Diversity of Life Taxonomy
... It is clear that the above can lead to confusion when scientists of different countries are trying to communicate with each other. Another example is the burrowing rodent called a gopher found throughout the western United States. In the southeastern United States the term gopher refers to a burrowi ...
... It is clear that the above can lead to confusion when scientists of different countries are trying to communicate with each other. Another example is the burrowing rodent called a gopher found throughout the western United States. In the southeastern United States the term gopher refers to a burrowi ...
Oct 2310:58 AM Comparing Cells Lab Analysis Questions
... Comparing Cells Lab Analysis Questions 1. Describe 3 differences between the plant cells and the animal cells you looked at. 2. Thinking about how the structure and arrangement of cells contributes to the functioning of the organism, propose reasons for the differences you mentioned. 3. Why do ...
... Comparing Cells Lab Analysis Questions 1. Describe 3 differences between the plant cells and the animal cells you looked at. 2. Thinking about how the structure and arrangement of cells contributes to the functioning of the organism, propose reasons for the differences you mentioned. 3. Why do ...
Topic 1 - Danielle`s science9 weebly
... The process of digestion breaks down the chemicals present in food. The molecules are small and soluble, which can then pass through membranes into your blood. These chemicals (nutrients) are then carried throughout your body to the cells which need them for energy, growth, body building and cell re ...
... The process of digestion breaks down the chemicals present in food. The molecules are small and soluble, which can then pass through membranes into your blood. These chemicals (nutrients) are then carried throughout your body to the cells which need them for energy, growth, body building and cell re ...
1.1 Where organisms live 1.2 - Pearson-Global
... seasons. The oak trees burst into leaf in late spring so that they gain the maximum amount of sunshine in the warmest conditions. Underneath the oak trees, holly trees have very thick dark green leaves to absorb as much light as possible in the shade of the bigger trees above. Squirrels are active d ...
... seasons. The oak trees burst into leaf in late spring so that they gain the maximum amount of sunshine in the warmest conditions. Underneath the oak trees, holly trees have very thick dark green leaves to absorb as much light as possible in the shade of the bigger trees above. Squirrels are active d ...
plants - Images
... • Some plants reproduce asexually by a process called vegetative propagation ...
... • Some plants reproduce asexually by a process called vegetative propagation ...
Inside The Living Body http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HBIYwiktPsQ
... (B.10) Science concepts. The student knows that biological systems are composed of multiple levels. The student is expected to (A) describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of regulation, nutrient absorption, reproduction, and defense from injury or illness in ani ...
... (B.10) Science concepts. The student knows that biological systems are composed of multiple levels. The student is expected to (A) describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of regulation, nutrient absorption, reproduction, and defense from injury or illness in ani ...
Specialized Cells, Tissues, Organs And Organ Systems
... This organizational concept (I-IV) is the way all living things are organized as well as humans. The hierarchy of structures starts with the smallest part (a cell) and works up to the largest structure which is the whole body of a living thing. This includes plants, animals, and other microscopi ...
... This organizational concept (I-IV) is the way all living things are organized as well as humans. The hierarchy of structures starts with the smallest part (a cell) and works up to the largest structure which is the whole body of a living thing. This includes plants, animals, and other microscopi ...
File - 8th Grade Science Ms. Neil
... 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to support life, cells can only come from other living cells AND because you are made of cells…duh. 5. 2 types of organisms: unicellular & multicellu ...
... 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to support life, cells can only come from other living cells AND because you are made of cells…duh. 5. 2 types of organisms: unicellular & multicellu ...
Photosynthesis / Cellular Respiration
... rings around the nucleus, as you can see within the image of oxygen to the right. The only ring of electrons that matters when it comes to how atoms are going to interact with other atoms is the outer ring. We call this outermost ring of electrons valence electrons. Basically, every single atom want ...
... rings around the nucleus, as you can see within the image of oxygen to the right. The only ring of electrons that matters when it comes to how atoms are going to interact with other atoms is the outer ring. We call this outermost ring of electrons valence electrons. Basically, every single atom want ...
Proteins
... • _________________ as we know it cannot exist without water. • Special properties of water allow it to break things apart into ________________ _____________________. • When the particles of water and broken down substance become equally mixed, they form a solution. • A solution is a mixture in whi ...
... • _________________ as we know it cannot exist without water. • Special properties of water allow it to break things apart into ________________ _____________________. • When the particles of water and broken down substance become equally mixed, they form a solution. • A solution is a mixture in whi ...
cms/lib/NY01001456/Centricity/Domain/535/TaxHsilent teaparty
... The KINGDOM that is has organisms with eukaryotic cells, are usually multicellular, have filamentous structures that are multinucleate, lack chloroplasts, are heterotrophic, lack a digestive system, are absorptive feeders, and are classified as decomposers. ...
... The KINGDOM that is has organisms with eukaryotic cells, are usually multicellular, have filamentous structures that are multinucleate, lack chloroplasts, are heterotrophic, lack a digestive system, are absorptive feeders, and are classified as decomposers. ...
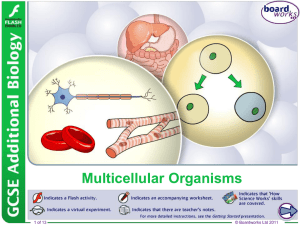
Multicellular Organisms - Thomas A. Stewart Secondary School
... All multicellular organisms begin as stem cells. These are unspecialized cells capable of developing into many different types of cell. Stem cells found in embryos are called embryonic stem cells and develop into all the different types of cell in the body. In the earliest stages of development, ste ...
... All multicellular organisms begin as stem cells. These are unspecialized cells capable of developing into many different types of cell. Stem cells found in embryos are called embryonic stem cells and develop into all the different types of cell in the body. In the earliest stages of development, ste ...
