chapter 4: tissues - Warner Pacific College
... cells with central nuclei; no striations; cells arranged closely to form sheets. Function: Propels substances or objects (foodstuffs, urine, a baby) along internal passageways; involuntary control. Location: Mostly in the walls of hollow organs. ...
... cells with central nuclei; no striations; cells arranged closely to form sheets. Function: Propels substances or objects (foodstuffs, urine, a baby) along internal passageways; involuntary control. Location: Mostly in the walls of hollow organs. ...
PACT Review for 7th Grade Science
... Plants cells usually have one or more large vacuole(s), while animal cells have smaller vacuoles, if any are present. Large vacuoles help provide shape and allow the plant to store water and food for future use. It is not essential for students to know other organelles in plant and animal cells or t ...
... Plants cells usually have one or more large vacuole(s), while animal cells have smaller vacuoles, if any are present. Large vacuoles help provide shape and allow the plant to store water and food for future use. It is not essential for students to know other organelles in plant and animal cells or t ...
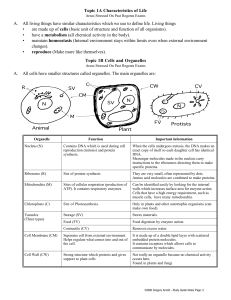
Topic 1A Characteristics of Life A. All living things have similar
... Areas Stressed On Past Regents Exams ...
... Areas Stressed On Past Regents Exams ...
File - MR. Wilson`s 8th Grade Science Class
... 30. ______________________: An organism that can make it’s own food 31. ______________________: Synonym of “consumer” 32. ______________________: Synonym of “producer “ 33. ______________________: Process in which organisms use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make food and oxygen 34. ________ ...
... 30. ______________________: An organism that can make it’s own food 31. ______________________: Synonym of “consumer” 32. ______________________: Synonym of “producer “ 33. ______________________: Process in which organisms use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make food and oxygen 34. ________ ...
Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have
... If a cell contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, it is ...
... If a cell contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, it is ...
Scaling up Delivery Guide
... understand the electrical and ‘mechanical’ activity of the heart. With the increasing size of the population, the need for food production is vital. Food production depends greatly on the environmental conditions the water levels and nutrient ability. The transport systems in plants are important fo ...
... understand the electrical and ‘mechanical’ activity of the heart. With the increasing size of the population, the need for food production is vital. Food production depends greatly on the environmental conditions the water levels and nutrient ability. The transport systems in plants are important fo ...
Ch. 20 Presentation
... the environment Every organism is an open system that must exchange matter and energy with its surroundings. Cells in small and flat animals can exchange materials directly with the environment. ...
... the environment Every organism is an open system that must exchange matter and energy with its surroundings. Cells in small and flat animals can exchange materials directly with the environment. ...
Organization of the Human Body
... • All Systems Go at http://sciencenetlinks.com/interactives/systems.html ...
... • All Systems Go at http://sciencenetlinks.com/interactives/systems.html ...
Homeostasis: process of maintaining consistent
... A balance of positive and negative charges is maintained in each compartment, but by different ions. ...
... A balance of positive and negative charges is maintained in each compartment, but by different ions. ...
BIOC31 H3 Molecular Aspects of Plant Development Fall 2013
... Course prerequisites: BIOB10H (Cell Biology) BIOB11H (Molecular Aspects of Cellular & Genetic Processes) BIOB31H (Plant Physiology) ...
... Course prerequisites: BIOB10H (Cell Biology) BIOB11H (Molecular Aspects of Cellular & Genetic Processes) BIOB31H (Plant Physiology) ...
Juice/Broth Cleansing Program
... effectiveness of fasting as curative and rejuvenating therapy! - your body will just decompose and burn those cells and tissues which are diseased, damaged, aged or dead. In fasting, your body feeds itself on the most impure and inferior materials, such as dead cells and morbid accumulations, tumors ...
... effectiveness of fasting as curative and rejuvenating therapy! - your body will just decompose and burn those cells and tissues which are diseased, damaged, aged or dead. In fasting, your body feeds itself on the most impure and inferior materials, such as dead cells and morbid accumulations, tumors ...
Chapter 17: Cellular Mechanisms of Development
... and animals share many key elements. However, the mechanisms used to achieve body form are quite different. While animal cells follow an orchestrated series of movements during development, plant cells are encased within stiff cellulose walls, and, therefore, cannot move. Each cell in a plant is fix ...
... and animals share many key elements. However, the mechanisms used to achieve body form are quite different. While animal cells follow an orchestrated series of movements during development, plant cells are encased within stiff cellulose walls, and, therefore, cannot move. Each cell in a plant is fix ...
GCSE Biology Textbook sample
... The size of sub-cellular structures is important. Mitochondria and chloroplasts vary in size and shape. The complexity of a mitochondrion indicates how active a cell is. Chloroplast size varies from one species to another. Scientists sometimes investigate the ratio of the area of the cytoplasm t ...
