Foundation Year Programme Entrance Tests BIOLOGY
... 8.2. Sources of continuous variation: a. Recall that variation can be genetic/inherited. b. Recall that variation can be environmental. 8.3. Sources of discontinuous variation: a. Understand that discontinuous variation is caused by genes alone and results in a limited number of distinct phenotypes ...
... 8.2. Sources of continuous variation: a. Recall that variation can be genetic/inherited. b. Recall that variation can be environmental. 8.3. Sources of discontinuous variation: a. Understand that discontinuous variation is caused by genes alone and results in a limited number of distinct phenotypes ...
Evolution of Metabolism Puzzle Race
... means that cells can share jobs and resources. For example, multiple cells can bind together for protection. Cells do not have special jobs. 2. Metabolism - the process an organism uses to break down food for energy, and then use that energy to grow, reproduce, and maintain its body. 3. Multi-cellul ...
... means that cells can share jobs and resources. For example, multiple cells can bind together for protection. Cells do not have special jobs. 2. Metabolism - the process an organism uses to break down food for energy, and then use that energy to grow, reproduce, and maintain its body. 3. Multi-cellul ...
Introduction to Animals
... General Features of Animals • Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic organisms with cells that lack cell walls. • Multicellular (made of more than one cell) • Heterotrophs- organism that obtains food by eating other organisms. – Filter feeders = catch particles of food that drift by in the water. ...
... General Features of Animals • Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic organisms with cells that lack cell walls. • Multicellular (made of more than one cell) • Heterotrophs- organism that obtains food by eating other organisms. – Filter feeders = catch particles of food that drift by in the water. ...
name date ______ period
... School Website: www.esperanzahs.com have three school days to Look for Freeman under “Teachers” make up labs/quizzes/tests, etc. before or after school. BIOLOGY CALENDAR SEMESTER 1 WEEK 16 TOPICS: BIOCHEMISTRY CA State Standards Covered This Week: ...
... School Website: www.esperanzahs.com have three school days to Look for Freeman under “Teachers” make up labs/quizzes/tests, etc. before or after school. BIOLOGY CALENDAR SEMESTER 1 WEEK 16 TOPICS: BIOCHEMISTRY CA State Standards Covered This Week: ...
Finding Patterns in Protein Sequence and Structure
... is the study of the interactions between the components of a biological system, and how these interactions give rise to the function and behaviour of that system (for example, the enzymes and metabolites in a metabolic pathway). The aim is to quantitatively understand the system and to be able to pr ...
... is the study of the interactions between the components of a biological system, and how these interactions give rise to the function and behaviour of that system (for example, the enzymes and metabolites in a metabolic pathway). The aim is to quantitatively understand the system and to be able to pr ...
Survival Need or Necessary Life Function?
... 6. Excretion – removal of wastes from the body 7. Reproduction – cellular and organismal levels Cellular – an original cell divides and produces two identical daughter cells that may be used for body growth or repair Organismal – sperm and egg unite to make a whole new person 8. Growth – increas ...
... 6. Excretion – removal of wastes from the body 7. Reproduction – cellular and organismal levels Cellular – an original cell divides and produces two identical daughter cells that may be used for body growth or repair Organismal – sperm and egg unite to make a whole new person 8. Growth – increas ...
How do Humans and other complex mammals maintain
... Midterm exam 1: 15 marks Midterm exam 2: 15 marks Practice exam: 30 marks Final exam: 40 Total: … /100 ...
... Midterm exam 1: 15 marks Midterm exam 2: 15 marks Practice exam: 30 marks Final exam: 40 Total: … /100 ...
DRILLING #3 Subject : Science Name : Chapter : Diversity of Living
... b. Three kingdoms, there are fungi, plantae, and animalia c. Four kingdoms, there are Protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia d. Five kingdoms, there are monera, Protista, fungi, plantae, animalia The plant organ which produces a male reproductive cell (sperm) in ferns is…. (produce:menghasilkan,male ...
