Measuring and Modelling Potential Change
... Fecundity: potential for species to produce offspring in their life Open population: pop. # and density are determined by birth, death, immigration, emigration Closed Population: pop. size/density measured with natality (birth rates) and mortality (death rates). Only natality and mortality can be me ...
... Fecundity: potential for species to produce offspring in their life Open population: pop. # and density are determined by birth, death, immigration, emigration Closed Population: pop. size/density measured with natality (birth rates) and mortality (death rates). Only natality and mortality can be me ...
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
... Areolar and adipose tissues are the most common of the soft connective tissues. Areolar, or loose tissue, connects the skin to underlying muscle and also functions as mucous membranes, such as those in the digestive and respiratory systems. Adipose tissue, on the other hand, is a storage place for e ...
... Areolar and adipose tissues are the most common of the soft connective tissues. Areolar, or loose tissue, connects the skin to underlying muscle and also functions as mucous membranes, such as those in the digestive and respiratory systems. Adipose tissue, on the other hand, is a storage place for e ...
Marine Invertebrate Zoology Laboratory Procedures
... The life cycle of Plasmodium is complex and includes several generations with both sexual and asexual reproduction. The life cycle can best be understood by starting with the zygote in the gut of a mosquito, one of the two hosts necessary for the completion of the life cycle. The zygote becomes moti ...
... The life cycle of Plasmodium is complex and includes several generations with both sexual and asexual reproduction. The life cycle can best be understood by starting with the zygote in the gut of a mosquito, one of the two hosts necessary for the completion of the life cycle. The zygote becomes moti ...
MUSINGU HIGH SCHOOL
... Heat/hot conditions: Increased sweating; to lose heat through latent heat of vaporization; dilation of arterioles under the skin; to bring more blood to the skin surface to lose heat to the atmosphere; decreased body metabolism; to reduce heat generation; erector pili muscles relax; making hair foll ...
... Heat/hot conditions: Increased sweating; to lose heat through latent heat of vaporization; dilation of arterioles under the skin; to bring more blood to the skin surface to lose heat to the atmosphere; decreased body metabolism; to reduce heat generation; erector pili muscles relax; making hair foll ...
Section 2: Enzymes and Digestion
... Large pieces of food are broken down into smaller pieces by processes such as chewing and the churning of food in the stomach. This makes it possible to not only absorb food but to increase its surface area, thus making it easier for chemical absorption. ...
... Large pieces of food are broken down into smaller pieces by processes such as chewing and the churning of food in the stomach. This makes it possible to not only absorb food but to increase its surface area, thus making it easier for chemical absorption. ...
Exam 1A key
... a) Increased numbers of mitochondria within muscle fibers b) Increased vascularization of the muscles c) Greatly increased numbers of myofibrils within muscle fibers d) Increased myoglobin concentrations within muscle fibers e) A, B, and D are true 22. When an organism dies, its muscles remain in a ...
... a) Increased numbers of mitochondria within muscle fibers b) Increased vascularization of the muscles c) Greatly increased numbers of myofibrils within muscle fibers d) Increased myoglobin concentrations within muscle fibers e) A, B, and D are true 22. When an organism dies, its muscles remain in a ...
Homeobox genes
... Homeobox genes show astonishing similarity across widely different species of animal, from fruit flies, which are insects, to mice and humans, which are mammals. The sequences of these genes have remained relatively unchanged throughout evolutionary history and the same genes control embryonic de ...
... Homeobox genes show astonishing similarity across widely different species of animal, from fruit flies, which are insects, to mice and humans, which are mammals. The sequences of these genes have remained relatively unchanged throughout evolutionary history and the same genes control embryonic de ...
data table - Ms. V Biology
... VOLUME. This amount of air provides enough oxygen for a person who is resting. It is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully - the maximum amount of air moved in and out of the lungs is called the VITAL CAPACITY. In this activity, you will be measuring the vital capacity and the tidal volume o ...
... VOLUME. This amount of air provides enough oxygen for a person who is resting. It is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully - the maximum amount of air moved in and out of the lungs is called the VITAL CAPACITY. In this activity, you will be measuring the vital capacity and the tidal volume o ...
Complete and Incomplete Metamorphosis
... The eggs hatch into nymphs. Nymphs looks like small adults, but usually don't have wings. Insect nymphs eat the same food that the adult insect eats. Nymphs shed or molt their exoskeletons and replace them with larger ones 4-8 times as they grow. ...
... The eggs hatch into nymphs. Nymphs looks like small adults, but usually don't have wings. Insect nymphs eat the same food that the adult insect eats. Nymphs shed or molt their exoskeletons and replace them with larger ones 4-8 times as they grow. ...
Human-Physiology-Lecture-IV-CellMembranes
... A molecule of ATP is used with each “swap of Na/K ions Regents Biology ...
... A molecule of ATP is used with each “swap of Na/K ions Regents Biology ...
Chapter 15 Practice Test 2012
... 10. The structure that prevents the entry of liquids or solid food into the respiratory passageways during swallowing is the a. glottis b. artenoids cartilage c. epiglottis d. thyroid cartilage 11. The amount of air moved into or out of the lungs during a single respiratory cycle is the: a. respirat ...
