AP Biology Summer Assignment 2013
... Discuss if the trends you see match what you would expect based on your knowledge of the subject. □ Scientific Method: What were three possible sources of errors – and what effect might they have on such an experiment? If you find data that does not seem to fit with expected trends, be sure to discu ...
... Discuss if the trends you see match what you would expect based on your knowledge of the subject. □ Scientific Method: What were three possible sources of errors – and what effect might they have on such an experiment? If you find data that does not seem to fit with expected trends, be sure to discu ...
Respiration Fill in Blank Notes - Bremen High School District 228
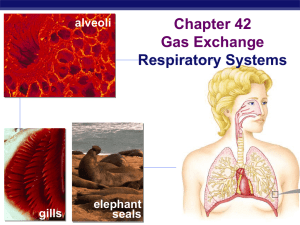
... of gill capillary maximizing O2 transfer from water to blood ...
... of gill capillary maximizing O2 transfer from water to blood ...
Word Roots - Jennifer`s e
... auto- = self; troph- = food, nourishment (autotroph: an organism that obtains organic food molecules without eating other organisms) aux- = grow, enlarge (auxins: a class of plant hormones, including indoleacetic acid, having a variety of effects, such as phototropic response through the stimulation ...
... auto- = self; troph- = food, nourishment (autotroph: an organism that obtains organic food molecules without eating other organisms) aux- = grow, enlarge (auxins: a class of plant hormones, including indoleacetic acid, having a variety of effects, such as phototropic response through the stimulation ...
Animal Circulatory System
... Exchange of materials Animal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, CO2) ...
... Exchange of materials Animal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, CO2) ...
Evolution and Cognition - Fred Heeren, Science Journalist
... “explosion” of new body plans. The plentiful fossil evidence for Haikouella— 305 specimens, many in excellent condition—finally confirms what many had suspected in recent years: Our own phylum arrived on the scene along with most of the others, during the surprisingly quick radiation of new major an ...
... “explosion” of new body plans. The plentiful fossil evidence for Haikouella— 305 specimens, many in excellent condition—finally confirms what many had suspected in recent years: Our own phylum arrived on the scene along with most of the others, during the surprisingly quick radiation of new major an ...
Answers to examination questions in Chapters 1
... is transferred by transformation / a plasmid / other methods; the bacteria with the gene / resistant bacteria will divide; natural selection favours the resistant bacteria / non-resistant bacteria will die; over time the population of bacteria will become resistant so the antibiotic can no longer be ...
... is transferred by transformation / a plasmid / other methods; the bacteria with the gene / resistant bacteria will divide; natural selection favours the resistant bacteria / non-resistant bacteria will die; over time the population of bacteria will become resistant so the antibiotic can no longer be ...
Biology - Eastern Mennonite University
... Introductory course for biology majors or those interested in the biology major, emphasizing science as a method of learning about life. This course focuses on two biological issues of current interest to society—the impact of invasive species on ecosystems, and the challenge of infectious diseases. ...
... Introductory course for biology majors or those interested in the biology major, emphasizing science as a method of learning about life. This course focuses on two biological issues of current interest to society—the impact of invasive species on ecosystems, and the challenge of infectious diseases. ...
2 Adaptation Scavenger
... camouflage in their surroundings. Their mouth and gills are found under their body, but they also have spiracles (holes) on their head to help them breathe if they are on the ocean floor. Pick a ray to watch in the Ray Lagoon. Can you locate the ray’s mouth when it swims by? Can you find its spiracl ...
... camouflage in their surroundings. Their mouth and gills are found under their body, but they also have spiracles (holes) on their head to help them breathe if they are on the ocean floor. Pick a ray to watch in the Ray Lagoon. Can you locate the ray’s mouth when it swims by? Can you find its spiracl ...
Chapter 1 The Framework of Biology
... Fermentation by fungi produces alcohol and carbon dioxide. Humans use fungi to ferment food sources producing bread, alcohol and cheese. Fungi are used for medicines. It was discovered that fungi produce a chemical which affects bacterial growth, now used by humans as antibiotics. 16.4 Animals are a ...
... Fermentation by fungi produces alcohol and carbon dioxide. Humans use fungi to ferment food sources producing bread, alcohol and cheese. Fungi are used for medicines. It was discovered that fungi produce a chemical which affects bacterial growth, now used by humans as antibiotics. 16.4 Animals are a ...
AP Biology Survey of the Kingdoms CHAPTER 27 – Bacteria and
... _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 8. What is a capsule and what advant ...
... _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 8. What is a capsule and what advant ...
answers
... describe the role of body systems in the exchange of material and how they interact with each other. (Digestive system…breaks food down into useable nutrients; circulatory system transports those to all parts of the body, and also takes oxygen from the respiratory system…and carries CO2…to be excret ...
