* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download data table - Ms. V Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
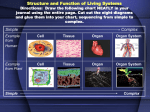
Animal Form and Function A Study of the Organ Systems Image Name _________________________ Period ___________ (Draw and color one of the eleven systems in the body outline above) 1 Introduction Cells are ____________________ ____________________________ _____________________________ Examples of different types of cells are _________________________________ _________________________________ Tissues are __________________ ____________________________ _____________________________ Describe the types of tissues and give an example: Epithelial Tissue = __________________________ Ex. _____________________________ Connective Tissue = _________________________ Ex. ______________________________ Nervous Tissue = ____________________________ Ex. ______________________________ Muscle Tissue = _____________________________ Ex. ______________________________ Identify the different types of connective tissue: fibrous connective tissue, cartilage, adipose tissue, bone, blood, and loose connective tissue Organs are ________________________________________________________ Give me five examples of organs: 1. ________________ 2. ________________ 3. ________________ 4. ________________ 5. ________________ Organs Systems are ____________________ _______________________________________ Match the Organ to the System Identify the three different types of Hypothalamus - ________________________________ muscle tissue: smooth, cardiac, Pancreas - ____________________________ ________ and skeletal. Tibia - ________________________________ Pituitary - ______________________________ Bronchi - ________________________________ 2 Animal Form and Function A Study of the Organ Systems Muscular System Function: ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ Major Structures: ________________________________ ________________________________ _______________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ _____________________________ Works closely with the ___________ Place the following words in the diagrams – system to_______________________ endoskeleton and exoskeleton use once, with the help of ___________________ flexor and extensor use twice. Organization of Skeletal Muscle ____________________ = fibers cell membrane ___________________ = cells cytoplasm, containing _______________, __________ and ______________ for energy. Each muscle fiber itself contains cylindrical organelles known as _________________ Myofibrils made up of _________________________ proteins which run the length of the muscle fiber and are Important in muscle contraction known as the _________________. What is a strain? ______________________________ ____________________________________________ What is a sprain? _____________________________ _____________________________________________ What are ligaments?___________________________ What are tendons?____________________________ _____________________________________________ 3 Animal Form and Function A Study of the Organ Systems Skeletal System Three types of skeletal systems 1. ______________________________ 2. ______________________________ 3. ______________________________ Function: ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ Types of Cells: ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ Works closely with the _____________ system to___________________________ ___________________________________ In the outline to the right draw and label the following structures: clavicle, femur, fibula, humerus, patella, pelvis, radius, ribs, scapula, skull, sternum, tibia & ulna What are the Haversian Canals? _____________ _________________________________________ Using the diagram above, name 3 types of joints and give an example of each. 1. _____________________/_________________ 2. _____________________/_________________ 3. _____________________/_________________ 4 Animal Form and Function A Study of the Organ Systems Nervous System Function: __________________________________ On the diagram below draw the CNS __________________________________________ and PNS using two different colors. __________________________________________ Major Structures: CNS = ______________________________ PNS = ______________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 3 Types of Neurons:__________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Works closely with the ______________ _____________ and the five senses to ____________________________________. Using the letters label the neuron above and indicate the direction of the impulse: A = dendrite, B = nodes of Ranvier, C = cell body, D = Schwann cell, E = axon, F = myelin sheath, G = synaptic terminal and H = nucleus. In your own words describe the four steps of a synapse then on the diagram to the right CLEARLY place the number where the steps occur. 