notes 32,33,34
... What is the adaptive advantage of bilateral symmetry? cephalization Which group has no symmetry? Profiera ...
... What is the adaptive advantage of bilateral symmetry? cephalization Which group has no symmetry? Profiera ...
Chapter 1 Cells
... organism because it can live in more extreme (hotter) areas and one type actually makes methane and might be responsible for the high methane levels long ago. ...
... organism because it can live in more extreme (hotter) areas and one type actually makes methane and might be responsible for the high methane levels long ago. ...
Protostome Animals
... easily the most species rich clade, but its overall numbers on this planet surpass even the imagination – Within one single acre of rural land in England an estimated 17, 825, 000 beetles will reside – At any time, it is estimated that there are some 10 quintillion (10,000,000,000,000,000,000) indiv ...
... easily the most species rich clade, but its overall numbers on this planet surpass even the imagination – Within one single acre of rural land in England an estimated 17, 825, 000 beetles will reside – At any time, it is estimated that there are some 10 quintillion (10,000,000,000,000,000,000) indiv ...
B2 Glossary - physicsinfo.co.uk
... Movement of molecules against concentration gradient using energy A base in DNA that pairs with thymine A stem cell in differentiated tissue that can produce a few kinds of cells Respiration that needs oxygen The muscular tube that runs from the mouth to the anus Different types of a gene eg. brown ...
... Movement of molecules against concentration gradient using energy A base in DNA that pairs with thymine A stem cell in differentiated tissue that can produce a few kinds of cells Respiration that needs oxygen The muscular tube that runs from the mouth to the anus Different types of a gene eg. brown ...
TWO TYPES OF CELLS
... All living things are made up of cells! (including you!) Cells do all the life functions that we do: - grow - make energy - reproduce - get rid of wastes - need food (to make energy) - die ...
... All living things are made up of cells! (including you!) Cells do all the life functions that we do: - grow - make energy - reproduce - get rid of wastes - need food (to make energy) - die ...
Systematics and Ecology - School of Ocean and Earth Science and
... Some organisms carry their developing eggs and larvae around with them, a behavior known as brooding. The majority, however, produce free-swimming larvae which drift in the water and are known as plankton. Spawning occurs when adults release eggs and sperm into the water column, where they must come ...
... Some organisms carry their developing eggs and larvae around with them, a behavior known as brooding. The majority, however, produce free-swimming larvae which drift in the water and are known as plankton. Spawning occurs when adults release eggs and sperm into the water column, where they must come ...
Part 1: Developmental Genetics
... How do cells acquire positional information about their location in a developing embryo? Explain the function of bicoid. What are the homeobox genes? What do they do in a developing animal? ...
... How do cells acquire positional information about their location in a developing embryo? Explain the function of bicoid. What are the homeobox genes? What do they do in a developing animal? ...
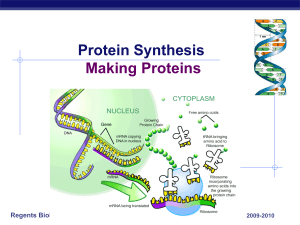
Protein Synthesis Making Proteins
... How do proteins do all the work Proteins proteins run living organisms enzymes ...
... How do proteins do all the work Proteins proteins run living organisms enzymes ...
Animal Anatomy
... Cells have important structures that allow them to function. Protoplasm within a cell carries out important chemical activities. Multi-cellular organisms have many cells. These cells form specialized systems to carry out life processes. ...
... Cells have important structures that allow them to function. Protoplasm within a cell carries out important chemical activities. Multi-cellular organisms have many cells. These cells form specialized systems to carry out life processes. ...
Tutorial Kit (Applied Biology and Biotechnology-100 L)
... Highlight the basic features that can be used to classify animals. List the four classes of the phylum Cnidarian and give at least one example of each class. Describe the life cycle of Obelia What are the distinguishing characteristics of the phylum Platyhelminthes. Describe the life cycle of Ascari ...
... Highlight the basic features that can be used to classify animals. List the four classes of the phylum Cnidarian and give at least one example of each class. Describe the life cycle of Obelia What are the distinguishing characteristics of the phylum Platyhelminthes. Describe the life cycle of Ascari ...
2nd Semester Final Exam Review 2016
... 4. Describe the force of the vacuole and cell wall in a plant with high turgor pressure. The force of the vacuole will be GREATER than the force of the cell wall in high turgor pressure 5. What is an example of positive stimulus? A plant bending towards light, roots growing downward in the direction ...
