Test Hints – gravity
... center, there is a feeling of being forced away from the center to the third law. This sensation is called the centrifugal force. Centrifugal force is a fictitious force. Centripetal force is always caused by some real force; tension in a string, friction, gravity, magnetic force, &tc. Problem gouge ...
... center, there is a feeling of being forced away from the center to the third law. This sensation is called the centrifugal force. Centrifugal force is a fictitious force. Centripetal force is always caused by some real force; tension in a string, friction, gravity, magnetic force, &tc. Problem gouge ...
Motion: a change in position, measured by distance and time
... Newton's First Law describes motion produced by balanced forces. An object at rest will remain at rest, and a moving object will remain at a constant velocity unless unbalanced forces act on it. Newton was first to use the term inertia to describe the tendency of objects to remain in motion or stay ...
... Newton's First Law describes motion produced by balanced forces. An object at rest will remain at rest, and a moving object will remain at a constant velocity unless unbalanced forces act on it. Newton was first to use the term inertia to describe the tendency of objects to remain in motion or stay ...
13.11. Visualize: Solve: Torque by a force is defined as τ = Frsinφ
... Assess: To establish rotational equilibrium, the choice for the pivot is arbitrary. We can take torques about any point on the body of interest. ...
... Assess: To establish rotational equilibrium, the choice for the pivot is arbitrary. We can take torques about any point on the body of interest. ...
Physics - Partners4results
... D. go in the direction it is moving 21. Newton’s Second Law applied to rotational mechanics may read A. the torque on a body is directly proportional to the angular acceleration, but inversely proportional to the rotational inertia of that body. B. the angular acceleration of a body is directly prop ...
... D. go in the direction it is moving 21. Newton’s Second Law applied to rotational mechanics may read A. the torque on a body is directly proportional to the angular acceleration, but inversely proportional to the rotational inertia of that body. B. the angular acceleration of a body is directly prop ...
Introduction to Applied Physics
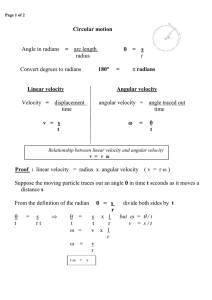
... Units will be in meters per second (m/s), miles per hour (mph), or other combinations of distance and time ...
... Units will be in meters per second (m/s), miles per hour (mph), or other combinations of distance and time ...
8th Grade Physical Science
... 3. Distance – how far something has moved 4. Displacement – the distance and direction of the change in position from a starting point 5. Speed – distance traveled in a given amount of time ...
... 3. Distance – how far something has moved 4. Displacement – the distance and direction of the change in position from a starting point 5. Speed – distance traveled in a given amount of time ...
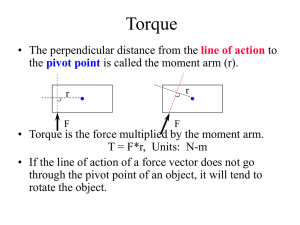
Torque
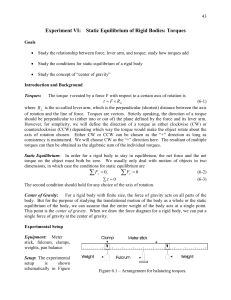
... torques. Experimental Procedure and Data Analysis A. Torques 1. Adjust the location of the fulcrum so that the meter stick, with no weights hanging on it, is in static equilibrium (balance) in a horizontal position. The position of the fulcrum is roughly the center of gravity of the meter stick. Not ...
... torques. Experimental Procedure and Data Analysis A. Torques 1. Adjust the location of the fulcrum so that the meter stick, with no weights hanging on it, is in static equilibrium (balance) in a horizontal position. The position of the fulcrum is roughly the center of gravity of the meter stick. Not ...
Example
... with each particle in the body moving on a circular path. We now expand the definition of torque so that it can describe the motion of a particle that moves along any path relative to a fixed point. If r is the position vector of a particle on which a force F is acting, the torque is defined as ...
... with each particle in the body moving on a circular path. We now expand the definition of torque so that it can describe the motion of a particle that moves along any path relative to a fixed point. If r is the position vector of a particle on which a force F is acting, the torque is defined as ...
Basis of Motor Action
... Now suppose that a dc motor is running at some constant angular velocity at some external load. What happens if we increase the external load? We expect that the increase in load will cause the motor to slow down. We have experienced this driving a car and coming to a hill. If we don’t press on th ...
... Now suppose that a dc motor is running at some constant angular velocity at some external load. What happens if we increase the external load? We expect that the increase in load will cause the motor to slow down. We have experienced this driving a car and coming to a hill. If we don’t press on th ...
The Gyroscope - dfcd.net: Articles
... We are only concerned with the centripetal tension, which is dependent on angular frequency. Observe the effect of the vertical component of the centripetal tensions in the diagram to the left. Each is causing the rim to be torqued in the same direction as the applied torque. However, since Newton’s ...
... We are only concerned with the centripetal tension, which is dependent on angular frequency. Observe the effect of the vertical component of the centripetal tensions in the diagram to the left. Each is causing the rim to be torqued in the same direction as the applied torque. However, since Newton’s ...