1. ________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 3. ________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 4. ________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 5 Place the number next to the correct part, provide a 1 word functions & color each of the four lobes a different color Hypothalamus Medulla Cerebellum Corpus Collosum Thalamus Cerebrum Temporal Lobe Occipital Lobe Parietal Lobe Frontal Lobe Cerebro-spinal Fluid Record your Stroop test times & make a conclusion 1st ________/2nd _________ _______________________________________ Senses Affiliated Organ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ 6. 3. 2. 7. 1. 8. 4. 1. ________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________ 5. What other reflex test do doctors use? _________ __________________________________________ RECORD YOUR AVG TIME AND RATING ON THE REACTION GAME: ________________________ 6 h e r e 5. ________________________________________ Place the following words in the boxes: motor neuron, effector, sensory neuron, interneuron, receptor, stimulus, spinal cord and gray matter e a r 3. ________________________________________ 4. ________________________________________ T a p e Read the paper on reflexes & record the steps. Animal Form and Function A Study of the Organ Systems Circulatory System T a p e H e a r t Function: ____________________________ _____________________________________ Label & use 2 colors 8. Major Structures: ______________________ 1. 9. _____________________________________ 2. 10. 3. 11. Using the stethoscope, listen to your heartbeat 4. 12. and record. Explain the sound: 5. 13. 1st Sound (LUB): ___________________________ 6. 14. 7. 15. Types of Cells: ________________________ _____________________________________ __________________________________________ 2nd Sound (DUB): ___________________________ __________________________________________ Diastolic pressure is ______________________ Systolic pressure is ______________________ What is your blood pressure _______/_______ What is your pulse rate and what does it mean? _______________________________________ What level of the organ system hierarchy is Blood? ________________________________ % Read “Relationships..” handout & describe how the circulatory and digestive systems depend on each other. Using the diagram on the back, list 3 more systems that work w/ the circulatory system. _______________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ 1. ___________________________________ 2. ___________________________________ Complete the following table Component Plasma made up of H e r e Color 3. ___________________________________ Use the “Travels of a red blood cell” cards to complete the following. A red blood cell begins within the ____________ canals that are found Cellular Elements Types 1. Functions 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. in your bone marrow. The next destination are ____________ and then they bring oxygen poor blood to the __________ by way of the _______ _______. At which point they enter the _______ atrium. Passing the ____________ valve and entering the __________ ventricle passing through the ______________ valve going to the ________ arteries. The red blood cell goes to the _______ for loading up on oxygen. The red blood cell travels through the ________________ veins to the _________ atrium passing the _______ valve and into the final pumping chamber, _______ ventricle. The last valve is the ____________ valve and it leads to the _______. The last part of your vascular system that carries oxygen to your body is the ___________. 7 Animal Form and Function A Study of the Organ Systems Respiratory System Function:__________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ Major Structures: ___________________ __________________________________ Key Parts: _________________________ __________________________________ Works closely with the ______________ system to _________________________ Identify another function that is performed by the respiratory system and what parts of our body are used to perform that function. _____________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________ USING THE LUNG MODEL Which part of the model represents the following and then describe the function: The exchange of CO2 and O2 is what kind of passive transport? _______________ What is your diagnosis and what are your recommendations? Patient #__ - _________________ Trachea = ________________________ _________________________________ Bronchi = ________________________ _________________________________ ____________________________ Lung = __________________________ ____________________________ _________________________________ ____________________________ Diaphragm = _______________________________ Patient #__ - _________________ __________________________________________ ____________________________ What happens when you pull down on the large balloon? __________________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ Read the article entitled “Everest/First Ascents: Altitude Danger Begins in Pheriche” and answer the eight questions. 