... The size of sub-cellular structures is important. Mitochondria and chloroplasts vary in size and shape. The complexity of a mitochondrion indicates how active a cell is. Chloroplast size varies from one species to another. Scientists sometimes investigate the ratio of the area of the cytoplasm t ...
Animal Primary Tissues
... Adipose tissue, or fat tissue, is considered a connective tissue even though it does not have broblasts or a real matrix and only has a few bers. Adipose tissue is made up of cells called adipocytes that collect and store fat in the form of triglycerides, for energy metabolism. Adipose tissues add ...
... Adipose tissue, or fat tissue, is considered a connective tissue even though it does not have broblasts or a real matrix and only has a few bers. Adipose tissue is made up of cells called adipocytes that collect and store fat in the form of triglycerides, for energy metabolism. Adipose tissues add ...
jan 1998
... a) Draw a graph that compares the pH to the amount of egg white remaining in each test tube. Label the x-axis (horizontal axis) as pH. ...
... a) Draw a graph that compares the pH to the amount of egg white remaining in each test tube. Label the x-axis (horizontal axis) as pH. ...
Chapter 1 honors review questions
... Each successive generation will include more members with the new advantageous C)variations. In the end, most members of a species have the same adaptations to their D)environment. E)Evolution can be used to explain the unity and diversity of life. ...
... Each successive generation will include more members with the new advantageous C)variations. In the end, most members of a species have the same adaptations to their D)environment. E)Evolution can be used to explain the unity and diversity of life. ...
Unit 3 _Human Anat and Phys
... from their father, and that sexually produced offspring resemble, but are not identical to, either of their parents. (4.6) ...
... from their father, and that sexually produced offspring resemble, but are not identical to, either of their parents. (4.6) ...
Ventilation!
... • ___________: process of gas _________ between the ___________ and the ______ • Wall of the ________ are made of ________ __________ cells • Respiratory __________: squamous ________ cells ___ cell layers thick that ________ air in the _______ from ______ in the capillary – Contains basement me ...
... • ___________: process of gas _________ between the ___________ and the ______ • Wall of the ________ are made of ________ __________ cells • Respiratory __________: squamous ________ cells ___ cell layers thick that ________ air in the _______ from ______ in the capillary – Contains basement me ...
Communicating Research to the General Public
... disadvantage is that we don't look at the molecule in its native state, but we have more control over the modifications on the molecule and the environment, and can obtain more physical parameters. A third approach is in silico, or computational analysis. In silico analyses observe the molecule's pa ...
... disadvantage is that we don't look at the molecule in its native state, but we have more control over the modifications on the molecule and the environment, and can obtain more physical parameters. A third approach is in silico, or computational analysis. In silico analyses observe the molecule's pa ...
Unit 3 Revision Notes - St. Mary`s Independent School
... Most of the transpiration is through stomata. The size of stomata is controlled by guard cells which surround them. If plants lose water faster than the roots replace it, the stomata can close to prevent ...
... Most of the transpiration is through stomata. The size of stomata is controlled by guard cells which surround them. If plants lose water faster than the roots replace it, the stomata can close to prevent ...
Identify the features that animals have in common. • Distinguish
... a. Almost all animals reproduce sexually by producing gametes, as do many plants, fungi, and protists. b. The females’ egg cells are much larger than the males’ sperm cells. c. Unlike the egg cells, the sperm cells of animals have flagella and are highly mobile. 6. Absence of a Cell Wall a. Among th ...
... a. Almost all animals reproduce sexually by producing gametes, as do many plants, fungi, and protists. b. The females’ egg cells are much larger than the males’ sperm cells. c. Unlike the egg cells, the sperm cells of animals have flagella and are highly mobile. 6. Absence of a Cell Wall a. Among th ...
22 THE ANIMAL BODY AND HOW IT MOVES
... wastes from one point within the body to another. 2. Adipose tissue stores fat for future use. 3. The blood transports nutrients, gases, and wastes using its individual components: erythrocytes, also known as red blood cells, transport oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body, and plasma carrie ...
... wastes from one point within the body to another. 2. Adipose tissue stores fat for future use. 3. The blood transports nutrients, gases, and wastes using its individual components: erythrocytes, also known as red blood cells, transport oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body, and plasma carrie ...
BIOL 2401 Unit and Final Exam Study Guides
... 10. The thigh bone is also called … 11. The hip joint is composed of the acetabulum and … 12. The three fused bones which make up the hipbone (coxae) are … 13. Name the different processes found on the bone and define them. 14. What bones make up the axial skeleton? 15. Give two examples of so ...
... 10. The thigh bone is also called … 11. The hip joint is composed of the acetabulum and … 12. The three fused bones which make up the hipbone (coxae) are … 13. Name the different processes found on the bone and define them. 14. What bones make up the axial skeleton? 15. Give two examples of so ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.