Interactions in Animals
... takes three to five hours, as only small amounts of blood are being filtered at any time. The Reproductive System Animals can pass on their genes by producing offspring during reproduction. Some animals reproduce asexually, while others, including mammals, reproduce sexually. In asexual reproduction ...
... takes three to five hours, as only small amounts of blood are being filtered at any time. The Reproductive System Animals can pass on their genes by producing offspring during reproduction. Some animals reproduce asexually, while others, including mammals, reproduce sexually. In asexual reproduction ...
The Respiratory System Quiz
... A. The tube connecting the lungs to the outside of the body. B. The network of second-largest air sacs within each lung. C. The outermost lining of the lungs. 3. What is the diaphragm? A. The seal of tissue at the top of the trachea that stops food or drink from being inhaled. B. A sheet of muscle b ...
... A. The tube connecting the lungs to the outside of the body. B. The network of second-largest air sacs within each lung. C. The outermost lining of the lungs. 3. What is the diaphragm? A. The seal of tissue at the top of the trachea that stops food or drink from being inhaled. B. A sheet of muscle b ...
Porifera
... • Basal disc – bottom end of the gastrovascular cavity • Mouth – opening to the gastrovascular cavity • Tentacles – structures that capture prey and shove them into the mouth • Cnidocytes – capsule cell containing a fine coiled thread, which, when discharged, functions in defense and prey capture • ...
... • Basal disc – bottom end of the gastrovascular cavity • Mouth – opening to the gastrovascular cavity • Tentacles – structures that capture prey and shove them into the mouth • Cnidocytes – capsule cell containing a fine coiled thread, which, when discharged, functions in defense and prey capture • ...
Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes
... cell death caused by heat, electricity, UV, chemicals. a. body loses fluids 1. rule of nine – divides body into 11 sections, 9 % each to determine % of body burned. b. infection occurs c. type of burns 1. 1st degree burns –only epidermis is damage. (sunburn usually). ...
... cell death caused by heat, electricity, UV, chemicals. a. body loses fluids 1. rule of nine – divides body into 11 sections, 9 % each to determine % of body burned. b. infection occurs c. type of burns 1. 1st degree burns –only epidermis is damage. (sunburn usually). ...
The Excretory System
... Thyroid gland The small brownish glandular mass found on either side of the anterior end of the trachea. ...
... Thyroid gland The small brownish glandular mass found on either side of the anterior end of the trachea. ...
paramedics - anatomy and physiology.indb
... All living things are composed of cells, which are the smallest units of life and are so small they can only be viewed through a microscope. Cells are made from pre-existing cells through cell replication and division. The human body is composed of billions of cells which are specially adapted for t ...
... All living things are composed of cells, which are the smallest units of life and are so small they can only be viewed through a microscope. Cells are made from pre-existing cells through cell replication and division. The human body is composed of billions of cells which are specially adapted for t ...
Chapter 1
... a) The cardiovascular system, made up of the heart and blood vessels, distributes oxygen and nutrients throughout the body while removing wastes from the cells. b) The lymphatic system, consisting of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen, drains excess tissue fluid and includes cells of ...
... a) The cardiovascular system, made up of the heart and blood vessels, distributes oxygen and nutrients throughout the body while removing wastes from the cells. b) The lymphatic system, consisting of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen, drains excess tissue fluid and includes cells of ...
Z - Characteristics of Animals and Body Plans
... composed of many cells. – The cells that make up animal bodies are eukaryotic, containing a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. ...
... composed of many cells. – The cells that make up animal bodies are eukaryotic, containing a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. ...
Organ Systems of the Body
... Regional – all structures in one part of the body (such as the abdomen or leg) Systemic – gross anatomy of the body studied by system Surface – study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin ...
... Regional – all structures in one part of the body (such as the abdomen or leg) Systemic – gross anatomy of the body studied by system Surface – study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin ...
Modified Notes
... 2. What types of tissues make up the skeletal system? Connective tissue Cartilage made of protein fibers Bone is formed during “ossification” when cartilage hardens 3. What are bones? A solid network of LIVING cells and protein fibers that are surrounded by deposits of calcium salts. 4. What i ...
... 2. What types of tissues make up the skeletal system? Connective tissue Cartilage made of protein fibers Bone is formed during “ossification” when cartilage hardens 3. What are bones? A solid network of LIVING cells and protein fibers that are surrounded by deposits of calcium salts. 4. What i ...
ExamView - Anatomy REVIEW for Final Exam 2015.tst
... ____ 48. Which type of tissue provides support for the body? a. epithelial c. nerve b. connective d. muscle ____ 49. The process by which organ systems maintain relatively constant internal conditions is called a. circulation. c. homeostasis. b. organization. d. teamwork. ____ 50. Which process enab ...
... ____ 48. Which type of tissue provides support for the body? a. epithelial c. nerve b. connective d. muscle ____ 49. The process by which organ systems maintain relatively constant internal conditions is called a. circulation. c. homeostasis. b. organization. d. teamwork. ____ 50. Which process enab ...
