South Pasadena · Chemistry
... 2. When n = 3, l can have values of ___________________________. For the 3d orbital, l has a value of ___. When n = 4, l can have values of ___________________________. For the 4p orbital, l has a value of ___. When n = 2, l can have values of ___________________________. For the 2s orbital, l has a ...
... 2. When n = 3, l can have values of ___________________________. For the 3d orbital, l has a value of ___. When n = 4, l can have values of ___________________________. For the 4p orbital, l has a value of ___. When n = 2, l can have values of ___________________________. For the 2s orbital, l has a ...
class (Recovered)
... (Z_2)^n and Z_(2^n). The Hidden subgroup problem. FFT and HSP. Discrete Log. ...
... (Z_2)^n and Z_(2^n). The Hidden subgroup problem. FFT and HSP. Discrete Log. ...
Study Questions and Problems
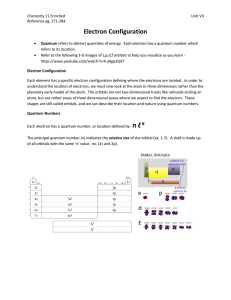
... The principal quantum n can have any integer value from 1, 2, 3, 4...to infinity. The secondary (or angular momentum) quantum number l can have values from 0, 1, 2, 3, to a maximum of n –1. The magnetic quantum number ml can have integer values from –l through 0 to +l. The number of different values ...
... The principal quantum n can have any integer value from 1, 2, 3, 4...to infinity. The secondary (or angular momentum) quantum number l can have values from 0, 1, 2, 3, to a maximum of n –1. The magnetic quantum number ml can have integer values from –l through 0 to +l. The number of different values ...
Chemistry 441: Quantum Chemistry
... will deal with the concepts and formalism of quantum mechanics. Several systems (free particle, 1-D, 2-D and 3-D boxes, harmonic oscillator and rigid rotor) will be discussed to illustrate the formulation and solution of basic quantum mechanics problems. The application of quantum mechanics to chemi ...
... will deal with the concepts and formalism of quantum mechanics. Several systems (free particle, 1-D, 2-D and 3-D boxes, harmonic oscillator and rigid rotor) will be discussed to illustrate the formulation and solution of basic quantum mechanics problems. The application of quantum mechanics to chemi ...
PowerPoint
... # of protons and neutrons according to the atomic # and mass # of the atom 2) Fill energy levels (orbitals) with the required # of electrons starting from the lowest available energy level and following Pauli and Hund rules (this is called Aufbau principle) ...
... # of protons and neutrons according to the atomic # and mass # of the atom 2) Fill energy levels (orbitals) with the required # of electrons starting from the lowest available energy level and following Pauli and Hund rules (this is called Aufbau principle) ...
The Quantum Mechanical Picture of the Atom
... 1) Build the nucleus by adding the required # of protons and neutrons according to the atomic # and mass # of the atom 2) Fill energy levels (orbitals) with the required # of electrons starting from the lowest available energy level and following Pauli and Hund rules (this is called Aufbau principle ...
... 1) Build the nucleus by adding the required # of protons and neutrons according to the atomic # and mass # of the atom 2) Fill energy levels (orbitals) with the required # of electrons starting from the lowest available energy level and following Pauli and Hund rules (this is called Aufbau principle ...