Human Body Systems - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... Divided into 3 phases: follicular, ovulation, and luteal phases If no fertilization occurs, endometrium is shed Can be sexually active anytime ...
... Divided into 3 phases: follicular, ovulation, and luteal phases If no fertilization occurs, endometrium is shed Can be sexually active anytime ...
Topic 5 - cloudfront.net
... Vitamin K (phylloquinone) is needed by the human body for a. formation of red blood cells b. clotting of blood c. hydrogen transport in mitochondria d. production of collagen ...
... Vitamin K (phylloquinone) is needed by the human body for a. formation of red blood cells b. clotting of blood c. hydrogen transport in mitochondria d. production of collagen ...
AP Biology Summer Assignment 2015 Students must complete this
... Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit, and respond to information critical to life processes. Big Idea 4: Biological systems interact, and these interactions possess complex properties. ...
... Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit, and respond to information critical to life processes. Big Idea 4: Biological systems interact, and these interactions possess complex properties. ...
- Schoolnet
... The muscular system provides oxygen to the body, while the respiratory system allows the person to lift the weights. ...
... The muscular system provides oxygen to the body, while the respiratory system allows the person to lift the weights. ...
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: BLOOD 28 JULY 2014 Lesson
... a.) Complete the table below using the information in Fig. 1.1 to help you. ...
... a.) Complete the table below using the information in Fig. 1.1 to help you. ...
Unit Four : Classification of Living Organisms
... For example, at the time you read these words, the nerve cells in your eyes carry messages of what you read to the brain cells and the muscular cells connected to your eyeballs move your eyes across the page. Cells are collected together to form tissues such as the nerve tissue or muscular tissue. I ...
... For example, at the time you read these words, the nerve cells in your eyes carry messages of what you read to the brain cells and the muscular cells connected to your eyeballs move your eyes across the page. Cells are collected together to form tissues such as the nerve tissue or muscular tissue. I ...
File
... combine inside the body External fertilization occurs when the sperm and egg combine outside the body (i.e. in water) ...
... combine inside the body External fertilization occurs when the sperm and egg combine outside the body (i.e. in water) ...
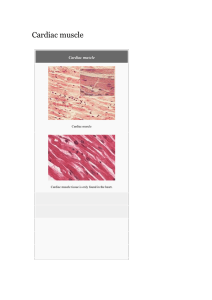
Cardiac muscle File
... that belief.[10] Olaf Bergmann and his colleagues at theKarolinska Institute in Stockholm tested samples of heart muscle from people born before 1955 who had very little cardiac muscle around their heart, many showing with disabilities from this abnormality. By using DNA samples from many hearts, t ...
... that belief.[10] Olaf Bergmann and his colleagues at theKarolinska Institute in Stockholm tested samples of heart muscle from people born before 1955 who had very little cardiac muscle around their heart, many showing with disabilities from this abnormality. By using DNA samples from many hearts, t ...
Exam question (5 marks)
... Name five tissues, cells or cell structures found in the mammalian gas exchange system and explain the function of each [5 marks] ...
... Name five tissues, cells or cell structures found in the mammalian gas exchange system and explain the function of each [5 marks] ...
1-Functional Organization of the Human Body
... secrete chemicals (especially hormones) into bloodstream (e.g. pituitary gland, pancreas secretes insulin into the blood ...
... secrete chemicals (especially hormones) into bloodstream (e.g. pituitary gland, pancreas secretes insulin into the blood ...
Section 3 - Studying Life
... development. During development, a single fertilized egg cell divides again and again to produce the many cells of mature organisms. As those cells divide, they change in shape and structure to form cells such as liver cells, brain cells, and muscle cells. This process is called differentiation, bec ...
... development. During development, a single fertilized egg cell divides again and again to produce the many cells of mature organisms. As those cells divide, they change in shape and structure to form cells such as liver cells, brain cells, and muscle cells. This process is called differentiation, bec ...
Domains/Kingdoms
... Cases of walking pneumonia are most common in the late summer and fall. But infections can occur with no particular pattern throughout the year. And, even though the disease is contagious, it spreads slowly. The contagious period in most cases lasts less than 10 days. Researchers also think it take ...
... Cases of walking pneumonia are most common in the late summer and fall. But infections can occur with no particular pattern throughout the year. And, even though the disease is contagious, it spreads slowly. The contagious period in most cases lasts less than 10 days. Researchers also think it take ...
