a force
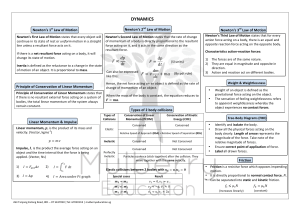
... Momentum (p) – the mass of an object times its velocity (p=mv) Force (f) – anything that can cause a change in an object’s momentum As long as the object’s mass does not change, a force causes a change in velocity, or an acceleration (a) ...
... Momentum (p) – the mass of an object times its velocity (p=mv) Force (f) – anything that can cause a change in an object’s momentum As long as the object’s mass does not change, a force causes a change in velocity, or an acceleration (a) ...
Motion in an Inverse-Square Central Force Field
... where r̂ is the unit vector in the direction of ~r. In the case of planetary motion, K = GM , where G is the universal gravitational constant and M is the mass of the sun. In the case of motion in the electric field of a static charged particle, K = Cq, where C is a universal constant and q is the p ...
... where r̂ is the unit vector in the direction of ~r. In the case of planetary motion, K = GM , where G is the universal gravitational constant and M is the mass of the sun. In the case of motion in the electric field of a static charged particle, K = Cq, where C is a universal constant and q is the p ...
lecture 17 slides
... Centripetal Acceleration • Centripetal refers to “center-seeking” • The direction of the velocity changes, the ...
... Centripetal Acceleration • Centripetal refers to “center-seeking” • The direction of the velocity changes, the ...
hw 1246914222829 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Yes. If the object moves at a constant speed in a straight line, then the net force on the object is equal to zero. This is referred to in the book as dynamic equilibrium. ...
... Yes. If the object moves at a constant speed in a straight line, then the net force on the object is equal to zero. This is referred to in the book as dynamic equilibrium. ...
Monday, Nov. 10, 2003
... angular momentum of the system can change. Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system where the two exert forces on each other. ...
... angular momentum of the system can change. Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system where the two exert forces on each other. ...
Rotation and Centripetal Force
... The rotational analog of force Depends on direction and where applied Equals force times lever arm times sine of angle between them t = rFsinq Unit is meter Newton Lever arm is perpendicular distance of axis of rotation to line of action of force ...
... The rotational analog of force Depends on direction and where applied Equals force times lever arm times sine of angle between them t = rFsinq Unit is meter Newton Lever arm is perpendicular distance of axis of rotation to line of action of force ...