Human body systems
... • There are different types of jointsimmoveable (skull), moveable (ball and socket) , and slightly moveable (vertebrate). ...
... • There are different types of jointsimmoveable (skull), moveable (ball and socket) , and slightly moveable (vertebrate). ...
Bio Notes Last modified January 9, 2017 at 5:21 am
... Muscle fibres: nerves tell them to contract, so calcium is released onto the fibres, which causes them to contract (myosin and actin attach.) ATP removes calcium and myosin and ...
... Muscle fibres: nerves tell them to contract, so calcium is released onto the fibres, which causes them to contract (myosin and actin attach.) ATP removes calcium and myosin and ...
ZOO 362-COMPARATIVE ANIMAL PHYSIOLOGY The study
... from the cell body. Most axons, and only axons, are ensheathed in lamellae derived from the cellular membranes of SCHWANN CELLS which enclose lipids and proteins and help to coat the axons, this coating is called MYELIN SHEATH. The portion of the axon coated by myelin is the AXON CYLINDER and the po ...
... from the cell body. Most axons, and only axons, are ensheathed in lamellae derived from the cellular membranes of SCHWANN CELLS which enclose lipids and proteins and help to coat the axons, this coating is called MYELIN SHEATH. The portion of the axon coated by myelin is the AXON CYLINDER and the po ...
Chapter 4 - Tracy Jubenville Nearing
... different skeletons, including a different elbow angle. Males have slightly thicker and longer legs and arms; females have a wider pelvis and a larger space within the pelvis, through which babies travel when they are born. ...
... different skeletons, including a different elbow angle. Males have slightly thicker and longer legs and arms; females have a wider pelvis and a larger space within the pelvis, through which babies travel when they are born. ...
Transport Systems
... Reproductive Adaptations • Plants produce their gametes in protective structures called gametangia to protect them from dehydration. • Most plants rely on wind or animals to disperse pollen or seeds for fertilization. ...
... Reproductive Adaptations • Plants produce their gametes in protective structures called gametangia to protect them from dehydration. • Most plants rely on wind or animals to disperse pollen or seeds for fertilization. ...
Lab 2: Cells and Tissues Pre Lab 2 Test
... TISSUES In animals, most cells have differentiated into distinct tissues. • Tissues are composed of differentiated cells that aggregate to perform specific functions. For example, the connective tissue blood is formed from red blood cells (which specialize in carrying O2 and CO2), white blood cells, ...
... TISSUES In animals, most cells have differentiated into distinct tissues. • Tissues are composed of differentiated cells that aggregate to perform specific functions. For example, the connective tissue blood is formed from red blood cells (which specialize in carrying O2 and CO2), white blood cells, ...
Honeybee Heart
... Honeybee Heart Life is an emergent property, defined in terms of a cell, limited by a membrane, which separates the boundary of the living system inside from the non-living outside. This is simply true for the vast world of unicellular organisms. Larger organisms - plants and animals - that are mult ...
... Honeybee Heart Life is an emergent property, defined in terms of a cell, limited by a membrane, which separates the boundary of the living system inside from the non-living outside. This is simply true for the vast world of unicellular organisms. Larger organisms - plants and animals - that are mult ...
The Circulatory System
... When your heart beats it pushes blood out of the right ventricle to the lungs. The bloods cells that are carried to the lungs release carbon dioxide and gain oxygen so that when you breath in you inhale oxygen and when you exhale your lungs release carbon dioxide. Then the red blood cells take oxyge ...
... When your heart beats it pushes blood out of the right ventricle to the lungs. The bloods cells that are carried to the lungs release carbon dioxide and gain oxygen so that when you breath in you inhale oxygen and when you exhale your lungs release carbon dioxide. Then the red blood cells take oxyge ...
How is it different from traditional agricultural breeding and genetic
... Synthetic biology is a new way of combining biology and engineering to create new or modified living organisms and materials that do not currently exist in the natural world. Scientists are developing a library of standard biological parts with known functions that can be put together in combinations ...
... Synthetic biology is a new way of combining biology and engineering to create new or modified living organisms and materials that do not currently exist in the natural world. Scientists are developing a library of standard biological parts with known functions that can be put together in combinations ...
Bacteria 1
... Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction is a process that involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent. During this process, a cell duplicates its genetic material and then divides into two separate cells. Each new cell gets its own ...
... Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction is a process that involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent. During this process, a cell duplicates its genetic material and then divides into two separate cells. Each new cell gets its own ...
Hydra magnipapillata Taxonomy -
... Hydra shows extreme regeneration capability: when hydra polyps are cut to pieces they regenerate the missing structures completely. The hydra's body can even be macerated into individual cells that after brief centrifugation form aggregates, from which heads and feet will appear over the course of a ...
... Hydra shows extreme regeneration capability: when hydra polyps are cut to pieces they regenerate the missing structures completely. The hydra's body can even be macerated into individual cells that after brief centrifugation form aggregates, from which heads and feet will appear over the course of a ...
Review Key
... 48. Sample Dihybrid Cross Question: The table below shows a cross between two pea plants both heterozygous for yellow seeds (Bb) and round seeds (Rr). What phenotype ratio would you expect in the offspring? ...
... 48. Sample Dihybrid Cross Question: The table below shows a cross between two pea plants both heterozygous for yellow seeds (Bb) and round seeds (Rr). What phenotype ratio would you expect in the offspring? ...
Mr. Altorfer Science
... ► Human sperm cells and human egg cells have 23 chromosomes. ► 23 chromosomes from the sperm and 23 chromosomes from the egg gives you a complete set of 46 chromosomes. ...
