EOC Review 2015 answer key A
... 4) Explain the function(s) of the following organelles: (Be sure you can identify these in a picture!) a. Nucleus- directs all of the cell’s activities and is where the genetic information is stored. b. Mitochondria – the “powerhouses” of the cell that convert energy in food molecules to energy the ...
... 4) Explain the function(s) of the following organelles: (Be sure you can identify these in a picture!) a. Nucleus- directs all of the cell’s activities and is where the genetic information is stored. b. Mitochondria – the “powerhouses” of the cell that convert energy in food molecules to energy the ...
Unit 4 Notes #3Terrestrial Plants and Their Adaptations To Land
... Terrestrial Plants and Their Adaptations To Land A) Adaptation To Land - To achieve larger___________and to inhabit ___________ environments, plants needed a different design than the ________________ plants (Chlorophyta) or the __________________________ Bryophytes. 1) Development of ______________ ...
... Terrestrial Plants and Their Adaptations To Land A) Adaptation To Land - To achieve larger___________and to inhabit ___________ environments, plants needed a different design than the ________________ plants (Chlorophyta) or the __________________________ Bryophytes. 1) Development of ______________ ...
File - Once Upon A Cell
... 16. Study the diagram and the description above. If Michelle were able to find an onion cell that had completed division, what products of cell division would she see? a. four different cells b. only one cell c. two identical cells d. four identical cells 17. Study the diagram and the statement abov ...
... 16. Study the diagram and the description above. If Michelle were able to find an onion cell that had completed division, what products of cell division would she see? a. four different cells b. only one cell c. two identical cells d. four identical cells 17. Study the diagram and the statement abov ...
Reading Guide 04- Digestion
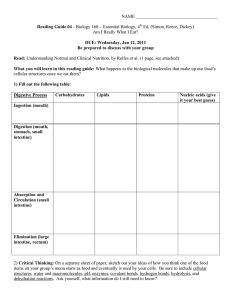
... What you will learn in this reading guide: What happens to the biological molecules that make up our food’s cellular structures once we eat them? 1) Fill out the following table: Digestive Process ...
... What you will learn in this reading guide: What happens to the biological molecules that make up our food’s cellular structures once we eat them? 1) Fill out the following table: Digestive Process ...
Protists Topics in Biodiversity
... All five groups of protozoans include some sessile species but most are swimmers. Ciliates use their many tiny cilia, in controlled waves, to propel themselves through the water. Flagellates have a single posterior flagella that pushes them forward in much the same way as a motor boat uses its prope ...
... All five groups of protozoans include some sessile species but most are swimmers. Ciliates use their many tiny cilia, in controlled waves, to propel themselves through the water. Flagellates have a single posterior flagella that pushes them forward in much the same way as a motor boat uses its prope ...
AP Biology Study Guide Part II: Cells Describe the structure and
... 1. Describe the structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells AND those found only in plant cells or only in animal cells. 2. What is a peroxisome? How is this an example of compartmentalization being crucial to function? 3. Why are membranes selectively permeable? Give an ex ...
... 1. Describe the structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells AND those found only in plant cells or only in animal cells. 2. What is a peroxisome? How is this an example of compartmentalization being crucial to function? 3. Why are membranes selectively permeable? Give an ex ...
B2 Knowledge Powerpoint
... • Fossil record – The collection of fossils identified from different periods of time that can be interpreted to form a hypothesis about the evolution of life on Earth. • Fossil – The preserved traces or remain of an organism which lived a very long time ago • Pentadactyl – five fingered organism Fo ...
... • Fossil record – The collection of fossils identified from different periods of time that can be interpreted to form a hypothesis about the evolution of life on Earth. • Fossil – The preserved traces or remain of an organism which lived a very long time ago • Pentadactyl – five fingered organism Fo ...
B2 Knowledge Powerpoint
... • Fossil record – The collection of fossils identified from different periods of time that can be interpreted to form a hypothesis about the evolution of life on Earth. • Fossil – The preserved traces or remain of an organism which lived a very long time ago • Pentadactyl – five fingered organism Fo ...
... • Fossil record – The collection of fossils identified from different periods of time that can be interpreted to form a hypothesis about the evolution of life on Earth. • Fossil – The preserved traces or remain of an organism which lived a very long time ago • Pentadactyl – five fingered organism Fo ...
Patterns_In_Nature
... Diffusion Diffusion is the movement of a substance from where it is more concentrated to where it is less concentrated. ...
... Diffusion Diffusion is the movement of a substance from where it is more concentrated to where it is less concentrated. ...
A Biology and Engineering Cooperative Project
... A Biology and Engineering Cooperative Project James W. Stevens M. Karen Newell University of Colorado at Colorado Springs 30 April 2005 ...
