Depressants
... • a Benzodiazepine used in the short-term treatment of insomnia and as a preanesthetic medication • similar to valium in effect but 10 times stronger • effects begin within 30 minutes, may last for 8 hours or more ...
... • a Benzodiazepine used in the short-term treatment of insomnia and as a preanesthetic medication • similar to valium in effect but 10 times stronger • effects begin within 30 minutes, may last for 8 hours or more ...
Specific NT systems
... •Narcotic comes from the Greek word, “narke”, meaning stupor and referred to any drug that induced sleep ...
... •Narcotic comes from the Greek word, “narke”, meaning stupor and referred to any drug that induced sleep ...
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
... more effectively than the l-isomer 2. l-isomer (levoamphetamine) - stimulates the cardiovasculature system more than the d-isomer ...
... more effectively than the l-isomer 2. l-isomer (levoamphetamine) - stimulates the cardiovasculature system more than the d-isomer ...
Comer, Abnormal Psychology, 8th edition
... Opioids bind to the receptors in the brain that ordinarily receive endorphins (NTs that naturally help relieve pain and decrease emotional tension) When these sites receive opioids, they produce pleasurable and calming feelings, just as endorphins do In addition to reducing pain and tension, opi ...
... Opioids bind to the receptors in the brain that ordinarily receive endorphins (NTs that naturally help relieve pain and decrease emotional tension) When these sites receive opioids, they produce pleasurable and calming feelings, just as endorphins do In addition to reducing pain and tension, opi ...
Stimulants
... ingredients, dosage, etc. Advertised as ‘research chemicals’, ‘plant food’, ‘bath salts’ or ‘glass cleaner’ Taken orally or by inhaling, sometimes injected desired effects are increase in energy, empathy, openness, and libido ...
... ingredients, dosage, etc. Advertised as ‘research chemicals’, ‘plant food’, ‘bath salts’ or ‘glass cleaner’ Taken orally or by inhaling, sometimes injected desired effects are increase in energy, empathy, openness, and libido ...
Chapter 16
... • Routes of administration: – Sniffing (“snorting”) it as a white powder – Injecting it directly into the bloodstream – Smoking it in the form of “free base” or “crack” • Produces tolerance, physical dependence, and withdrawal. • Potential for psychological dependence with cocaine is very high. ...
... • Routes of administration: – Sniffing (“snorting”) it as a white powder – Injecting it directly into the bloodstream – Smoking it in the form of “free base” or “crack” • Produces tolerance, physical dependence, and withdrawal. • Potential for psychological dependence with cocaine is very high. ...
Anti-psychotic drugs 2006
... • Some have actions against the D4 receptor • All have other effects - to varying degrees – Serotonin blockade (may improve negative symptoms) – Histamine H1 blockade (drowsiness) – Alpha adrenoceptor blockade (postural hypotension) ...
... • Some have actions against the D4 receptor • All have other effects - to varying degrees – Serotonin blockade (may improve negative symptoms) – Histamine H1 blockade (drowsiness) – Alpha adrenoceptor blockade (postural hypotension) ...
drugs of abuse
... • Derived from a coca plant,is a crystalline tropane alkaloid. • It come as an off- white powder or ‘rock’ • It modifies the action of dopamine in the brain by inhibiting its re-uptake from the synaptic cleft and thus causing prolonged postsynaptic stimulation. • Mostly act on the ‘reward pathway 'w ...
... • Derived from a coca plant,is a crystalline tropane alkaloid. • It come as an off- white powder or ‘rock’ • It modifies the action of dopamine in the brain by inhibiting its re-uptake from the synaptic cleft and thus causing prolonged postsynaptic stimulation. • Mostly act on the ‘reward pathway 'w ...
Pre-Lecture Quiz
... Pre-Lecture Quiz, Chapter 52, Drug Therapy for Seizure Disorders and Spasticity ...
... Pre-Lecture Quiz, Chapter 52, Drug Therapy for Seizure Disorders and Spasticity ...
Document
... Why wasn't cocaine smoked very often prior to the 1980s; what changed that? How do the different routes of administration affect plasma levels of cocaine? Cocaethylene How does cocaine work at the synapse (make sure to include NTs and relative affinities)? Cocaine psychosis Self administration of co ...
... Why wasn't cocaine smoked very often prior to the 1980s; what changed that? How do the different routes of administration affect plasma levels of cocaine? Cocaethylene How does cocaine work at the synapse (make sure to include NTs and relative affinities)? Cocaine psychosis Self administration of co ...
The drugs discussed in this chapter are used to alter an individual`s
... Paradoxical effect of calming hyperexcitability through CNS stimulation seen in attention-deficit syndrome is believed to be related to increased stimulation of an immature RAS, which leads to the ability to be more selective in response to incoming stimuli. ...
... Paradoxical effect of calming hyperexcitability through CNS stimulation seen in attention-deficit syndrome is believed to be related to increased stimulation of an immature RAS, which leads to the ability to be more selective in response to incoming stimuli. ...
Drugs Of Abuse: A Pharmacological Perspective
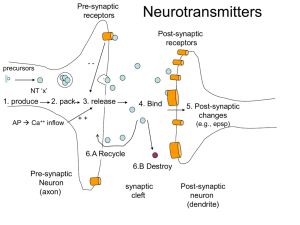
... – Includes Norepinephrine, Serotonin, Dopamine, Glutamate, Endorphins etc (> 100 neurotransmitters known) – Neurotransmitters are released into the synapse: Pre/Post Junctional – Neurotransmitter re-uptake sites and metabolism to stop effect – Drugs can mimic neurotransmitters or block their effect ...