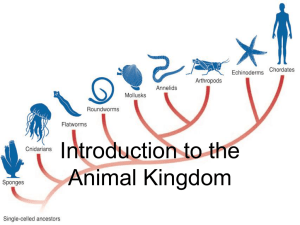
Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
... Introduction to the Animal Kingdom • Animals are multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph whose cells lack cell walls • Vertebrates: 5% of animal species with backbones • Invertebrates: 95% of animal species WITHOUT backbones • Cell specialization – special shape, physical structure, and chemical compo ...
... Introduction to the Animal Kingdom • Animals are multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph whose cells lack cell walls • Vertebrates: 5% of animal species with backbones • Invertebrates: 95% of animal species WITHOUT backbones • Cell specialization – special shape, physical structure, and chemical compo ...
SURFIN` THROUGH STAAR Session 2: Cellular Processes
... 16. Study the diagram and the description above. If Michelle were able to find an onion cell that had completed division, what products of cell division would she see? a. four different cells b. only one cell c. two identical cells d. four identical cells 17. Study the diagram and the statement abov ...
... 16. Study the diagram and the description above. If Michelle were able to find an onion cell that had completed division, what products of cell division would she see? a. four different cells b. only one cell c. two identical cells d. four identical cells 17. Study the diagram and the statement abov ...
Bacteria (multiple kingdoms)
... environment consistent with life – Growth and development—consistent growth and development controlled by DNA – Energy processing—acquiring energy and transforming it to a form useful for the organism ...
... environment consistent with life – Growth and development—consistent growth and development controlled by DNA – Energy processing—acquiring energy and transforming it to a form useful for the organism ...
Holiday Packet 2
... a. digestive, circulatory, and immune b. excretory, respiratory, and reproductive c. respiratory, excretory, and digestive d. respiratory, nervous, and endocrine Muscle cells in athletes often have more mitochondria than muscle cells in nonathletes. Based on this observation, it can be inferred that ...
... a. digestive, circulatory, and immune b. excretory, respiratory, and reproductive c. respiratory, excretory, and digestive d. respiratory, nervous, and endocrine Muscle cells in athletes often have more mitochondria than muscle cells in nonathletes. Based on this observation, it can be inferred that ...
174 kb
... Standard 4: Key Idea 1: Performance Indicator 1.1: Compare and contrast the parts of plants, animals, and one-celled organisms. Essential Knowledge/Skills (Major Understandings) 1.1a Living things are composed of cells. Cells provide the structure and carry on the major functions to sustain life. C ...
... Standard 4: Key Idea 1: Performance Indicator 1.1: Compare and contrast the parts of plants, animals, and one-celled organisms. Essential Knowledge/Skills (Major Understandings) 1.1a Living things are composed of cells. Cells provide the structure and carry on the major functions to sustain life. C ...
Click Here for Science Words in Word DOC format
... Herbivore – any animal that feeds chiefly on grass and other plants. Heterozygous – when there are two different alleles for a trait. Homeostasis – organisms regulation of its internal environment to maintain conditions suitable for survival; a characteristic of all living things. Process of maintai ...
... Herbivore – any animal that feeds chiefly on grass and other plants. Heterozygous – when there are two different alleles for a trait. Homeostasis – organisms regulation of its internal environment to maintain conditions suitable for survival; a characteristic of all living things. Process of maintai ...
Science Words in Adobe Reader PDF format
... Herbivore – any animal that feeds chiefly on grass and other plants. Heterozygous – when there are two different alleles for a trait. Homeostasis – organisms regulation of its internal environment to maintain conditions suitable for survival; a characteristic of all living things. Process of maintai ...
... Herbivore – any animal that feeds chiefly on grass and other plants. Heterozygous – when there are two different alleles for a trait. Homeostasis – organisms regulation of its internal environment to maintain conditions suitable for survival; a characteristic of all living things. Process of maintai ...
Leaving Certificate Revision Notes Higher and Ordinary
... 7. Movement: self-generated change of posture or position of an organism in response to an external or internal change in its environment. To remember these use a mnemonic such as Only Nutty Elephants Run Round Grabbing Mangroves Continuity of Life ...
... 7. Movement: self-generated change of posture or position of an organism in response to an external or internal change in its environment. To remember these use a mnemonic such as Only Nutty Elephants Run Round Grabbing Mangroves Continuity of Life ...
Cells
... Antonie van Leewenhoek - first person to see cells. Robert Hooke coined the term “cell” and illustrated what he saw. ...
... Antonie van Leewenhoek - first person to see cells. Robert Hooke coined the term “cell” and illustrated what he saw. ...
agustiniano ciudad salitre school science area circulation in living
... Phloem is formed by living cells interconnected by holes. It transports the ____________________ ____________________ resulting from the process of ____________________, composed by substances produced in metabolism, which descend through holes in the phloem and it is distributed throughout the pla ...
... Phloem is formed by living cells interconnected by holes. It transports the ____________________ ____________________ resulting from the process of ____________________, composed by substances produced in metabolism, which descend through holes in the phloem and it is distributed throughout the pla ...
PhD Project Template
... The main aim of the DNA Damage Response group led by Dr. Carty is to elucidate the molecular basis of the response of human primary cells and cancer cells to DNA damaging agents, with a specific interest in cancer therapeutics such as platinum-based drugs that interfere with DNA replication. Title & ...
... The main aim of the DNA Damage Response group led by Dr. Carty is to elucidate the molecular basis of the response of human primary cells and cancer cells to DNA damaging agents, with a specific interest in cancer therapeutics such as platinum-based drugs that interfere with DNA replication. Title & ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.