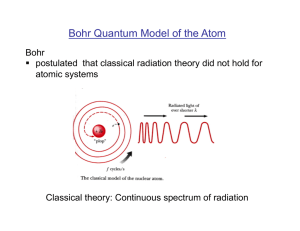
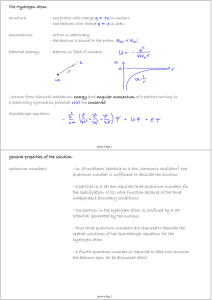
Electrons in Atoms
... ‘In classical systems (described by Newton’s laws) the position of an object can be specified exactly’. ‘In quantum systems, we can only talk about the probability of a particle being at a particular location: some regions have higher probability, and some lower’. ...
... ‘In classical systems (described by Newton’s laws) the position of an object can be specified exactly’. ‘In quantum systems, we can only talk about the probability of a particle being at a particular location: some regions have higher probability, and some lower’. ...
Chapter 9a Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
... Compton scattering cannot be understood on the basis classical electromagnetic theory. On the basis of classical principles, the scattering mechanism is induced by motion of electrons in the material, caused by the incident radiation. This motion must have the same frequency as that of incident wav ...
... Compton scattering cannot be understood on the basis classical electromagnetic theory. On the basis of classical principles, the scattering mechanism is induced by motion of electrons in the material, caused by the incident radiation. This motion must have the same frequency as that of incident wav ...
PROBset3_2015 - University of Toronto, Particle Physics and
... energies emitted from a reactor is 1043 cm 2 . Compute the thickness of water absorber needed to reduce the intensity of an antineutrino beam by a factor of 2. (b) Since neutrinos are very penetrating particles, they are difficult to detect. A liquid scintillator is an organic liquid which emits sm ...
... energies emitted from a reactor is 1043 cm 2 . Compute the thickness of water absorber needed to reduce the intensity of an antineutrino beam by a factor of 2. (b) Since neutrinos are very penetrating particles, they are difficult to detect. A liquid scintillator is an organic liquid which emits sm ...
β - Indico
... 5. Aharonov Y., Cohen E., Elitzur A.C. (2012), Coexistence of past and future measurements’ effects, predicted by the Two-State-Vector-Formalism and revealed by weak measurement. Submitted to Phys. Rev. A. http://arxiv.org/abs/1207.0667 . 6. Aharonov Y., Cohen E., Grossman D., Elitzur A.C. (2012), C ...
... 5. Aharonov Y., Cohen E., Elitzur A.C. (2012), Coexistence of past and future measurements’ effects, predicted by the Two-State-Vector-Formalism and revealed by weak measurement. Submitted to Phys. Rev. A. http://arxiv.org/abs/1207.0667 . 6. Aharonov Y., Cohen E., Grossman D., Elitzur A.C. (2012), C ...
Non-linear gates enabling universal quantum computation
... In the above described endeavour, non-linear quantum systems are crucial. Given that, as said above, experimental research has recently seen impressive developments in terms of scalability, accessing to non-linearities would be the next big step. The reason is that non-linearities are necessary for ...
... In the above described endeavour, non-linear quantum systems are crucial. Given that, as said above, experimental research has recently seen impressive developments in terms of scalability, accessing to non-linearities would be the next big step. The reason is that non-linearities are necessary for ...
Chapter 4.2 Quantum Models
... The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle ...
... The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle ...
Sections 4 - Columbia Physics
... (a) Find expressions for the energy, E, and momentum magnitude, p, of the particle in terms of its velocity β. (b) What are the maximum and minimum velocities for the particle and at what values of E and p are the maximum and minimum velocities attained? (c) Suppose a measurement of the velocity of ...
... (a) Find expressions for the energy, E, and momentum magnitude, p, of the particle in terms of its velocity β. (b) What are the maximum and minimum velocities for the particle and at what values of E and p are the maximum and minimum velocities attained? (c) Suppose a measurement of the velocity of ...
Particle in a box

In quantum mechanics, the particle in a box model (also known as the infinite potential well or the infinite square well) describes a particle free to move in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example a ball trapped inside a large box, the particle can move at any speed within the box and it is no more likely to be found at one position than another. However, when the well becomes very narrow (on the scale of a few nanometers), quantum effects become important. The particle may only occupy certain positive energy levels. Likewise, it can never have zero energy, meaning that the particle can never ""sit still"". Additionally, it is more likely to be found at certain positions than at others, depending on its energy level. The particle may never be detected at certain positions, known as spatial nodes.The particle in a box model provides one of the very few problems in quantum mechanics which can be solved analytically, without approximations. This means that the observable properties of the particle (such as its energy and position) are related to the mass of the particle and the width of the well by simple mathematical expressions. Due to its simplicity, the model allows insight into quantum effects without the need for complicated mathematics. It is one of the first quantum mechanics problems taught in undergraduate physics courses, and it is commonly used as an approximation for more complicated quantum systems.