... b. Three kingdoms, there are fungi, plantae, and animalia c. Four kingdoms, there are Protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia d. Five kingdoms, there are monera, Protista, fungi, plantae, animalia The plant organ which produces a male reproductive cell (sperm) in ferns is…. (produce:menghasilkan,male ...
Sample Questions for Exam One Multiple Choice. Choose the
... If you are asked to look into a microscope to see a plant cell, you will be looking for a cell that , a. has a membrane bound nucleus b. does not have a membrane bound nucleus c. does not use DNA as instructions to make proteins d. makes up most of the tissues of your boy e. none of the above ...
... If you are asked to look into a microscope to see a plant cell, you will be looking for a cell that , a. has a membrane bound nucleus b. does not have a membrane bound nucleus c. does not use DNA as instructions to make proteins d. makes up most of the tissues of your boy e. none of the above ...
File - Westpine Biology EOC
... cannot be “proven,” significant evidence can be used to support it. What kind of evidence has led biologists to accept modern evolutionary theory? A. comparing the sequence of DNA base pairs of different species B. comparing different literary accounts of the origin of life on Earth C. comparing the ...
... cannot be “proven,” significant evidence can be used to support it. What kind of evidence has led biologists to accept modern evolutionary theory? A. comparing the sequence of DNA base pairs of different species B. comparing different literary accounts of the origin of life on Earth C. comparing the ...
multicellular organisms
... of the digestive system; animals may have a gastrovascular cavity with one opening or a specialised alimentary canal with two opening; specialisation of alimentary canals is related to diet, for example, herbivores and carnivores. ...
... of the digestive system; animals may have a gastrovascular cavity with one opening or a specialised alimentary canal with two opening; specialisation of alimentary canals is related to diet, for example, herbivores and carnivores. ...
Grade 8 Science Unit 4: “Cells, Tissues, Organs & Organ Systems”
... •Within your control Include: •Diet •Smoking •Drugs and alcohol •Lack of exercise ...
... •Within your control Include: •Diet •Smoking •Drugs and alcohol •Lack of exercise ...
Science 14 Unit C Review
... torpor, dormancy, hibernation, estivation, vascular skin, sweat gland behaviour) • identify organs and systems in plants and animals that carry out the above life functions • identify the major human organ systems that perform critical life functions; i.e., energy conversion, response to the environ ...
... torpor, dormancy, hibernation, estivation, vascular skin, sweat gland behaviour) • identify organs and systems in plants and animals that carry out the above life functions • identify the major human organ systems that perform critical life functions; i.e., energy conversion, response to the environ ...
Unit 8-B Study Guide Questions
... 28) Create a flow chart that includes and explain the following terms nervous system, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, sensory neurons, motor neurons, somatic nervous system, and autonomic nervous system. 29) What are the three main parts of the brain, and what is there function? 3 ...
... 28) Create a flow chart that includes and explain the following terms nervous system, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, sensory neurons, motor neurons, somatic nervous system, and autonomic nervous system. 29) What are the three main parts of the brain, and what is there function? 3 ...
Exam Review Notes
... Plant cells have centrioles whereas cells of animals usually do not. Vacuoles are larger in plant cells whereas animal cells usually have several small vacuoles. Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes. Plant cells have a cell wall which provides support The cell membrane controls what enters or leaves ...
... Plant cells have centrioles whereas cells of animals usually do not. Vacuoles are larger in plant cells whereas animal cells usually have several small vacuoles. Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes. Plant cells have a cell wall which provides support The cell membrane controls what enters or leaves ...
The Fundamental Units of Life Classwork Name: 7th Grade PSI 1
... 3. Yes; humans exhibit the four characteristics of living things (growth, respond to stimuli, reproduce, use energy for growth and reproduction) AND humans can function on their own. 4. Rocks are nonliving. They are not composed of cells. 5. Bacteria are unicellular and prokaryotic. 6. Cells are fou ...
