DNA and Protein Synthesis - Garnet Valley School District
... • The codons code for 20 amino acids • Just like the alphabet has 26 letters to make all the words we know, the 20 amino acids make all the different proteins found in living organisms • The codons are the template for protein synthesis, which takes place on the ribosomes (rRNA) in the cytoplasm ...
... • The codons code for 20 amino acids • Just like the alphabet has 26 letters to make all the words we know, the 20 amino acids make all the different proteins found in living organisms • The codons are the template for protein synthesis, which takes place on the ribosomes (rRNA) in the cytoplasm ...
How Proteins Are Made Newsletter
... bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine). DNA has the “plan” to make all of the proteins. However, DNA is a large molecule and it can’t fit through the nuclear pores. It has to remain inside the nucleus. So, how does the information get to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm for the production of pr ...
... bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine). DNA has the “plan” to make all of the proteins. However, DNA is a large molecule and it can’t fit through the nuclear pores. It has to remain inside the nucleus. So, how does the information get to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm for the production of pr ...
Biotechnology II PPT
... Source of the DNA for Transformation? Scientists must go from mRNA back to DNA to make the process easier. This is a tough thing to do because: - Prokaryotic DNA does not have introns. - Modified mRNA must be collected after it leaves the nucleus and turned back into DNA. - Use reverse transcriptas ...
... Source of the DNA for Transformation? Scientists must go from mRNA back to DNA to make the process easier. This is a tough thing to do because: - Prokaryotic DNA does not have introns. - Modified mRNA must be collected after it leaves the nucleus and turned back into DNA. - Use reverse transcriptas ...
bch224 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... Hershey and Chase (1952): show that when the bacterial virus (bacteriophage) T2 infects its host cell, Escherichia coli, it is the phosphorus-containing DNA of the viral particle, not the sulfur-containing protein of the viral coat, that enters the host cell and furnishes the genetic information for ...
... Hershey and Chase (1952): show that when the bacterial virus (bacteriophage) T2 infects its host cell, Escherichia coli, it is the phosphorus-containing DNA of the viral particle, not the sulfur-containing protein of the viral coat, that enters the host cell and furnishes the genetic information for ...
Nucleic Acids
... • List properties of nucleic acids that make them suitable as carriers of hereditary information Linear molecule, polarity, quickly transcribed, synthesizing four nucleotides is efficient, simple codons call for all amino acids and starts and stops, and mutable ...
... • List properties of nucleic acids that make them suitable as carriers of hereditary information Linear molecule, polarity, quickly transcribed, synthesizing four nucleotides is efficient, simple codons call for all amino acids and starts and stops, and mutable ...
Amgen Lab 8
... of the gel tray. • Place gel tray into gel box with buffer ensuring that the wells are closest to the black electrode! • Add 4ul of orange G (loading dye) to your PCR sample and load 20ul of your sample into one of the wells. • Once everyone has loaded their sample plug red electrode to red and blac ...
... of the gel tray. • Place gel tray into gel box with buffer ensuring that the wells are closest to the black electrode! • Add 4ul of orange G (loading dye) to your PCR sample and load 20ul of your sample into one of the wells. • Once everyone has loaded their sample plug red electrode to red and blac ...
The nitrogen base that RNA has but DNA does not What is uracil?
... A group of three nitrogen bases that codes for a specific amino acid. ...
... A group of three nitrogen bases that codes for a specific amino acid. ...
Slides - gserianne.com
... – Uses Uridine (U) rather than Thymine (T) – Uses the pentose sugar, ribose – Usually single-stranded ...
... – Uses Uridine (U) rather than Thymine (T) – Uses the pentose sugar, ribose – Usually single-stranded ...
013368718X_CH15_229-246.indd
... 18. An organism that contains one or more genes from another species is inbred. 19. Transgenic organisms can be made by inserting recombinant DNA into the genome of the host organism. 20. Examining the properties of a transgenic organism allows scientists to discover the function of the transferred ...
... 18. An organism that contains one or more genes from another species is inbred. 19. Transgenic organisms can be made by inserting recombinant DNA into the genome of the host organism. 20. Examining the properties of a transgenic organism allows scientists to discover the function of the transferred ...
Fruit Salad—Hold the DNA, Please
... All the genetic information for a living organism is contained in its DNA, which is housed in the nucleus of its cells. DNA is made up of nucleotides and a sugar phosphate backbone that bond together in a double-helix form. It is a very long molecule made of millions of nucleotides. Between two indi ...
... All the genetic information for a living organism is contained in its DNA, which is housed in the nucleus of its cells. DNA is made up of nucleotides and a sugar phosphate backbone that bond together in a double-helix form. It is a very long molecule made of millions of nucleotides. Between two indi ...
three possibile models for replication
... 8) Viruses with RNA genomes are typically those that infect animal cells 9) These viruses are called retroviruses (ex: HIV) 10) They contain the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which uses viral RNA to make a complementary DNA strand 11) Reverse transcriptase can then synthesize the other DNA strand fr ...
... 8) Viruses with RNA genomes are typically those that infect animal cells 9) These viruses are called retroviruses (ex: HIV) 10) They contain the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which uses viral RNA to make a complementary DNA strand 11) Reverse transcriptase can then synthesize the other DNA strand fr ...
K`NEX Activity
... Activity 1: Building a Basic DNA Molecule You will build a molecule of DNA using the procedure outlined on pp 4-5 in the following way. 1. Assemble nucleotides (24 total) Remember to make sure your bases match up (if you build 7 guanines how many cytosines should you build?) 2. Assemble your 12 ba ...