... describe the role of body systems in the exchange of material and how they interact with each other. (Digestive system…breaks food down into useable nutrients; circulatory system transports those to all parts of the body, and also takes oxygen from the respiratory system…and carries CO2…to be excret ...
1. Which phrase is an example of autotrophic
... Body weight is considered to be a risk factor for diseases such as diabetes and high blood pressure. The Body Mass Index (BMI) chart can be used as a guide to determine if a person’s body weight puts them at risk for such diseases. A portion of this chart is shown below ...
... Body weight is considered to be a risk factor for diseases such as diabetes and high blood pressure. The Body Mass Index (BMI) chart can be used as a guide to determine if a person’s body weight puts them at risk for such diseases. A portion of this chart is shown below ...
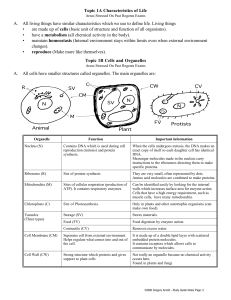
Topic 1A Characteristics of Life A. All living things have similar
... Organisms will react in ways that will maintain an internal environment allowing the chemical activities of life to occur regardless if the external environment changes. This process is known as homeostasis (steady state). For example, the heart and breathing rate will change due to various levels o ...
... Organisms will react in ways that will maintain an internal environment allowing the chemical activities of life to occur regardless if the external environment changes. This process is known as homeostasis (steady state). For example, the heart and breathing rate will change due to various levels o ...
RNA Polymerase II: Reading in Loops to get Different Tails Abstract
... The RNA polymerase II is the multi-subunit enzyme able to transcribe the protein-encoding genes in eukaryotic cells producing the messenger RNA (mRNA). Two critical steps in eukaryotic mRNA biogenesis, for its correct 3´-end processing are: cleavage and polyadenylation. This is necessary to achieve ...
... The RNA polymerase II is the multi-subunit enzyme able to transcribe the protein-encoding genes in eukaryotic cells producing the messenger RNA (mRNA). Two critical steps in eukaryotic mRNA biogenesis, for its correct 3´-end processing are: cleavage and polyadenylation. This is necessary to achieve ...
Quantitative Biology Minor Worksheet
... 2) At least two of the courses used to fulfill the Quantitative Biology minor must not be used to fulfill course the requirements of another major, minor or certificate. 3) Students must earn a “C” or better in all required courses. A course taken on a P/F basis will not count toward the minor. 4) A ...
... 2) At least two of the courses used to fulfill the Quantitative Biology minor must not be used to fulfill course the requirements of another major, minor or certificate. 3) Students must earn a “C” or better in all required courses. A course taken on a P/F basis will not count toward the minor. 4) A ...
Garrett Odell simulates cellular activity with computer
... models in multiple dimensions the interactions among molecules and between cells that are critical for cellular activities such as growth and movement. Because these complicated interactions overwhelm traditional “reductionist” research approaches, computer modeling is used as a more powerful way fo ...
... models in multiple dimensions the interactions among molecules and between cells that are critical for cellular activities such as growth and movement. Because these complicated interactions overwhelm traditional “reductionist” research approaches, computer modeling is used as a more powerful way fo ...
living environment
... the number of the choice that, of those given, best completes each statement or answers each question. For all other questions in this part, follow the directions given and record your answers in the spaces provided. 44 State one way insect pests in an apple orchard can be controlled without using c ...
... the number of the choice that, of those given, best completes each statement or answers each question. For all other questions in this part, follow the directions given and record your answers in the spaces provided. 44 State one way insect pests in an apple orchard can be controlled without using c ...
Prokaryotes 1. How common are prokaryotes on earth? 2. List and
... 10. Review the six lineages of the Protists and take notes on their key characteristics as well as listing an example organism. FUNGI 1. How common are fungi on earth? 2. How do fungi acquire nutrients? 3. Because of their mode of nutrition, fungi have evolved what structure to provide for both ext ...
... 10. Review the six lineages of the Protists and take notes on their key characteristics as well as listing an example organism. FUNGI 1. How common are fungi on earth? 2. How do fungi acquire nutrients? 3. Because of their mode of nutrition, fungi have evolved what structure to provide for both ext ...
Dispositions and Causal Processes in Biology
... populations). Our main thesis is that certain (implicit) assumptions that are traditionally made about the nature of dispositions need to be revised in the light of these biological examples. First, the traditional picture of dispositions is inadequate with respect to biology since it obscures the g ...
... populations). Our main thesis is that certain (implicit) assumptions that are traditionally made about the nature of dispositions need to be revised in the light of these biological examples. First, the traditional picture of dispositions is inadequate with respect to biology since it obscures the g ...
Winter 2016 USC Stem Cell Newsletter
... territory as the winner of the Hearst Fellowship, which will launch his early scientific career with a generous startup package including salary and benefits for a year. “None of the immunologists think about the hematopoietic stem cells, and none of the hematopoietic stem cell people think about th ...
