Noncommutative Quantum Mechanics
... Obtain a phase-space formulation of a noncommutative extension of QM in arbitrary number of dimensions; Show that physical previsions are independent of the chosen SW map. ...
... Obtain a phase-space formulation of a noncommutative extension of QM in arbitrary number of dimensions; Show that physical previsions are independent of the chosen SW map. ...
Simulation of Quantum Computation with Wolfram
... area of modern science and technology. Quantum computers are to be able to perform certain computational tasks much more efficiently than classical computers. At the same time a realistic quantum computer is still not available and the majority of studies in this field are theoretical ones. This stimul ...
... area of modern science and technology. Quantum computers are to be able to perform certain computational tasks much more efficiently than classical computers. At the same time a realistic quantum computer is still not available and the majority of studies in this field are theoretical ones. This stimul ...
Photoluminescence in quantum-confined SnO2 nanocrystals
... since the mean particle size is close to the value of the exciton Bohr radius. The same behavior can be seen in the photoluminescence characterization 关Fig. 2共b兲兴. The decrease in particle radius created a blueshift in the photon energy emitted. The PL spectra consisted of single broad bands peaked ...
... since the mean particle size is close to the value of the exciton Bohr radius. The same behavior can be seen in the photoluminescence characterization 关Fig. 2共b兲兴. The decrease in particle radius created a blueshift in the photon energy emitted. The PL spectra consisted of single broad bands peaked ...
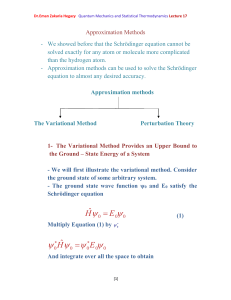
Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
... varitional parameters and there by determine the best possible ground-state energy that can be obtained from our trial wave function. As a specific example, consider the ground state of the hydrogen atom. Although we know that we can solve this problem exactly , let’s assume that we cannot and use t ...
... varitional parameters and there by determine the best possible ground-state energy that can be obtained from our trial wave function. As a specific example, consider the ground state of the hydrogen atom. Although we know that we can solve this problem exactly , let’s assume that we cannot and use t ...
Abstract - The Budker Group
... 2003); additionally, quantum computers based on diamonds (Stoneham et al 2009), optical lattices, and many other two-level systems have been proposed by physicists and engineers. Still, we are decades away from a quantum computer which can match all of the capabilities of a contemporary classical co ...
... 2003); additionally, quantum computers based on diamonds (Stoneham et al 2009), optical lattices, and many other two-level systems have been proposed by physicists and engineers. Still, we are decades away from a quantum computer which can match all of the capabilities of a contemporary classical co ...
B.3 Time dependent quantum mechanics
... satisfied, will always be satisfied. The solutions to eq. 9 can be very complex (pun intended) functions of position and time. The timedependent Schrödinger equation has one particularly simple kind of solution when the wave function can be split into position and time-dependent parts of the form i ...
... satisfied, will always be satisfied. The solutions to eq. 9 can be very complex (pun intended) functions of position and time. The timedependent Schrödinger equation has one particularly simple kind of solution when the wave function can be split into position and time-dependent parts of the form i ...
Particle in a box

In quantum mechanics, the particle in a box model (also known as the infinite potential well or the infinite square well) describes a particle free to move in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example a ball trapped inside a large box, the particle can move at any speed within the box and it is no more likely to be found at one position than another. However, when the well becomes very narrow (on the scale of a few nanometers), quantum effects become important. The particle may only occupy certain positive energy levels. Likewise, it can never have zero energy, meaning that the particle can never ""sit still"". Additionally, it is more likely to be found at certain positions than at others, depending on its energy level. The particle may never be detected at certain positions, known as spatial nodes.The particle in a box model provides one of the very few problems in quantum mechanics which can be solved analytically, without approximations. This means that the observable properties of the particle (such as its energy and position) are related to the mass of the particle and the width of the well by simple mathematical expressions. Due to its simplicity, the model allows insight into quantum effects without the need for complicated mathematics. It is one of the first quantum mechanics problems taught in undergraduate physics courses, and it is commonly used as an approximation for more complicated quantum systems.