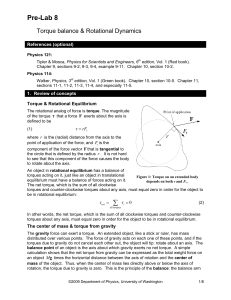
Rotational Motion
... string) by Newton’s third law. Fhc can be computed by using Newton’s second law on the falling mass. ...
... string) by Newton’s third law. Fhc can be computed by using Newton’s second law on the falling mass. ...
Lecture 12
... A body may be in one of three states of static equilibrium: neutral, stable, and unstable: •Stable Equilibrium: A body is in stable equilibrium if it returns to its equilibrium position after it has been displaced slightly. •Unstable Equilibrium: A body is in unstable equilibrium if it does not ret ...
... A body may be in one of three states of static equilibrium: neutral, stable, and unstable: •Stable Equilibrium: A body is in stable equilibrium if it returns to its equilibrium position after it has been displaced slightly. •Unstable Equilibrium: A body is in unstable equilibrium if it does not ret ...
Physics-1 Recitation-7
... incline are frictionless. If the pulley is wound conterclockwise so that the spring is stretched a distance d from its unstretched position and is then released from rest, find a) The angular speed of the pulley when the spring is again unstretched and b) A numerical value for the angular speed at t ...
... incline are frictionless. If the pulley is wound conterclockwise so that the spring is stretched a distance d from its unstretched position and is then released from rest, find a) The angular speed of the pulley when the spring is again unstretched and b) A numerical value for the angular speed at t ...
Document
... Impulse produces a change in momentum. If you apply a force to an object for a period of time, its velocity will change. The larger the force or the longer the time, the greater the change in its momentum. Newton originally expressed his second law of motion (F = ma) in terms of the rate of change o ...
... Impulse produces a change in momentum. If you apply a force to an object for a period of time, its velocity will change. The larger the force or the longer the time, the greater the change in its momentum. Newton originally expressed his second law of motion (F = ma) in terms of the rate of change o ...
Lecture 17 Circular Motion (Chapter 7) Angular Measure Angular
... The units are typically radians/second, but revolutions/minute (rpm) are alos common units. The direction is defined based on whether the speed is clockwise or counter-clockwise. The rule to follow is to use your right hand and wrap it in the direction of motion. If the angular speed is counterclock ...
... The units are typically radians/second, but revolutions/minute (rpm) are alos common units. The direction is defined based on whether the speed is clockwise or counter-clockwise. The rule to follow is to use your right hand and wrap it in the direction of motion. If the angular speed is counterclock ...
Chapter 11 Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium
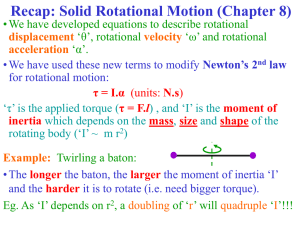
... distance. It saves forces, but nothing can save work. • Newton’s second law for rotation: Angular acceleration = total torque / rotational inertia ...
... distance. It saves forces, but nothing can save work. • Newton’s second law for rotation: Angular acceleration = total torque / rotational inertia ...
Version B
... that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius R0 and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and mB. [Solution] FBD for each object • Don’t use a point to represent a rotating object; • Don’t shift forces sideways. ...
... that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius R0 and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and mB. [Solution] FBD for each object • Don’t use a point to represent a rotating object; • Don’t shift forces sideways. ...