... 4. Describe the force of the vacuole and cell wall in a plant with high turgor pressure. The force of the vacuole will be GREATER than the force of the cell wall in high turgor pressure 5. What is an example of positive stimulus? A plant bending towards light, roots growing downward in the direction ...
AP Biology Free-Response Question Preparation
... 17°C. Show your work (including your setup and calculation). (b) Explain the relationship between metabolism and oxygen consumption. Discuss the effect of temperature on metabolism for each variety of seedlings. (c) In a second experiment, variety A seedlings at both temperatures were treated with a ...
... 17°C. Show your work (including your setup and calculation). (b) Explain the relationship between metabolism and oxygen consumption. Discuss the effect of temperature on metabolism for each variety of seedlings. (c) In a second experiment, variety A seedlings at both temperatures were treated with a ...
effective: september 2003 curriculum guidelines
... Be able to explain the molecular basis and significance of proteins, nucleic acids, lipids and carbohydrates, and their relationship to cellular respiration and photosynthesis and general metabolism. ...
... Be able to explain the molecular basis and significance of proteins, nucleic acids, lipids and carbohydrates, and their relationship to cellular respiration and photosynthesis and general metabolism. ...
Science Ch. 1 notes - Mrs. Gann`s 6th grade class
... things Do you think these organisms are find in the Dead Sea? ...
... things Do you think these organisms are find in the Dead Sea? ...
Study Guide - Wisconsin Media Lab
... H (hydrogen) from another are removed, forming H2O (water). Such reactions, known as condensation reactions, can assemble building block molecules into long chains of repeating units called polymers. Four kinds of biologically produced polymers play major roles in life: carbohydrates – lipids – prot ...
... H (hydrogen) from another are removed, forming H2O (water). Such reactions, known as condensation reactions, can assemble building block molecules into long chains of repeating units called polymers. Four kinds of biologically produced polymers play major roles in life: carbohydrates – lipids – prot ...
ap biology exam review guide
... (2) Nucleotide made up of sugar, phosphate and base (3) Used to store genetic information (4) DNA is double stranded, has deoxyribose, A, G, C, T (5) RNA is single stranded, has ribose, A, G, C, U (6) mRNA- copies genetic message; rRNA- attaches mRNA and makes up ribosomes (most common); tRNA- carri ...
... (2) Nucleotide made up of sugar, phosphate and base (3) Used to store genetic information (4) DNA is double stranded, has deoxyribose, A, G, C, T (5) RNA is single stranded, has ribose, A, G, C, U (6) mRNA- copies genetic message; rRNA- attaches mRNA and makes up ribosomes (most common); tRNA- carri ...
Final Exam Part B 2014 Pittman
... 35. Food chains and food webs are models in science, which visually show us the different relationships within an ecosystem. The primary difference between the food chain and the food web is… a. a food chain shows how energy is stored b. a food web shows how energy is used c. a food web is a comple ...
... 35. Food chains and food webs are models in science, which visually show us the different relationships within an ecosystem. The primary difference between the food chain and the food web is… a. a food chain shows how energy is stored b. a food web shows how energy is used c. a food web is a comple ...
Chapter 43.
... higher temperature helps defense inhibits bacterial growth stimulates phagocytosis speeds up repair of tissues causes liver & spleen to store ...
... higher temperature helps defense inhibits bacterial growth stimulates phagocytosis speeds up repair of tissues causes liver & spleen to store ...
Cellular Respiration PPt
... Plants make both FOOD & ENERGY animals are consumers plants are producers ...
... Plants make both FOOD & ENERGY animals are consumers plants are producers ...
Third Grade Science Chapter 1-2 Study Guide pg 1
... Stem- holds up a plant and its leaves. Carries water, nutrients and food trough a plant. Leaf- where a plant makes food. Photosynthesis is the process of plants using energy from the sun to make food. ...
... Stem- holds up a plant and its leaves. Carries water, nutrients and food trough a plant. Leaf- where a plant makes food. Photosynthesis is the process of plants using energy from the sun to make food. ...
Foundation Year Programme Entrance Tests BIOLOGY
... 6.1. Understand that chromosomes contain DNA. 6.2. Describe the structure of DNA. 6.3. Protein synthesis: a. Understand that genes carry the code for proteins. b. Understand that the genetic code is ‘read’ as triplets and each triplet codes for an amino acid. c. Know that there are four bases, A, T, ...
... 6.1. Understand that chromosomes contain DNA. 6.2. Describe the structure of DNA. 6.3. Protein synthesis: a. Understand that genes carry the code for proteins. b. Understand that the genetic code is ‘read’ as triplets and each triplet codes for an amino acid. c. Know that there are four bases, A, T, ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.