... A Biology and Engineering Cooperative Project James W. Stevens M. Karen Newell University of Colorado at Colorado Springs 30 April 2005 ...
unit-review-key
... 2. Cellulose: a polysaccharide contained in the cell walls of plants; gives strength and rigidity to plant cells. 3. Glycogen: a common storage form of glucose in animals (stored in the muscles and liver to be used as quick energy) II. Lipids (include fats, oils, waxes, etc.) i. Class of macromolecu ...
... 2. Cellulose: a polysaccharide contained in the cell walls of plants; gives strength and rigidity to plant cells. 3. Glycogen: a common storage form of glucose in animals (stored in the muscles and liver to be used as quick energy) II. Lipids (include fats, oils, waxes, etc.) i. Class of macromolecu ...
The 56th Annual - State Science Day
... 1. Which of the following is not true concerning biology? A) Diversity is the result of evolution B) The behavior of individual organisms is dependent upon their evolutionary history C) The characteristics of any living organism are under the control of a chemical D) The diversity of living organism ...
... 1. Which of the following is not true concerning biology? A) Diversity is the result of evolution B) The behavior of individual organisms is dependent upon their evolutionary history C) The characteristics of any living organism are under the control of a chemical D) The diversity of living organism ...
Vertebrate and Invertebrate Notes
... How do animals and humans use their senses? • Animals and humans have sensory organs that allow them to detect changes in the environment • When change is detected organisms respond with certain behaviors • Senses tell animals what they need to know about their environment Sensory organs are any par ...
... How do animals and humans use their senses? • Animals and humans have sensory organs that allow them to detect changes in the environment • When change is detected organisms respond with certain behaviors • Senses tell animals what they need to know about their environment Sensory organs are any par ...
Course Guide - Universitat de València
... The plasma membrane establish life boundaries: their selective permeability and transport are essential for maintaining integrity of the cell as a coordinated chemical system. Communication mechanisms are based on extracellular signal molecules produced by cells to communicate with their neighbors o ...
... The plasma membrane establish life boundaries: their selective permeability and transport are essential for maintaining integrity of the cell as a coordinated chemical system. Communication mechanisms are based on extracellular signal molecules produced by cells to communicate with their neighbors o ...
Cells Alive - Net Start Class
... Increase the magnification by powers of 10. a. In this animation, what is the smallest object illustrated? ____________________________________ b. How big is it? ___________________________ c. What is the size relationship between ragweed pollen and Staphylococcus bacteria? _________________________ ...
... Increase the magnification by powers of 10. a. In this animation, what is the smallest object illustrated? ____________________________________ b. How big is it? ___________________________ c. What is the size relationship between ragweed pollen and Staphylococcus bacteria? _________________________ ...
Major Organ Systems Graphic Organizer
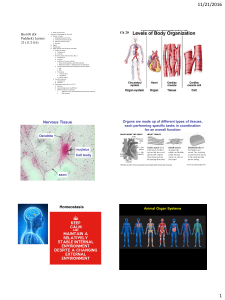
... Introduction: Scientists organize multi-cellular structures into 5 basic levels from cells to organisms. Organs are different types of tissue that work together to as a part of an organ system. Examples of organs are the lungs, brains, and eyes. Organ systems are made of two or more organs. Organ sy ...
... Introduction: Scientists organize multi-cellular structures into 5 basic levels from cells to organisms. Organs are different types of tissue that work together to as a part of an organ system. Examples of organs are the lungs, brains, and eyes. Organ systems are made of two or more organs. Organ sy ...
Plain Local Schools 5th Grade Science
... Many organisms have adaptations. For example, organisms that live in the water breathe in oxygen from the water through their gills. Organisms that live outside the pond breathe oxygen from the air through their lungs. Some animals can swim in the water but still breathe once out of the pond on land ...
... Many organisms have adaptations. For example, organisms that live in the water breathe in oxygen from the water through their gills. Organisms that live outside the pond breathe oxygen from the air through their lungs. Some animals can swim in the water but still breathe once out of the pond on land ...
Organic Chemistry
... account for the physical characteristics and activities of living organisms. • The fundamental components of biological molecules • Carbon: the indispensable element While some biological molecules are small and relatively simple, many of the carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are ma ...
... account for the physical characteristics and activities of living organisms. • The fundamental components of biological molecules • Carbon: the indispensable element While some biological molecules are small and relatively simple, many of the carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are ma ...
Intro to Biology
... 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to support life, cells can only come from other living cells AND because you are made of cells…duh. 5. 2 types of organisms: unicellular & multicellu ...
... 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to support life, cells can only come from other living cells AND because you are made of cells…duh. 5. 2 types of organisms: unicellular & multicellu ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.