... – Includes Norepinephrine, Serotonin, Dopamine, Glutamate, Endorphins etc (> 100 neurotransmitters known) – Neurotransmitters are released into the synapse: Pre/Post Junctional – Neurotransmitter re-uptake sites and metabolism to stop effect – Drugs can mimic neurotransmitters or block their effect ...
abnormal PSYCHOLOGY Third Canadian Edition
... • Sedatives (downers) slow activities of body and reduce responsiveness. – Includes opiates—opium and its derivatives, morphine, heroin, and codeine – and synthetic barbiturates and tranquilizers, such as secobarbital (Seconal) and diazepam ...
... • Sedatives (downers) slow activities of body and reduce responsiveness. – Includes opiates—opium and its derivatives, morphine, heroin, and codeine – and synthetic barbiturates and tranquilizers, such as secobarbital (Seconal) and diazepam ...
Week 8
... 1943 – re-examine product and accidental ingestion hallucinogenic properties of the drug 1947 – launched as Delysid for psychotherapy 1970s – product banned and abandoned ...
... 1943 – re-examine product and accidental ingestion hallucinogenic properties of the drug 1947 – launched as Delysid for psychotherapy 1970s – product banned and abandoned ...
Unit 2 OTC-RX-Illegal drugs
... Cold medications that contains an ingredient pseudoephedrine Pseudoephedrine must be kept behind the pharmacy counter. These medications are used to make highly addictive, illegal drugs - METH ...
... Cold medications that contains an ingredient pseudoephedrine Pseudoephedrine must be kept behind the pharmacy counter. These medications are used to make highly addictive, illegal drugs - METH ...
Guidance regarding Psychoactive Substances
... Severe or life threatening intoxication if taken in large doses. They can affect the nervous system and lead to seizures, increased heart rate, high blood pressure, sweating, increased body temperature and agitation. ...
... Severe or life threatening intoxication if taken in large doses. They can affect the nervous system and lead to seizures, increased heart rate, high blood pressure, sweating, increased body temperature and agitation. ...
Our work in prevention
... effects of meth/amphetamine Sought after effects are similar to that of cocaine, but cheaper and longer lasting. Methamphetamine is more quickly and fully absorbed by the brain than amphetamine, therefore the effects are stronger. Short term negative effects: State of agitation that can lead ...
... effects of meth/amphetamine Sought after effects are similar to that of cocaine, but cheaper and longer lasting. Methamphetamine is more quickly and fully absorbed by the brain than amphetamine, therefore the effects are stronger. Short term negative effects: State of agitation that can lead ...
LC/MS/MS and GC/MS Applications in Testing Illicit Substances
... • Acute versus chronic toxicity – Acute • Local damage or systematic change as result of ONE exposure to a relatively large amount of substance ...
... • Acute versus chronic toxicity – Acute • Local damage or systematic change as result of ONE exposure to a relatively large amount of substance ...
What is the Block Grant? - Florida Alcohol and Drug Abuse Association
... • Intoxication (use): depressant effect, many reports of stimulant effects at lower doses • Withdrawal: Acute: previous slide, remember half-life determines length of time Chronic: depression, irritability, anxiety, insomnia ...
... • Intoxication (use): depressant effect, many reports of stimulant effects at lower doses • Withdrawal: Acute: previous slide, remember half-life determines length of time Chronic: depression, irritability, anxiety, insomnia ...
Description and Effects of Drug
... Gammahydroxybutrate (GHB) and GBL (gammabutyrolactone) are closely related, dangerous drugs with anaesthetic effects. GBL converts to GHB shortly after entering the body. Both can kill you and are particularly dangerous when used with alcohol and other “slowing-down” substances. GHB and GBL produc ...
... Gammahydroxybutrate (GHB) and GBL (gammabutyrolactone) are closely related, dangerous drugs with anaesthetic effects. GBL converts to GHB shortly after entering the body. Both can kill you and are particularly dangerous when used with alcohol and other “slowing-down” substances. GHB and GBL produc ...
Effects of Drugs on the Developing Brain
... Children of Parents with Substance Abuse Disorder have a 4 to 7 fold higher risk of developing Substance Use Disorder.1 Genetic Component of liability to SUD estimated at 0.31 in males and 0.22 in females and can reach as high as 0.79 in some studies. (higher for stimulants 0.44) The Environmental C ...
... Children of Parents with Substance Abuse Disorder have a 4 to 7 fold higher risk of developing Substance Use Disorder.1 Genetic Component of liability to SUD estimated at 0.31 in males and 0.22 in females and can reach as high as 0.79 in some studies. (higher for stimulants 0.44) The Environmental C ...
Stimulant

Stimulants (also referred to as psychostimulants) are psychoactive drugs that induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical functions or both. Examples of these kinds of effects may include enhanced alertness, wakefulness, and locomotion, among others. Due to their rendering a characteristic ""up"" feeling, stimulants are also occasionally referred to as ""uppers"". Depressants or ""downers"", which decrease mental and/or physical function, are in stark contrast to stimulants and are considered to be their functional opposites. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines and without prescription both as legal substances and illicit substances of recreational use or abuse.