1. ____ 2. ____ 3. ____ 4. ____ 5. ____ 8 6. ____ 7. ____ 8. ____ Measuring Lung Capacity The amount of air that you move in and out of your lungs while breathing normally is called TIDAL VOLUME. This amount of air provides enough oxygen for a person who is resting. It is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully - the maximum amount of air moved in and out of the lungs is called the VITAL CAPACITY. In this activity, you will be measuring the vital capacity and the tidal volume of your own lungs, this actual number can then be compared with a number derived from an equation that measures vital capacity. In effect, you are measuring an actual number, based on laboratory measurements, to a theoretical number, based on an equation. If you have any breathing difficulties (asthma or other condition), you should not participate in this activity, instead only take the data on your lab partner or group. Materials - Balloons, metric ruler, meter stick, bathroom scale (optional) How to Take Measurements with a Balloon 1. Measuring Tidal Volume -- Stretch a round balloon several times to stretch it out. Inhale normally and then exhale normally into the balloon. Do not force your breathing. Pinch the end of the balloon and measure its diameter. Repeat this so that you have 3 total measurements and can take the average and record in the data table. 2. Measuring Vital Capacity - Repeat the procedure, only this time inhale as much air as you can and exhale forcefully. Record three measurements in the data table. 3. Convert the diameters to a volume using the graph and record this in your table. 4. Estimated Vital Capacity - Research has shown that the capacity of a person's lungs is proportional to the surface area of his or her body. To find the surface area, you will need to know your height and weight. There are a couple of different ways to calculate your body surface area mathematically. Either use the equation below or go to a website that has an automatic calculator. (A Google search on "body surface area calculator will yield many pages that have these calculators) Once you have calculated your surface area, a second equation will calculate your estimated vital capacity. Males: SA x 2500 Females SA x 2000 9 DATA TABLE Tidal Volume Balloon Diameter Volume (from graph) Vital Capacity Balloon Diameter Volume (from graph) Trial Estimated Vital Capacity Height (cm) Mass (kg) 1 Surface Area 2 Vital Capacity 3 Average ANALYSIS 1. Why is it important to measure tidal volume and vital capacity three times and then get an average? 2. How does your measured vital capacity compare to the vital capacity you estimated using the formula? Which do you think is more accurate and why? 3. How might an athlete's vital capacity compare to a non-athlete? Explain your reasoning. APPLICATION 1. Examine the data table of a person who entered into a training program. This person's vital capacity was measured over a 60 day period. Use the data to construct a graph DATA GRAPH Day of Training Vital Capacity 0 4800 10 4840 20 4890 30 4930 40 4980 50 5180 60 5260 2. What happened to the person's vital capacity over the course of the training period? 3. What probably caused the change? 4. How might vital capacity be important to a musician? 10 Animal Form and Function A Study of the Organ Systems Digestive System 12 Function: ____________________________________ ____________________________________________ Major Structures: _____________________________ ____________________________________________ Key Parts: ___________________________________ ____________________________________________ Works closely with the __________________ system to __________________________________________. 13 Match the number with the correct organ then indicate the type of digestion ME=mechanical and CH=Chemical. Then briefly describe the function. Indicate the pH if applicable and the enzyme produced by that organ. Rectum, Small Intestine (Ileum), Mouth/Oral Cavity, Salivary Glands, Large Intestine (colon), Pharynx, Esophagus/Gullet, Anus, Liver, Gall Bladder, Pancreas, Stomach and Pyloric Sphincter # ORGAN ME/CH FUNCTION pH FLUIDS SECRETED 1 2 12 7 8 13 3 4 5 6 9 10 11 DEFINE/Describe: Bolus =___________________________________________________________ Peristalsis = ______________________________________________________________________ Villi or microvilli = _________________________________________________________________ 11 Digestive System Puzzle Square: Arrange the cut out squares so that the touching sides match. The enzyme pancreatic amylase is manufactured and secreted by the pancreas into the small intestine. Pancreatic amylase breaks down starch into a smaller sugar. Pepsin is an enzyme that is released by the stomach and functions to break down proteins into amino acids. The following graph shows the pH at which both pepsin and pancreatic amylase can function in the body. If the pH of the body falls above or below the graphs for each enzyme respectively, that enzyme will denature and no longer function. The higher the curve of the graph, the more productive the enzyme. Which of the following statements is true with respect to Figure 1? 