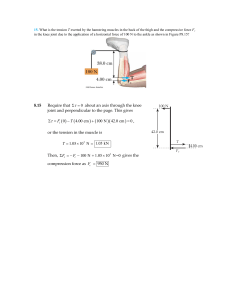
Dynamics of a mechanical particle
... Work of the gravitational force is independent of the path taken from A to B. It depends only on the coordinates of the two end points (initial and final points) of the path. Conservative force: If the force force is independent of the path taken from A to B. It depends only on the coordinates of th ...
... Work of the gravitational force is independent of the path taken from A to B. It depends only on the coordinates of the two end points (initial and final points) of the path. Conservative force: If the force force is independent of the path taken from A to B. It depends only on the coordinates of th ...
Chapter 7 – Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
... Why do our plants stay in the sun’s orbit? Why does the moon stay in orbit around the Earth? Gravitational force (field force) is the mutual force of attraction between particles of matter. It is a field force that always exists between any two masses, regardless of the medium that separates them. I ...
... Why do our plants stay in the sun’s orbit? Why does the moon stay in orbit around the Earth? Gravitational force (field force) is the mutual force of attraction between particles of matter. It is a field force that always exists between any two masses, regardless of the medium that separates them. I ...
Forces and Motion Notes
... NEWTON’S THIRD LAW OF MOTION – states that every time one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force that is equal in size and opposite in direction back on the first object. Balanced Forces – Action and Reaction – ...
... NEWTON’S THIRD LAW OF MOTION – states that every time one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force that is equal in size and opposite in direction back on the first object. Balanced Forces – Action and Reaction – ...
pdf file - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... Example: Two objects (a solid disk and a solid sphere) are rolling down a ramp. Both objects start from rest and from the same height. Which object reaches the bottom of the ramp first? Idea: the object with the largest linear velocity (v) at the bottom of the ramp will win the race! Apply conservat ...
... Example: Two objects (a solid disk and a solid sphere) are rolling down a ramp. Both objects start from rest and from the same height. Which object reaches the bottom of the ramp first? Idea: the object with the largest linear velocity (v) at the bottom of the ramp will win the race! Apply conservat ...
Review Questions
... rough the exact center of the flat surfaces? The hollo ~cylinder has the reater moment of ine I e solid cylinder has the greater momen 0 me la. C) Both cylinders have the same moment of inertia. D) The moment of inertia cannot be determined since it depends on the amount of material removed from the ...
... rough the exact center of the flat surfaces? The hollo ~cylinder has the reater moment of ine I e solid cylinder has the greater momen 0 me la. C) Both cylinders have the same moment of inertia. D) The moment of inertia cannot be determined since it depends on the amount of material removed from the ...
PPT
... Yes, D is the distance from CM to the new axis of rotation. Good, the moment of inertia has the smallest value for rotation about the center of mass! Any other axis will give a larger moment of inertia. When we say “moment of inertia” we’re not finished. We always have to say — or think — “moment of ...
... Yes, D is the distance from CM to the new axis of rotation. Good, the moment of inertia has the smallest value for rotation about the center of mass! Any other axis will give a larger moment of inertia. When we say “moment of inertia” we’re not finished. We always have to say — or think — “moment of ...
File - Phy 2048-0002
... I. Rotational variables Rigid body: body that can rotate with all its parts locked together and without shape changes. Rotation axis: every point of a body moves in a circle whose center lies on the rotation axis. Every point moves through the same angle during a particular time interval. Reference ...
... I. Rotational variables Rigid body: body that can rotate with all its parts locked together and without shape changes. Rotation axis: every point of a body moves in a circle whose center lies on the rotation axis. Every point moves through the same angle during a particular time interval. Reference ...
Ch. 9 Rotational Kinematics
... How would you write this kinetic energy expression in terms of angular speed? ...
... How would you write this kinetic energy expression in terms of angular speed? ...