create space between bases »Extra base is often added to fill space • Ethidium bromide is common intercalating agent –Potential carcinogen ...
DNA, RNA, Proteins Review
... D. DNA and proteins DNA replication results in two DNA molecules, ___________________________________________ A. each with two new strands B. one with two new strands and one with 2 original strands C. each with two original strands D. each with one new strand and one original strand Which type(s) o ...
... D. DNA and proteins DNA replication results in two DNA molecules, ___________________________________________ A. each with two new strands B. one with two new strands and one with 2 original strands C. each with two original strands D. each with one new strand and one original strand Which type(s) o ...
Making Sentences of DNA
... 4- What is it called when letters get either inserted or deleted from DNA? ...
... 4- What is it called when letters get either inserted or deleted from DNA? ...
Sex linked inheritance, sex linkage in Drosophila and man, XO, XY
... stacked at the center of the DNA molecule. This occurrence can lead to single-nucleotide-pair insertions and deletions. ...
... stacked at the center of the DNA molecule. This occurrence can lead to single-nucleotide-pair insertions and deletions. ...
12-1 DNA
... bonds are broken, 2 strands unwind) E. Free-floating nucleotides form hydrogen bonds with the template strand. Replication is fast and accurate. 8-4 Transcription converts a gene into a singlestranded RNA molecule. RNA and Protein Synthesis DNA → RNA → protein RNA – long, single-strand of nucleotide ...
... bonds are broken, 2 strands unwind) E. Free-floating nucleotides form hydrogen bonds with the template strand. Replication is fast and accurate. 8-4 Transcription converts a gene into a singlestranded RNA molecule. RNA and Protein Synthesis DNA → RNA → protein RNA – long, single-strand of nucleotide ...
Lecture 10: Nucleic acids (DNA & RNA)
... most organisms (humans, animals, bacteria, plants, and some viruses). 2) Ribonucleic acid (RNA): in some viruses, RNA serves as the genetic material. Nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information المعلومات الوراثية Organisms inherit ترثDNA from their parents. Each DNA molecule is v ...
... most organisms (humans, animals, bacteria, plants, and some viruses). 2) Ribonucleic acid (RNA): in some viruses, RNA serves as the genetic material. Nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information المعلومات الوراثية Organisms inherit ترثDNA from their parents. Each DNA molecule is v ...
DNA Replication Computer Gizmo
... 11. What 2 molecules make up the backbone (or sides) of the DNA molecule? _____________________________ and _______________________________ 12. What molecules make up the rungs (or middle) of the DNA molecule? ...
... 11. What 2 molecules make up the backbone (or sides) of the DNA molecule? _____________________________ and _______________________________ 12. What molecules make up the rungs (or middle) of the DNA molecule? ...
Genetic Engineering - slater science
... 6. When DNA from two different organisms is combined, it is called _______________ DNA 7. A DNA _____________ can be read to determine paternity or solve crimes ...
... 6. When DNA from two different organisms is combined, it is called _______________ DNA 7. A DNA _____________ can be read to determine paternity or solve crimes ...
Genetic Engineering
... 6. When DNA from two different organisms is combined, it is called _______________ DNA 7. A DNA _____________ can be read to determine paternity or solve crimes ...
... 6. When DNA from two different organisms is combined, it is called _______________ DNA 7. A DNA _____________ can be read to determine paternity or solve crimes ...
DNA The Double Helix
... a twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder are made of alternating sugar and phosphate molecules. The sugar is deoxyribose. Color all the phosphates pink (one is labeled with a "p"). Color all the deoxyriboses blue (one is labeled with a "D"). The rungs of the ladder are pairs of 4 types of nitrog ...
... a twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder are made of alternating sugar and phosphate molecules. The sugar is deoxyribose. Color all the phosphates pink (one is labeled with a "p"). Color all the deoxyriboses blue (one is labeled with a "D"). The rungs of the ladder are pairs of 4 types of nitrog ...
Chromosomal Structure HWK
... or three alleles are possible forrepeats. This variability far outweighs the two or three alleles that are possible for most genes found in coding regions. For most genes found in coding regions. For this reason, noncoding DNA comprising VNTRs is used to differentiate among individuals inthis reason ...
... or three alleles are possible forrepeats. This variability far outweighs the two or three alleles that are possible for most genes found in coding regions. For most genes found in coding regions. For this reason, noncoding DNA comprising VNTRs is used to differentiate among individuals inthis reason ...
I. Microbial Genetics (Chapter 7) A. Overview 1. all of the information
... (1) bacteria use pyrophosphate bond of NAD+ for energy (2) other ligases use ATP instead 11. pol III has proofreading ability where wrong bases are excised and correct ones inserted during replication D. Transcription 1. transcription = synthesis of RNA under direction of DNA a. RNA has sequence com ...
... (1) bacteria use pyrophosphate bond of NAD+ for energy (2) other ligases use ATP instead 11. pol III has proofreading ability where wrong bases are excised and correct ones inserted during replication D. Transcription 1. transcription = synthesis of RNA under direction of DNA a. RNA has sequence com ...
RESTRICTION ENZYMES
... HOW DO RESTRICTION ENZYMES WORK? Usually cut DNA at a “palindrome” such as GAATTC. Palindrome – word or phrase when spelled backwords, spells the same word or phrase ...
... HOW DO RESTRICTION ENZYMES WORK? Usually cut DNA at a “palindrome” such as GAATTC. Palindrome – word or phrase when spelled backwords, spells the same word or phrase ...
Unit 4 Genetics and Heredity Study Guide Below are some key
... 2. Be able to explain the DNA – Library metaphor presented in class. 3. What does DNA stand for and where is it found? What is the purpose of DNA? 4. What are the three parts of a nucle ...
... 2. Be able to explain the DNA – Library metaphor presented in class. 3. What does DNA stand for and where is it found? What is the purpose of DNA? 4. What are the three parts of a nucle ...
DNA polymerase

The DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this process, DNA polymerase “reads” the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerase is required to help duplicate the cell’s DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each of the daughter cells. In this way, genetic information is transmitted from generation to generation.Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightly woven form. This opens up or “unzips” the double-stranded DNA to give two single strands of DNA that can be used as templates for replication.