... ► Human sperm cells and human egg cells have 23 chromosomes. ► 23 chromosomes from the sperm and 23 chromosomes from the egg gives you a complete set of 46 chromosomes. ...
Exam 2A key
... animals? (1 pt) List one other physical feature of water that would make an insect-like respiratory system unsuitable for a crustacean. (1 pt, 2 pts total) The solubility of O2 in water is very low (i.e., water cannot hold much O2). Two possible features as well: i) Water is very dense and ii) diffu ...
... animals? (1 pt) List one other physical feature of water that would make an insect-like respiratory system unsuitable for a crustacean. (1 pt, 2 pts total) The solubility of O2 in water is very low (i.e., water cannot hold much O2). Two possible features as well: i) Water is very dense and ii) diffu ...
Exam 2B key
... CD4 and the CCR5 receptor (CD4 and CRXR5/fusin okay too, although these appear more important in the latter stages of infection) 12. Briefly, why is the decline in helper T cells seen in AIDS so crippling for the immune system? Helper T cells play a critical role in stimulating other components of t ...
... CD4 and the CCR5 receptor (CD4 and CRXR5/fusin okay too, although these appear more important in the latter stages of infection) 12. Briefly, why is the decline in helper T cells seen in AIDS so crippling for the immune system? Helper T cells play a critical role in stimulating other components of t ...
Kingdom Eubacteria
... Cell membrane – surround the cell and give it its’ __________. Nucleus – control center of the cell. Nuclear membrane – surrounds and protects the _______________. Chromosomes – the DNA of the cell (information) Ribosomes – make protein for the cell. (remember, DNA makes RNA, RNA moves out of the nu ...
... Cell membrane – surround the cell and give it its’ __________. Nucleus – control center of the cell. Nuclear membrane – surrounds and protects the _______________. Chromosomes – the DNA of the cell (information) Ribosomes – make protein for the cell. (remember, DNA makes RNA, RNA moves out of the nu ...
foreign antigen
... higher temperature helps defense inhibits bacterial growth stimulates phagocytosis speeds up repair of tissues causes liver & spleen to store ...
... higher temperature helps defense inhibits bacterial growth stimulates phagocytosis speeds up repair of tissues causes liver & spleen to store ...
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
... In animal cells, the cell membrane is the partially permeable membrane that allows osmosis to occur. If red blood cells are placed into a hypotonic solution (i.e. distilled water), the water will cross ...
... In animal cells, the cell membrane is the partially permeable membrane that allows osmosis to occur. If red blood cells are placed into a hypotonic solution (i.e. distilled water), the water will cross ...
AS BIOLOGY UNITS
... In multicellular organisms, stem cells are modified to produce many different types of specialised cell. Understanding how stems cells can be modified has huge potential in medicine. To understand how a whole organism functions, it is essential to understand the importance of cooperation between cel ...
... In multicellular organisms, stem cells are modified to produce many different types of specialised cell. Understanding how stems cells can be modified has huge potential in medicine. To understand how a whole organism functions, it is essential to understand the importance of cooperation between cel ...
Glossary of Terms and Acronyms
... Pneumoconiosis: A condition characterized by the deposition of mineral dust in the lungs as a result of occupational or environmental exposure. Pulmonary edema: The accumulation of abnormally large amounts of watery fluid within the pulmonary alveoli. Pulmonary fibrosis: The accumulation of abnormal ...
... Pneumoconiosis: A condition characterized by the deposition of mineral dust in the lungs as a result of occupational or environmental exposure. Pulmonary edema: The accumulation of abnormally large amounts of watery fluid within the pulmonary alveoli. Pulmonary fibrosis: The accumulation of abnormal ...
human anatomy
... A) All humans (and most other organisms) begin life as a single cell. 1. This single cell is called a zygote. 2. The nucleus of this cell has all the genes needed to become a complete organism. B) Humans grow as a result of mitosis (cell division). 1. This quickly increases the number of cells in th ...
... A) All humans (and most other organisms) begin life as a single cell. 1. This single cell is called a zygote. 2. The nucleus of this cell has all the genes needed to become a complete organism. B) Humans grow as a result of mitosis (cell division). 1. This quickly increases the number of cells in th ...
powerpoint note presentation
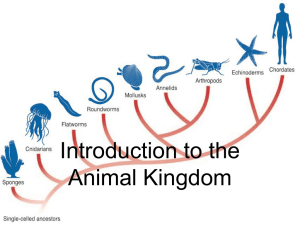
... • Animals are multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph whose cells lack cell walls, digestion is internal • Vertebrates: 5% of animal species with backbones • Invertebrates: 95% of animal species WITHOUT backbones • Cell specialization – special shape, physical structure, and chemical composition to per ...
... • Animals are multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph whose cells lack cell walls, digestion is internal • Vertebrates: 5% of animal species with backbones • Invertebrates: 95% of animal species WITHOUT backbones • Cell specialization – special shape, physical structure, and chemical composition to per ...
B2 Revision Pack F1
... body cells 1.14 Recall that mitosis occurs during growth, repair and asexual reproduction 1.15 Recall that, at fertilisation, haploid gametes combine to form a diploid zygote 1.16 Describe the division of a cell by meiosis as the production of four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromo ...
... body cells 1.14 Recall that mitosis occurs during growth, repair and asexual reproduction 1.15 Recall that, at fertilisation, haploid gametes combine to form a diploid zygote 1.16 Describe the division of a cell by meiosis as the production of four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromo ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are