1) _____ : Pepsin and pancreatic amylase could never function together in the same part of the body at the same time. 2) _____: Pancreatic amylase could function in the stomach with a pH of 1-2. 3) _____ : The optimal pH for the functioning of pepsin is approximately 8.5 to 9. 4) _____: Pancreatic amylase is used in the small intestine. Normally, the small intestine must be slightly acidic in order for it to function. 12 Animal Form and Function A Study of the Organ Systems Excretory System Function: ____________________________________ _____________________________________________ Major Structures: _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Key Parts: _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Works closely with the _____________ system to ____________________________________________. Add the following labels to the diagram Kidney, urinary bladder, ureters, urethra, renal artery, and vena cava Label the diagram of a kidney and color as indicated: capsuleorange; renal artery – red; renal vein – yellow; cortex green; medulla - pink; pelvis - brown; ureter – blue; pyramids - purple Filtration Structure ______ Function (use the words from the diagrams) Carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body ______ Carries deoxygenated blood away from the kidney ______ The inner region of the kidney ______ The outer region of the kidney ______ Carries oxygenated blood to the kidney ______ The part of the kidney that collects the urine before it passes down the ureter ______ The tough fibrous coat around the kidney ______ Stores urine before it is removed from body ______ The tube that carries urine away from the kidney ________ Converts blood to urine Organism R e a b s o r p t i o n Excretion Label the nephron diagram 1=Collecting duct, 2=renal artery, 3=loop of Henle, 4=distal convoluted tubule, 5=glomerulus, 6=proximal convoluted tubule, 7=Bowman’s capsule 13 Protists ______________ Cnidarians ______________ Platyhelminthes ______________ Annelids ______________ Insects ______________ Desert Animal Kangaroo Rat Specialized Excretory Organ Urinalysis Simulation Physical Properties Analysis – Color, Clarity, Specific Gravity Record the color of the specimen as pale yellow, yellow, brownish yellow, or red. Record the clarity of the urine specimen as clear, slightly cloudy, cloudy, or turbid. Specific gravity has already been recorded for you. Physical Properties of Urine Analysis Urine Sample Color Clarity Specific Gravity Control ~1.000 Patient A ~1.014 Patient B ~1.019 Patient C ~1.030 Place the urine colors from the above data table in the “Before” columns. To test for glucose you added Benedict’s solution to 3 ml of urine for each patient and then heated the tubes for 2 minutes in a hot water bath. The test tubes in the beaker labeled “Benedicts” are the samples after heating. Record the color change in your data table. A color change to orange, red, or brown indicates the presence of sugar. To test for protein you added Biuret solution to 3 mL of urine for each patient. The tubes in the beaker labeled “Biuret” are the samples after adding Biuret’s solution. Record the color change in your data table. A change from blue to purple indicates the presence of protein. Chemical Properties GLUCOSE PROTEIN of Urine Analysis Color before Color after Color before Color after Urine Sample heating heating adding Biuret adding Biuret Control Patient A Patient B Patient C Indicate the test(s) that provides a diagnosis for the following diseases: •Urinary tract infection ____________________________________ •Diabetes mellitus ________________________________________ •Kidney disease __________________________________________ 2. What is a potential diagnosis for patient A? ____________________________________ 3. What is a potential diagnosis for patient B? ____________________________________ 4. What is a potential diagnosis for patient C? ____________________________________ 5. Which patient had the highest concentration of dissolved substances? _______________ 6. Why was a control used in each test?_________________________________________ 14 Animal Form and Function A Study of the Organ Systems Lymphatic/Immune System Function: _________________ __________________________ Major Structures: Place the letter next to the name of the structure Works closely with the ________ system to __________________. Blood cells are produced in _____________ and Erythrocytes are called __________________ and Leukocytes are called_____________. The two types of Lymphocytes are _______________ and _____________. C H Lines of Defense 1st: Non-specific barrier, innate, broad external defense Types:_________________________________________ 2nd: ___________________________________________ - leukocytes attack pathogens but no memory 3rd: Specific, acquired defense w/memory, true immunity specific defense w/ memory:__________ & _______ responds to ___________ What is an ANTIGEN? __________________________ For example specific pathogen or toxin or cancer cell What is an ANTIBODY? ________________________ _____________________________________________ B-Cells – mature in ____________________________ - __________________ response attacks pathogens circulating in blood and lymph. They produce ______________. Types - _________ and ________. T-Cells – mature in _________. _________ response recognize and attack ____________________. Three types of T cells are ___________________________. Inflammatory Response – local non-specific trigger when tissue is damaged 1. ___________________________________ _____________________________________ 2. ___________________________________ _____________________________________ 3. ___________________________________ _____________________________________ 4. ___________________________________ _____________________________________ __ Vaccination: a form of active immunity when a weakened or inactive pathogen is given to ____________________________________________________________________________. Passive Immunity - __________________________________________________________________. HIV – infects and destroys _________ cells which then do not activate ___________ & __________ Why do you take an antihistamine? _____________________________________________________ 15 Immune System Defender Game Immune Responses http://www.nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/immunity/ www.nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/immuneresponses/about.html What happens in your body when you are wounded? __ _____________________________________________ What cell types are involved in the immune system? ___ _____________________________________________ How do immune cells remove bacteria? _____________ _____________________________________________ Some immune cells alert other immune cells about invading bacteria. Which ones? ___________________ _____________________________________________ What happens when our body is attacked by foreign substances? ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ What is immunity? _____________________________________ ____________________________________________________ How do vaccines work? _________________________________ ____________________________________________________ How does our body get rid of bacteria and viruses? ___________ ____________________________________________________ 16 Animal Form and Function A Study of the Organ Systems Endocrine System 12 Function: ________________________________ _________________________________________ Define Hormone:___________________________ _________________________________________. 2 Works closely with the ______________ system which ________________________ of _________ and _________________ system to deliver them. Place the correct number next to the structure _____ Hypothalamus _____ Uterus _____ Thyroid _____ Kidney _____ Parathyroid _____ Thymus _____ Adrenal _____ Pancreas _____ Testes _____ Ovary _____ Pituitary _____ Pineal GLAND/LOCATION HORMONE Hypothalamus Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid Pancreas Adrenal Ovaries Testes FUNCTION Control center for autonomic functions. Connects with the endocrine (hypothalamus) and nervous systems to maintain homeostasis and influence emotional responses. Contraction of uterus; tells kidneys to reabsorb water; protein synthesis & growth in bones; production and release of breast milk; stimulate production of ova & sperm; Stimulates the thyroid gland; tells adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids Stimulate and maintain Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), which is the amount of energy the body uses; ↓ blood Ca2+ level Raises blood calcium level Cluster of cells, islets of Langerhans, contain beta cells secrete insulin and ↓ blood glucose levels; alpha cells secrete glucagon and ↑ blood glucose levels Raise blood glucose level; increase metabolic activities; prepares the body for “fright, fight or flight”; promote reabsorption of Na+ and excretion of K+ in kidneys Stimulate uterine lining growth, development and maintenance of female secondary sex characteristics Support sperm formation, development and maintenance of male secondary sex characteristics 17 _________ FEEDBACK: MORE GETS YOU LESS _______ FEEDBACK: MORE GETS YOU MORE Here are several problems that describe feedback loops. Read each problem, decide if each is a positive or a negative feedback loop, and record your answers on your worksheets. Problem #1: When you become dehydrated, and the osmolality of the blood increases (meaning your blood has more salt and less water), osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus cause the posterior pituitary to secrete anti-diuretic hormone (ADH). ADH acts on the kidney to increase the reabsorption of water, and put the water back into your bloodstream. This helps prevent the osmolality of the blood from increasing even further. If you drink lots of water, ADH production decreases, and the kidneys remove water from the blood, again maintaining the osmolality of the blood. Is this a positive or negative feedback loop? Problem #2: During childbirth, the fetus is pushed against the uterine opening, causing it to