... territory as the winner of the Hearst Fellowship, which will launch his early scientific career with a generous startup package including salary and benefits for a year. “None of the immunologists think about the hematopoietic stem cells, and none of the hematopoietic stem cell people think about th ...
For Immediate Release Yvonne M. Psaila Director of Marketing
... networking activities. Submission of an abstract is not required, but it is encouraged as organizers typically select short talk speakers based on abstract submission. This presents a means for early-career scientists to be featured on the programs along with established experts. Abstracts and poste ...
... networking activities. Submission of an abstract is not required, but it is encouraged as organizers typically select short talk speakers based on abstract submission. This presents a means for early-career scientists to be featured on the programs along with established experts. Abstracts and poste ...
1 - UWA
... Atrazine to clean up weeds. There is now a choice between TT hybrids and Roundup Ready hybrids. Cowling explains that in a scenario of commercialization of GM canola in WA, he will sell the seed and the farmer signs a licence with Monsanto. Louise Cullen and Pauline Grierson have recently published ...
... Atrazine to clean up weeds. There is now a choice between TT hybrids and Roundup Ready hybrids. Cowling explains that in a scenario of commercialization of GM canola in WA, he will sell the seed and the farmer signs a licence with Monsanto. Louise Cullen and Pauline Grierson have recently published ...
B7 quiz questions - Fakenham Academy Norfolk
... gained (including heat released during respiration) and heat lost. 2. What do temperature receptors in the skin detect? 3. What do temperature receptors in the brain detect? 4. Where in the brain do you find the processing centre which receives information from the temperature receptors, and sends i ...
... gained (including heat released during respiration) and heat lost. 2. What do temperature receptors in the skin detect? 3. What do temperature receptors in the brain detect? 4. Where in the brain do you find the processing centre which receives information from the temperature receptors, and sends i ...
Biology
... (1635–1703), one of the first scientists to use a microscope to examine pond water, cork and other things, was the first to refer to the cavities he saw in cork as ‘cells’, Latin for chambers. Subsequent scientists developed Hooke’s discovery of the cell into the Cell Theory on which modern Biology ...
... (1635–1703), one of the first scientists to use a microscope to examine pond water, cork and other things, was the first to refer to the cavities he saw in cork as ‘cells’, Latin for chambers. Subsequent scientists developed Hooke’s discovery of the cell into the Cell Theory on which modern Biology ...
History of biology

The history of biology traces the study of the living world from ancient to modern times. Although the concept of biology as a single coherent field arose in the 19th century, the biological sciences emerged from traditions of medicine and natural history reaching back to ayurveda, ancient Egyptian medicine and the works of Aristotle and Galen in the ancient Greco-Roman world. This ancient work was further developed in the Middle Ages by Muslim physicians and scholars such as Avicenna. During the European Renaissance and early modern period, biological thought was revolutionized in Europe by a renewed interest in empiricism and the discovery of many novel organisms. Prominent in this movement were Vesalius and Harvey, who used experimentation and careful observation in physiology, and naturalists such as Linnaeus and Buffon who began to classify the diversity of life and the fossil record, as well as the development and behavior of organisms. Microscopy revealed the previously unknown world of microorganisms, laying the groundwork for cell theory. The growing importance of natural theology, partly a response to the rise of mechanical philosophy, encouraged the growth of natural history (although it entrenched the argument from design).Over the 18th and 19th centuries, biological sciences such as botany and zoology became increasingly professional scientific disciplines. Lavoisier and other physical scientists began to connect the animate and inanimate worlds through physics and chemistry. Explorer-naturalists such as Alexander von Humboldt investigated the interaction between organisms and their environment, and the ways this relationship depends on geography—laying the foundations for biogeography, ecology and ethology. Naturalists began to reject essentialism and consider the importance of extinction and the mutability of species. Cell theory provided a new perspective on the fundamental basis of life. These developments, as well as the results from embryology and paleontology, were synthesized in Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. The end of the 19th century saw the fall of spontaneous generation and the rise of the germ theory of disease, though the mechanism of inheritance remained a mystery.In the early 20th century, the rediscovery of Mendel's work led to the rapid development of genetics by Thomas Hunt Morgan and his students, and by the 1930s the combination of population genetics and natural selection in the ""neo-Darwinian synthesis"". New disciplines developed rapidly, especially after Watson and Crick proposed the structure of DNA. Following the establishment of the Central Dogma and the cracking of the genetic code, biology was largely split between organismal biology—the fields that deal with whole organisms and groups of organisms—and the fields related to cellular and molecular biology. By the late 20th century, new fields like genomics and proteomics were reversing this trend, with organismal biologists using molecular techniques, and molecular and cell biologists investigating the interplay between genes and the environment, as well as the genetics of natural populations of organisms.