... Activity 1: Building a Basic DNA Molecule You will build a molecule of DNA using the procedure outlined on pp 4-5 in the following way. 1. Assemble nucleotides (24 total) Remember to make sure your bases match up (if you build 7 guanines how many cytosines should you build?) 2. Assemble your 12 ba ...
Unit 4
... As an RNA polymerase molecule moves along a gene from the initiation site to the termination site., it synthesizes an RNA molecule that consists of the nucleotide sequence determined by the template strand of the gene. The entire stretch of DNA that is transcribed is called a transcription unit. Tra ...
... As an RNA polymerase molecule moves along a gene from the initiation site to the termination site., it synthesizes an RNA molecule that consists of the nucleotide sequence determined by the template strand of the gene. The entire stretch of DNA that is transcribed is called a transcription unit. Tra ...
5о end of mRNA 1 2 1 1 2 3 Protein Ribosome RNA
... Fill in the locations of all of the enzymes from the chart based on where they are likely to act. You can assume that each arm of the ‘Y’ is 500 bases long and that an Okazaki fragment is 150 bases long on average. – When finished, complete the replication bubble with the other fork. ...
... Fill in the locations of all of the enzymes from the chart based on where they are likely to act. You can assume that each arm of the ‘Y’ is 500 bases long and that an Okazaki fragment is 150 bases long on average. – When finished, complete the replication bubble with the other fork. ...
Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
... If your cells contained 12% adenine, how much of each of the other nitrogen bases do your cells contain? ...
... If your cells contained 12% adenine, how much of each of the other nitrogen bases do your cells contain? ...
honors biology Ch. 10 Notes DNA
... 10.4 Explain how the structure of DNA facilitates its replication. “It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.” Each strand can be revealed for copying by breaking the hydrogen bonds holding ...
... 10.4 Explain how the structure of DNA facilitates its replication. “It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.” Each strand can be revealed for copying by breaking the hydrogen bonds holding ...
Laboratory in Fundamentals of Molecular Biology
... The process of extracting DNA from a cell is the first step for many laboratory procedures in molecular biology. The scientist must be able to separate DNA from the unwanted substances of the cell gently enough so that the DNA is not sheared into smaller pieces or degraded. Such shearing – breaking ...
... The process of extracting DNA from a cell is the first step for many laboratory procedures in molecular biology. The scientist must be able to separate DNA from the unwanted substances of the cell gently enough so that the DNA is not sheared into smaller pieces or degraded. Such shearing – breaking ...
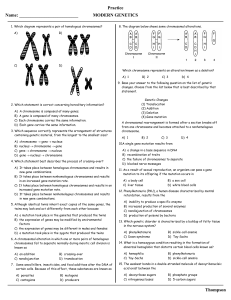
Modern Genetics questions and answer key
... 43. Although eukaryotic cells contain over a thousand times more DNA than is found in a prokaryotic cell, it only takes a eukaryotic cell a few hours to copy all of its genetic material because A) eukaryotic DNA polymerases delete unnecessary material as it is replicating B) eukaryotic cells follow ...
... 43. Although eukaryotic cells contain over a thousand times more DNA than is found in a prokaryotic cell, it only takes a eukaryotic cell a few hours to copy all of its genetic material because A) eukaryotic DNA polymerases delete unnecessary material as it is replicating B) eukaryotic cells follow ...
File
... Eukaryotic ALL living things Prokaryotic (prokaryotes & eukaryotes) contain DNA. All of the above None of the above ...
... Eukaryotic ALL living things Prokaryotic (prokaryotes & eukaryotes) contain DNA. All of the above None of the above ...
DNA - Fort Bend ISD
... surrounding her life and work as Rosalind Franklin. Franklin was responsible for much of the research and discovery work that led to the understanding of the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA. ...
... surrounding her life and work as Rosalind Franklin. Franklin was responsible for much of the research and discovery work that led to the understanding of the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA. ...
DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication
... What enzyme is responsible for breaking the hydrogen bonds that hold together the base pairs during replication? (also called “unzipping” the DNA strand) The enzyme helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between nitrogen base pairs during DNA replication. What enzyme is responsible for proofreading the ...
... What enzyme is responsible for breaking the hydrogen bonds that hold together the base pairs during replication? (also called “unzipping” the DNA strand) The enzyme helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between nitrogen base pairs during DNA replication. What enzyme is responsible for proofreading the ...
In meiosis, what is the difference between metaphase 1 and
... 5. How do a plant cell and an animal cell differ during cytokinesis? Animal= cleavage furrow forms, contractile ring is made from microfilaments, the ring squeezes and pinches cell apart Plant= plants have cell wall, new cell wall (cell plate) is built between daughter cells, no pinching to separate ...
... 5. How do a plant cell and an animal cell differ during cytokinesis? Animal= cleavage furrow forms, contractile ring is made from microfilaments, the ring squeezes and pinches cell apart Plant= plants have cell wall, new cell wall (cell plate) is built between daughter cells, no pinching to separate ...
DNA polymerase

The DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this process, DNA polymerase “reads” the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerase is required to help duplicate the cell’s DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each of the daughter cells. In this way, genetic information is transmitted from generation to generation.Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightly woven form. This opens up or “unzips” the double-stranded DNA to give two single strands of DNA that can be used as templates for replication.