stretch. Receptors that detect the stretching send signals to the brain. The brain sends both neural and hormonal signals which increase both the contraction force and the contraction frequency in the smooth muscles of the uterus. This continues until the baby is delivered through the birth canal. Is this a positive or negative feedback loop? Problem #3: An increase of carbon dioxide in the blood leads to a decrease in blood pH. The drop in blood pH is detected by chemoreceptors in the aorta and carotid artery. These receptors send nerve impulses to the respiratory center in the medulla oblongata in the brain, which then stimulates increased breathing. Increased breathing helps remove carbon dioxide from the blood, returning blood pH to normal levels. Is this a positive or negative feedback loop? Problem #4: After eating a meal, your blood glucose level increases. Islet cells in your pancreas detect the rise in blood sugar, and release insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin binds to receptors on cells throughout the body, allowing the cells to take up glucose from the blood. This lowers blood glucose levels back to a normal level. Is this a positive or negative feedback loop? Problem #5: When thyroxine levels in the body are low, the hypothalamus secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). TRH acts on the anterior pituitary causing the secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH, in turn, acts on the thyroid gland, causing secretion of thyroxine. Increased levels of thyroxine act on both the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary, decreasing the release of both TRH and TSH. Is this a positive or negative feedback loop? 18 Animal Form and Function A Study of the Organ Systems Integumentary System Main Function: _____________________ ___________________________________ EPIDERMIS -consists of ___ layers of __ kinds of cells How often do cells undergo cell division _________ Keratin is____________________________________ Major Structures: ___________________ ___________________________________ Melanin is ___________________________________ Works closely with the _______________ system ___________________________. ____________________________________________ FACTS: The Skin is the human body's ____________ __________. The word INTEGUMENT comes from LATIN and means ______________ OTHER FUNCTIONS 1. Serves as a _____________ against infection and injury. 2. Helps to regulate _______________. 3. Removes __________ from the body. Why does a small scratch not bleed?____________ DERMIS- ___________ layer composed of collagen, elastic fibers, fibroblasts, macrophage, fat cells hair, glands, nerve and blood vessels. ___________________ is the layer below the Dermis Two Glands are _____________ and _____________ HAIR is produced by _____________________ and it ______________ and _________________ the body. What causes hair to grow?_____________________ ____________________________________________ Why does hair get oily?________________________ 4. Provides _________________ against ultraviolet radiation from the sun. NAILS – grow from the ________________________ 5. Produces _____________________ and are located ________________of fingers & toes. Why are nails pink?___________________________ 1 Fat, Collagen, Fibroblasts 2 Hair 3 Subcutaneous Tissue 4 Dermis 5 Nerve 6 Arteriole 7 Muscle 8 Sebaceous Gland 9 Epidermis 10 Sensory Nerve Ending 11 Capillaries 12 Sweat Gland Which nails grow faster fingers or toes?(circle) Number the diagram. 19 Animal Form and Function A Study of the Animal Form and Function Reproductive System Function: __________________________________________________________________________ Major Structures: ____________________________________________________________________ Types of Cells: ______________________________________________________________________ Works closely with the _____________________ system to ________________________________. Match the correct structure with the function Structure Match the correct structure with the function. Structure Function pair of tubes that transport eggs from ovary to uterus pair of organs that produces eggs, estrogen and progesterone one of the small ovarian sacs containing an immature ovum hollow muscular organ that nourishes and develops embryo before birth yellow mass of tissue that forms in the ovary after ovulation & secretes progesterone mucous membrane that lines the womb & increases in thickness during menstruation narrow passage leading to the vagina Structure 20 Function coiled tube attached to testicle; stores sperm; connected to the vas deferens an expanding muscular sac that collects urine Fold of the body wall which contains the gonads O"-shaped gland; surrounds the urethra below the bladder, secreting a fluid into the semen pair of glands that secrete the fluid of semen into the ejaculatory duct Produce gametes & hormones Muscular duct running from epididymis & out of the scrotum Drains both the excretory & reproductive systems Function muscular tube that connects the cervix of the womb to the vulva