... 3. Yes; humans exhibit the four characteristics of living things (growth, respond to stimuli, reproduce, use energy for growth and reproduction) AND humans can function on their own. 4. Rocks are nonliving. They are not composed of cells. 5. Bacteria are unicellular and prokaryotic. 6. Cells are fou ...
The Fundamental Units of Life Classwork Name: 7th Grade PSI
... 3. Yes; humans exhibit the four characteristics of living things (growth, respond to stimuli, reproduce, use energy for growth and reproduction) AND humans can function on their own. 4. Rocks are nonliving. They are not composed of cells. 5. Bacteria are unicellular and prokaryotic. 6. Cells are fou ...
... 3. Yes; humans exhibit the four characteristics of living things (growth, respond to stimuli, reproduce, use energy for growth and reproduction) AND humans can function on their own. 4. Rocks are nonliving. They are not composed of cells. 5. Bacteria are unicellular and prokaryotic. 6. Cells are fou ...
SYLLABUS Advanced Cell Biology BIOL 3301 (3
... Final score will be calculated as follows: 1. Exam #1 2. Exam #2 3. Exam #3 4. Final Exam 5. In-class activities ...
... Final score will be calculated as follows: 1. Exam #1 2. Exam #2 3. Exam #3 4. Final Exam 5. In-class activities ...
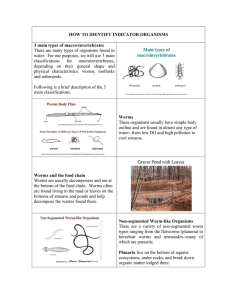
HOW TO IDENTIFY INDICATOR ORGANISMS
... under rocks or attached to a victims skin, sucking blood. Leeches Leeches can be found on fish, turtles or other aquatic organisms. Horsehair worms spend their youth growing inside crickets and grasshoppers, only to emerge as adults when they have totally devoured the host insect! These worms look l ...
... under rocks or attached to a victims skin, sucking blood. Leeches Leeches can be found on fish, turtles or other aquatic organisms. Horsehair worms spend their youth growing inside crickets and grasshoppers, only to emerge as adults when they have totally devoured the host insect! These worms look l ...
DNA History PPT - Mayfield City Schools
... Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Hershey & Chase (1952) Watson & Crick (1953) Meselson & Stahl (1958) ...
... Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Hershey & Chase (1952) Watson & Crick (1953) Meselson & Stahl (1958) ...
Investigating the Human Body - Curriculum links
... Activity 27 The Male and female reproductive systems Activity 28 Life goes on. Activity 32 Evolution of bacteria – resistance to antibiotics Activity 33 Viruses ...
... Activity 27 The Male and female reproductive systems Activity 28 Life goes on. Activity 32 Evolution of bacteria – resistance to antibiotics Activity 33 Viruses ...
Cells are the
... transport large molecules into the cell ______________their concentration gradients 1. Cell Membrane Pumps carrier proteins pump ions _______________________________________ 2. Endocytosis _______________ of _________________particles or liquids by plasma membrane Cells take in __________ by end ...
... transport large molecules into the cell ______________their concentration gradients 1. Cell Membrane Pumps carrier proteins pump ions _______________________________________ 2. Endocytosis _______________ of _________________particles or liquids by plasma membrane Cells take in __________ by end ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... Gap junctions (physical linkages connecting the cytosol between two cells) allow molecules to move from one cell to an adjacent cell without entering the extracellular fluid. Juxtacrine signaling is the chemical messenger not actually being released from the cell producing it, but rather is located ...
... Gap junctions (physical linkages connecting the cytosol between two cells) allow molecules to move from one cell to an adjacent cell without entering the extracellular fluid. Juxtacrine signaling is the chemical messenger not actually being released from the cell producing it, but rather is located ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.