... 10. The structure that prevents the entry of liquids or solid food into the respiratory passageways during swallowing is the a. glottis b. artenoids cartilage c. epiglottis d. thyroid cartilage 11. The amount of air moved into or out of the lungs during a single respiratory cycle is the: a. respirat ...
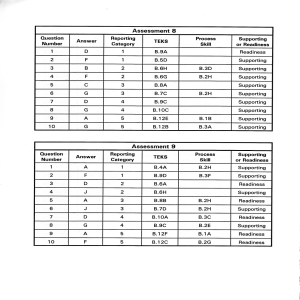
Assessment 8 Assessment I
... an environment responds to water vapors released by a plant through transpiration to create a micro-environment for an entire plant. hormones released by a plant cause other plants to release pollen to achieve fertilization and seed development. ...
... an environment responds to water vapors released by a plant through transpiration to create a micro-environment for an entire plant. hormones released by a plant cause other plants to release pollen to achieve fertilization and seed development. ...
This page should automatically redirect. If nothing is
... The Trachea consists of smooth muscle, elastic connective tissue, and incomplete rings of cartilage shaped like a series of letter C's. The open ends of the C's are held together by the trachealis muscle. The cartilage provides a rigid support so that the tracheal wall does not collapse inward and o ...
... The Trachea consists of smooth muscle, elastic connective tissue, and incomplete rings of cartilage shaped like a series of letter C's. The open ends of the C's are held together by the trachealis muscle. The cartilage provides a rigid support so that the tracheal wall does not collapse inward and o ...
Cells: The Basic Units of Life
... nucleus. The nucleus is one kind of membrane-bound organelle. A cell’s nucleus holds the cell’s DNA. Eukaryotic cells have other membrane-bound organelles as well. Organelles are like the different organs in your body. Each kind of organelle has a specific job in the cell. Together, organelles, such ...
... nucleus. The nucleus is one kind of membrane-bound organelle. A cell’s nucleus holds the cell’s DNA. Eukaryotic cells have other membrane-bound organelles as well. Organelles are like the different organs in your body. Each kind of organelle has a specific job in the cell. Together, organelles, such ...
On Your Own” Questions - Kingdom Builders Coop
... 1.7 You compare several organisms from different orders within a given class. You then compare organisms from different classes. In which case would you expect the differences to be greatest? ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________ ...
... 1.7 You compare several organisms from different orders within a given class. You then compare organisms from different classes. In which case would you expect the differences to be greatest? ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________ ...
The Human Body
... • The skeleton provides a framework against which the muscles can pull. One end of the muscle, the _______, is attached to a bone that remains stationary during the contraction. The other end of the muscle, the _____________, is attached to a bone that moves during the contraction. ...
... • The skeleton provides a framework against which the muscles can pull. One end of the muscle, the _______, is attached to a bone that remains stationary during the contraction. The other end of the muscle, the _____________, is attached to a bone that moves during the contraction. ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM
... a. consist of three to four generations - (20-23) b. epithelium is low cuboidal that flattens to simple squamous epithelium at the alveolar level c. gas exchange begins in this area where squamous cells begin d. alveoli appear e. the portion of the airway distal to a terminal bronchiole forms the "t ...
... a. consist of three to four generations - (20-23) b. epithelium is low cuboidal that flattens to simple squamous epithelium at the alveolar level c. gas exchange begins in this area where squamous cells begin d. alveoli appear e. the portion of the airway distal to a terminal bronchiole forms the "t ...
Presentation
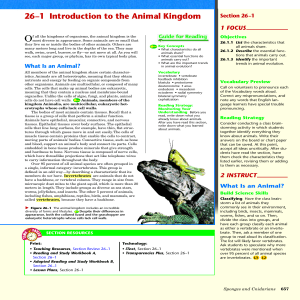
... tend to have high levels of cell specialization and internal body organization, bilateral body symmetry, a front end or head with sense organs, and a body cavity. In addition, the embryos of complex animals develop in layers. ...
... tend to have high levels of cell specialization and internal body organization, bilateral body symmetry, a front end or head with sense organs, and a body cavity. In addition, the embryos of complex animals develop in layers. ...
Using food and controlling growth - Delivery guide
... The video clip by cancer quest which is 11 minutes long provides detailed documentary on the formation of cancer. This provides a great opportunity for stretch and challenge of learners. The video clip makes links to a number of different areas of the specification incorporating organelles, membrane ...
... The video clip by cancer quest which is 11 minutes long provides detailed documentary on the formation of cancer. This provides a great opportunity for stretch and challenge of learners. The video clip makes links to a number of different areas of the specification incorporating organelles, membrane ...
Chapter 2: Cell Structure And Cell Organization
... P3-when the contractile vacuole is filled with water to its maximum size, it contracts to expel its Content from time to time ...
... P3-when the contractile vacuole is filled with water to its maximum size, it contracts to expel its Content from time to time ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are