The Human Body: An Orientation
... • The cell life cycle is the series of changes a cell goes through • Interphase • G1 phase—growth 1 or Gap 1 phase ...
... • The cell life cycle is the series of changes a cell goes through • Interphase • G1 phase—growth 1 or Gap 1 phase ...
Animalia Part 1: Invertebrates
... • Crustaceans, arachnids and insects • These animals have a hard outer covering called an exoskeleton. • They are divided into 3 classes: – Crustacean – Arachnida – Insecta ...
... • Crustaceans, arachnids and insects • These animals have a hard outer covering called an exoskeleton. • They are divided into 3 classes: – Crustacean – Arachnida – Insecta ...
Unit 2: Homeostasis and Immunity
... sugar level, etc. We refer to these small changes as dynamic equilibrium. It is because of these small changes that we maintain homeostasis ...
... sugar level, etc. We refer to these small changes as dynamic equilibrium. It is because of these small changes that we maintain homeostasis ...
Cause. - Cleveland Clinic
... self-correct some mistakes than others, and children appear to have better capacity for self-correction than do adults. For example, the immune systems of children usually are eventually able to correct the juvenile rheumatoid arthritis mistake, the juvenile dermatomyositis mistake, and even the lup ...
... self-correct some mistakes than others, and children appear to have better capacity for self-correction than do adults. For example, the immune systems of children usually are eventually able to correct the juvenile rheumatoid arthritis mistake, the juvenile dermatomyositis mistake, and even the lup ...
april 15 microviewer comparative digestion
... Microviewer 227: Comparative Digestive Systems Introduction This set is one of a series of lessons examining comparative life function systems. In these sets, you will examine slides of different animals, and see the way each organism is adapted to perform its vital life functions. The function of ...
... Microviewer 227: Comparative Digestive Systems Introduction This set is one of a series of lessons examining comparative life function systems. In these sets, you will examine slides of different animals, and see the way each organism is adapted to perform its vital life functions. The function of ...
Chapter 2: From a Cell to an Organism
... phase. The same is true for cells. The phase of a cell cycle when a cell is preparing to reproduce is called interphase. It usually lasts longer than other phases of the cell cycle. The phase when a eukaryotic cell reproduces is called the mitotic (mi TOH tik) phase. During the mitotic phase, the nu ...
... phase. The same is true for cells. The phase of a cell cycle when a cell is preparing to reproduce is called interphase. It usually lasts longer than other phases of the cell cycle. The phase when a eukaryotic cell reproduces is called the mitotic (mi TOH tik) phase. During the mitotic phase, the nu ...
Biology CST framework
... understanding this concept: 2.a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs of chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containing one chromosome of each type. Haploid gamete production through meiosis involves two cell ...
... understanding this concept: 2.a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs of chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containing one chromosome of each type. Haploid gamete production through meiosis involves two cell ...
TOPIC: REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
... This type of reproduction has only one parent. This type produces genetically identical offspring. The organisms in this type of repro have gonads and gametes. This type of repro produces offspring that are a combo ob both parents. 5. This type is very simple and primitive. 6. This type contains spe ...
... This type of reproduction has only one parent. This type produces genetically identical offspring. The organisms in this type of repro have gonads and gametes. This type of repro produces offspring that are a combo ob both parents. 5. This type is very simple and primitive. 6. This type contains spe ...
the respiratory system
... caused by the flu virus TUBERCULOSIS: a bacterial infection that damages the tissues of the lungs and interferes with gas exchange PNEUMONIA: an infection of the lungs that causes the alveoli to fill with pus and mucus ...
... caused by the flu virus TUBERCULOSIS: a bacterial infection that damages the tissues of the lungs and interferes with gas exchange PNEUMONIA: an infection of the lungs that causes the alveoli to fill with pus and mucus ...
Document
... Subunits form channel in center Distinguished from simple pores in a cell membrane by their ion selectivity and their changing states, or conformation Open and close at random due to thermal energy; gating increases the probability of being in a certain state ...
... Subunits form channel in center Distinguished from simple pores in a cell membrane by their ion selectivity and their changing states, or conformation Open and close at random due to thermal energy; gating increases the probability of being in a certain state ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are