Chapter 26: Sponges, Cnidarians, Flatworms and Roundworms
... Sessile - permanently attached to a surface for all of its adult life Get food by filter feeding (filter small particles of food from the water as it pass’s by or through some part of the organism) ...
... Sessile - permanently attached to a surface for all of its adult life Get food by filter feeding (filter small particles of food from the water as it pass’s by or through some part of the organism) ...
major organ systems in the human body
... homeostasis; regulates other organ systems; controls sensory and motor functions ...
... homeostasis; regulates other organ systems; controls sensory and motor functions ...
Primary embryonic germ layers
... Outer Body Covering • The body of some platyhelminthes (e.g., turbellarians) is covered by a ciliated epidermis. • Epidermal cells contain rod-shaped structures called rhabdites that when released into the surrounding water, expand and form a protective mucous coat around the animal ...
... Outer Body Covering • The body of some platyhelminthes (e.g., turbellarians) is covered by a ciliated epidermis. • Epidermal cells contain rod-shaped structures called rhabdites that when released into the surrounding water, expand and form a protective mucous coat around the animal ...
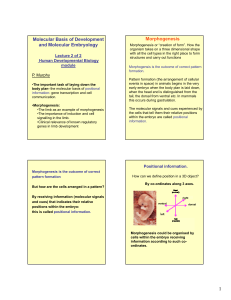
Molecular Basis of Development and Molecular Embryology
... proper bones and joints •This This is because the contractions generate mechanical stimuli that are needed for cell differentiation, cell division and morphogenesis. Change in skeletal rudiments 2 days of development apart ...
... proper bones and joints •This This is because the contractions generate mechanical stimuli that are needed for cell differentiation, cell division and morphogenesis. Change in skeletal rudiments 2 days of development apart ...
Biology 102 Exam II
... What part of this organ is responsible for delivering blood to the systemic body? How many valves does the heart have? What are the three main cell types found in blood? Which aspect of the body’s immune system is charged with defending against unknown agents or new infections? Which aspect of the b ...
... What part of this organ is responsible for delivering blood to the systemic body? How many valves does the heart have? What are the three main cell types found in blood? Which aspect of the body’s immune system is charged with defending against unknown agents or new infections? Which aspect of the b ...
The Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
... 1. Periostium - soft thin substance that covers and protects the bone. 2. Compact bone – tough, hard bone that can heal itself when broken. 3. Spongy bone – contains red marrow which produces red blood cells that carry oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the day 4. Marrow – soft, inner center of bo ...
... 1. Periostium - soft thin substance that covers and protects the bone. 2. Compact bone – tough, hard bone that can heal itself when broken. 3. Spongy bone – contains red marrow which produces red blood cells that carry oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the day 4. Marrow – soft, inner center of bo ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... (1) botulism and typhoid fever (2) tetanus and pneumonia 3. Which sequence lists the levels of organization (3) botulism and pneumonia (4) tetanus and typhoid fever in the human body from simplest to most complex? (1) organ system → tissue → cell → organ 7. The diagram shows a part of a human body s ...
... (1) botulism and typhoid fever (2) tetanus and pneumonia 3. Which sequence lists the levels of organization (3) botulism and pneumonia (4) tetanus and typhoid fever in the human body from simplest to most complex? (1) organ system → tissue → cell → organ 7. The diagram shows a part of a human body s ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... from smaller ones. The body stores water, food and oxygen for a time when the substances will be needed. • Catabolism - is the phase of metabolism that involves the breaking down of the stored larger substances into smaller one thus releasing the cells stored energy. Note: Anabolism and catabolism a ...
... from smaller ones. The body stores water, food and oxygen for a time when the substances will be needed. • Catabolism - is the phase of metabolism that involves the breaking down of the stored larger substances into smaller one thus releasing the cells stored energy. Note: Anabolism and catabolism a ...
Mayra Funes - El Camino College
... 31. The inflammatory response involves ________________: release of chemical alarm signals a. redness, swelling b. arrival of phagocytic white cells c. fever d. all of them 32. The location where gas exchange occurs in the mammalian lung is the ________. a. bronchus b. trachea c. diaphragm d. alveol ...
... 31. The inflammatory response involves ________________: release of chemical alarm signals a. redness, swelling b. arrival of phagocytic white cells c. fever d. all of them 32. The location where gas exchange occurs in the mammalian lung is the ________. a. bronchus b. trachea c. diaphragm d. alveol ...
C. Egg - Cloudfront.net
... By the 8th week of development, the embryo is recognizable as human. About 38 mm long at this point. ...
... By the 8th week of development, the embryo is recognizable as human. About 38 mm long at this point. ...
The circulatory system - Bingham-5th-2014
... abundant (existing or available in large quantities) cell type in the blood . Other major blood components include plasma, white blood cells, and platelets. The primary function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen to body cells and deliver carbon dioxide to the lungs . A red blood cell has wha ...
... abundant (existing or available in large quantities) cell type in the blood . Other major blood components include plasma, white blood cells, and platelets. The primary function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen to body cells and deliver carbon dioxide to the lungs . A red blood cell has wha ...